1998 United States Senate election in New York
The 1998 United States Senate election in New York was held November 3, 1998 along with elections to the United States Senate in other states as well as elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator Al D'Amato was running for re-election to a fourth term, but was defeated by Democrat Chuck Schumer in what was considered by many to be the "high[est] profile and nastiest" contest of the year.[1] This was the first election since 1950 in which a Democrat was elected to the Class 3 United States Senate seat from New York, and the first time since Robert F. Wagner's re-election in 1944 that New York had sent two Democrats to the United States Senate.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
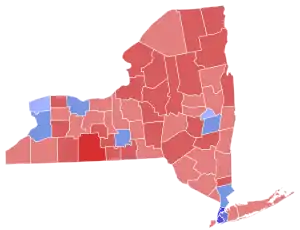 County results
Schumer: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in New York State |
|---|
 |
Democratic primary
Candidates
- Geraldine Ferraro, former U.S. Representative and nominee for Vice President in 1984
- Mark Green, New York City Public Advocate, and nominee in 1986
- Eric Ruano-Melendez, perennial candidate
- Chuck Schumer, U.S. Representative
Campaign
Ferraro was well known for having been the 1984 Democratic vice presidential nominee and had also run but lost in the Democratic primary in the 1992 U.S. Senate election in New York. Green had been the Democratic nominee in the 1986 election, but lost in the general election to D'Amato.
At the start of 1998, Ferraro had done no fundraising, out of fear of conflict of interest with her job hosting the CNN program Crossfire, but was nonetheless perceived as the front-runner by virtue of her name recognition;[2] indeed, December and January polls had her 25 percentage points ahead of Green in the race and even further ahead of Schumer.[3][4] Unlike her previous campaigns, Ferraro's family finances never became an issue in 1998.[3] However, she lost ground during the summer, with Schumer catching her in the polls by early August and then soon passing her.[5] Schumer, a tireless fundraiser, outspent her by a five-to-one margin, and Ferraro failed to establish a political image current with the times.[3][6] In the September 15, 1998, primary, she was beaten soundly by Schumer with a 51 percent to 26 percent margin.[3] Unlike the bitter 1992 Democratic senatorial primary, this contest was not divisive, and Ferraro and third-place finisher Green endorsed Schumer at a unity breakfast the following day.[7]
Polling
| Source | Date | Mark Green | Geraldine Ferraro | Charles Schumer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinnipiac | September 25, 1997 | 25% | 48% | 15% |
| Quinnipiac | December 11, 1997 | 25% | 48% | 12% |
| Quinnipiac | February 26, 1998 | 19% | 46% | 18% |
| Quinnipiac | March 26, 1998 | 20% | 50% | 15% |
| Quinnipiac | June 18, 1998 | 23% | 46% | 19% |
| Quinnipiac | July 16, 1998 | 24% | 39% | 28% |
Results
The primaries were held on September 15, 1998.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Chuck Schumer | 388,701 | 50.84% | ||
| Democratic | Geraldine Ferraro | 201,625 | 26.37% | ||
| Democratic | Mark J. Green | 145,819 | 19.07% | ||
| Democratic | Eric Ruano-Melendez | 28,493 | 3.73% | ||
Republican primary
Polling
| Source | Date | Alfonse D'Amato | Betsy McCaughey Ross |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quinnipiac | September 25, 1997 | 55% | 26% |
Other primaries
Independence
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independence | Chuck Schumer | 2,562 | 58.04% | ||
| Independence | Mark Green | 1,852 | 41.96% | ||
Right to life
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right to Life | Al D'Amato | 3,798 | 63.07% | ||
| Right to Life | Thomas Drolesky | 2,224 | 36.93% | ||
General election
Major
- Chuck Schumer (Democratic), U.S. Representative
- Al D'Amato (Republican), incumbent U.S. Senator
Minor
- Rose Ana Berbeo (Socialist Workers Party)
- Corinne Kurtz (Marijuana Reform Party)
- Joel Kovel (Green Party)
- William McMillen (Libertarian Party)
Campaign
During the campaign, D'Amato attempted to brand Schumer as a diehard liberal, while Schumer accused D'Amato of being a liar. When D'Amato's first strategy failed, D'Amato attacked his opponent's attendance record as a member of Congress, which Schumer refuted.[8][9]
Late in the campaign, D'Amato called Schumer a "putzhead" in a private meeting with Jewish supporters ("putz" is Yiddish for penis, and can be slang for "fool").[10] He later apologized for the comment.[1]
In the last days of the campaign, D'Amato campaigned with popular Governor George Pataki, who was also running for re-election, and was also supported by New York City Mayor Rudy Giuliani and former Mayor Ed Koch (a Democrat).[10]
Vice President Al Gore and First Lady Hillary Clinton personally campaigned for Schumer, as D'Amato was a prominent critic of President Bill Clinton[8] who led the investigation into Whitewater.[11] Though the Republican party was well organized, the Democratic party benefited from robocalls from President Clinton and mobilization from two big unions, United Federation of Teachers and 1199.[8]
Though D'Amato was effective in obtaining federal government funds for New York State projects during his Senate career, he failed to capitalize on this in the election.[8] Also, Schumer was a tenacious fund-raiser and was aggressive in his attacks.[11] The candidates spent $30 million during the race.[8]
Polling
| Source | Date | Al D'Amato (R) |
Chuck Schumer (D) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quinnipiac | September 25, 1997 | 40% | 43% |
| Quinnipiac | December 11, 1997 | 45% | 40% |
| Quinnipiac | February 26, 1998 | 45% | 41% |
| Quinnipiac | March 26, 1998 | 45% | 41% |
| Quinnipiac | June 18, 1998 | 49% | 37% |
| Quinnipiac | September 24, 1998 | 43% | 47% |
| Quinnipiac | October 14, 1998 | 45% | 46% |
| Quinnipiac | October 27, 1998 | 44% | 48% |
| Quinnipiac | November 2, 1998 | 42% | 50% |
Results
The race was not close, with Schumer defeating the incumbent D'Amato by just over 10%.[12] D'Amato did win a majority of New York's counties, but his wins were in less populated areas. Schumer's win is attributed to strong performance in New York City. Schumer also performed well in heavily populated upstate cities, like Buffalo, Syracuse, Rochester, and Albany. Schumer was sworn in on January 3, 1999.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Chuck Schumer | 2,386,314 | ||||
| Independence | Chuck Schumer | 109,027 | ||||
| Liberal | Chuck Schumer | 55,724 | ||||
| Total | Chuck Schumer | 2,551,065 | 54.62% | |||
| Republican | Al D'Amato | 1,680,203 | ||||
| Conservative | Al D'Amato | 274,220 | ||||
| Right to Life | Al D'Amato | 104,565 | ||||
| Total | Al D'Amato (incumbent) | 2,058,988 | 44.08% | |||
| Marijuana Reform | Corinne Kurtz | 34,281 | 0.73% | |||
| Green | Joel Kovel | 14,735 | 0.32% | |||
| Libertarian | William McMillen | 8,223 | 0.18% | |||
| Socialist Workers | Rose Ana Berbeo | 3,513 | 0.08% | |||
| Total votes | 4,670,805 | 100.00% | ||||
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||||
- Per New York State law, Schumer and D'Amato totals include minor party line votes: Independence Party and Liberal Party for Schumer, Right to Life Party for D'Amato.
See also
References
- Rothenburg, Stuart (November 3, 1998). "Schumer topples D'Amato in New York Senate race". CNN.
- Nagourney, Adam (January 4, 1998). "Friends Say Ferraro Will Seek D'Amato's Seat". The New York Times.
- Waldman, Amy (September 17, 1998). "The Farewell: For Ferraro, Early Promise, Lopsided Loss". The New York Times.
- Schumer, Chuck (2007). Positively American: Winning Back the Middle-Class Majority One Family at a Time. Rodale Books. ISBN 1-59486-572-8. p. 17.
- Schumer, Positively American, p. 31.
- Schumer, Positively American, pp. 18, 30.
- Schumer, Positively American, pp. 33, 39.
- Online NewsHour: 98 Election - The New York Wrap-up - November 4, 1998
- Online NewsHour: New York Senate Race - October 28, 1998
- "New York Senate race an old-fashioned street fight". CNN.
- Nagourney, Adam (November 4, 1998). "THE 1998 ELECTIONS: NEW YORK STATE -- THE SENATE; Schumer Uses D'Amato's Tactics To Win Senate Election Handily". The New York Times.
- "1998 General Election Results" (PDF). Elections.NY.gov.

