Timeline of space travel by nationality
Since the first human spaceflight by the Soviet Union, citizens of 41 countries have flown in space. For each nationality, the launch date of the first mission is listed. The list is based on the nationality of the person at the time of the launch. Only 3 of the 41 "first flyers" have been women (Helen Sharman for the United Kingdom in 1991, Anousheh Ansari for Iran in 2006, and Yi So-yeon for South Korea in 2008). Only three nations (Soviet Union/Russia, U.S., China) have launched their own crewed spacecraft, with the Soviets/Russians and the American programs providing rides to other nations' astronauts. Twenty-seven "first flights" occurred on Soviet or Russian flights while the United States carried thirteen.
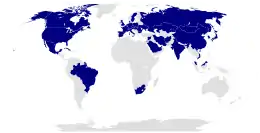
Note: citizens from the now-defunct East Germany, Czechoslovakia, and Soviet Union have also flown in space.
Timeline
Note: All dates given are UTC. Countries indicated in bold have achieved independent human spaceflight capability.
Notes
- The first cosmonaut, Yuri Gagarin, held citizenship in both the Soviet Union and the Russian SFSR, according to the applicable provisions of the Constitution of the Soviet Union. On 26 December 1991, the Soviet Union dissolved, and was replaced by Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan; Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania restored their independence. At the time of the dissolution, Sergei Krikalev and Alexander Volkov were orbiting Earth on Mir, having been launched into orbit as Soviet citizens, and having returned to the Earth as Russian citizens. Aleksandr Kaleri and Aleksandr Viktorenko were the first Russians to be launched into orbit as Russian citizens only, their launch having occurred subsequent to the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
- Under Fédération Aéronautique Internationale rules, the Vostok missions are not deemed true spaceflights, as cosmonauts did not land with the spacecraft (they ejected from the spacecraft and landed separately). The first Soviet mission that did fulfill this requirement was Voskhod 1. (Reference: "FAI Astronautic Records Commission – Sporting Code Section 8" (PDF). Fédération Aéronautique Internationale. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-05-26. Retrieved 2006-04-09.) However, despite this issue, the FAI does recognize Yuri Gagarin as the first person to complete a spaceflight. (Reference: "FAI Award: The Yuri A. Gagarin Gold Medal". Fédération Aéronautique Internationale. Archived from the original on 2007-10-13. Retrieved 2007-10-10.)
- Shepard's spaceflight was suborbital. The first American to be launched into Earth orbit was John Glenn, on 20 February 1962.
- In 1993, Czechoslovakia dissolved and was replaced by the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
- In 1978, both Jähn himself and the German Democratic Republic pronounced him the "first German in space", rather than the first "citizen of the German Democratic Republic in space". In 1990, the states of the former East Germany acceded to the Federal Republic of Germany. On 22 January 1992, Ulf Merbold again traveled into space, now representing the reunited Germany within the Federal Republic of Germany. Jähn is, nevertheless, still considered the first German in space, even in the states of the Federal Republic of Germany that comprised the former West Germany.
- This person flew as a commercial, non-governmental space traveller. Apart from Akiyama and Sharman, these space travellers are known as space tourists.
- Ilan Ramon was the first Israeli to go into space, but Ramon died during reentry during the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster. Again, this was not deemed a complete spaceflight under FAI rules.
- Although recognized as an Iranian citizen by Iranian law, Ansari is also an American citizen and was prohibited from wearing Iranian state symbols by both the United States and Russian governments.
Other claims
The above list uses the nationality at the time of launch. Lists with differing criteria might include the following people:
- Pavel Popovich, first launched 12 August 1962, was the first Ukrainian-born man in space. At the time, Ukraine was a part of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.
- Michael Collins, first launched 18 July 1966 was born in Italy to American parents and was an American citizen when he went into space.
- William Anders, American citizen, first launched 21 December 1968, was the first Hong Kong-born man in space.
- Vladimir Shatalov, first launched 14 January 1969, was the first Kazakh-born man in space. At the time, Kazakhstan was a part of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.
- Bill Pogue, first launched 16 November 1973, as an inductee to the 5 Civilized Tribes Hall of Fame can lay claim to being the first Native American in space. See John Herrington below regarding technicality of tribal registration.
- Pyotr Klimuk, first launched 18 December 1973, was the first Belorussian-born man in space. At the time, Belarus was a part of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.
- Vladimir Dzhanibekov, first launched 16 March 1978, was the first Uzbek-born man in space. At the time, Uzbekistan was a part of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.
- Paul D. Scully-Power, first launched 5 October 1984, was born in Australia, but was an American citizen when he went into space; Australian law at the time forbade dual-citizenship.
- Taylor Gun-Jin Wang, first launched 29 April 1985, was born in China to Chinese parents, but was an American citizen when he went into space.
- Lodewijk van den Berg, launched 29 April 1985, was born in the Netherlands, but was an American citizen when he went into space.
- Patrick Baudry, first launched 17 June 1985, was born in French Cameroun (now part of Cameroon), but was a French citizen when he went into space.
- Shannon Lucid, first launched 17 June 1985, was born in China to American parents of European descent, and was an American citizen when she went into space.
- Franklin Chang-Diaz, first launched 12 January 1986, was born in Costa Rica, but was an American citizen when he went into space[4]
- Musa Manarov, first launched 21 December 1987, was the first Azerbaijan-born man in space. At the time, Azerbaijan was a part of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.
- Anatoly Solovyev, first launched 7 June 1988, was the first Latvian-born man in space. At the time, Latvia was a part of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.
- Sergei Konstantinovich Krikalev and Aleksandr Aleksandrovich Volkov became Russian rather than Soviet citizens while still in orbit aboard Mir, making them the first purely Russian citizens in space.
- James H. Newman, American citizen, first launched 12 September 1993, was born in the portion of the United Nations Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands that is now the Federated States of Micronesia.
- Talgat Musabayev, first launched 1 July 1994, was born in the Kazakh SSR and is known in Kazakhstan as the "first cosmonaut of independent Kazakhstan",[5] but was a Russian citizen when he went into space.[6]
- Frederick W. Leslie, American citizen, launched 20 October 1995, was born in Panama Canal Zone (now Panama).
- Andy Thomas, first launched 19 May 1996, was born in Australia but like Paul D. Scully-Power was an American citizen when he went to space; Australian law at the time forbade dual-citizenship.
- Carlos I. Noriega, first launched 15 May 1997, was born in Peru, but was an American citizen when he went into space.
- Bjarni Tryggvason, launched 7 August 1997, was born in Iceland, but was a Canadian citizen when he went into space.
- Salizhan Sharipov, first launched 22 January 1998, was born in Kyrgyzstan (then the Kirghiz SSR), but was a Russian citizen when he went into space. Sharipov is of Uzbek ancestry.
- Philippe Perrin, first launched 5 June 2002, was born in Morocco, but was a French citizen when he went into space.
- John Herrington, an American citizen first launched 24 November 2002, is the first tribal registered Native American in space (Chickasaw). See also Bill Pogue above.
- Fyodor Yurchikhin, first launched 7 October 2002, was born in Georgia (then the Georgian SSR). He was a Russian citizen at the time he went into space and is of Pontian Greek descent.
- Joseph M. Acaba, first launched 15 March 2009, was born in the U.S. state of California to American parents of Puerto Rican descent.
Gallery
 The Soviet Union's Yuri Gagarin, the first person in space (1961)
The Soviet Union's Yuri Gagarin, the first person in space (1961) Alan Shepard from the United States of America, the second nation to send a person into space (1961)
Alan Shepard from the United States of America, the second nation to send a person into space (1961) Vladimír Remek of Czechoslovakia, the first Czechoslovak national in space (1978)
Vladimír Remek of Czechoslovakia, the first Czechoslovak national in space (1978) Mirosław Hermaszewski of Poland, the first Polish national in space (1978)
Mirosław Hermaszewski of Poland, the first Polish national in space (1978) Sigmund Jähn of East Germany, the first German in space (1978)
Sigmund Jähn of East Germany, the first German in space (1978) Rakesh Sharma, the first Indian in space (1984)
Rakesh Sharma, the first Indian in space (1984) Helen Sharman, the first person from the United Kingdom in space (1991)
Helen Sharman, the first person from the United Kingdom in space (1991) Yang Liwei of China, the third nation to launch a person into space (2003)
Yang Liwei of China, the third nation to launch a person into space (2003)
References
- "BBC News - Sci/Tech - Expensive ticket to ride". News.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 11 August 2017.
- "BBC News - SCI/TECH - Space tourist lifts off". News.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 11 August 2017.
- "BBC NEWS - Science/Nature - Lift-off for woman space tourist". News.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 11 August 2017.
- MAN IN THE NEWS: FRANKLIN R. CHANG-DIAZ; A DREAMER IN SPACE, Malcolm W. Browne, The New York Times, January 13, 1986
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-04-29. Retrieved 2015-08-19.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Bukharbayeva, Bagila (20 June 2004). "Kazakhstan Gets a Bigger Say in Space Launch Site". Articles.latimes.com. Retrieved 11 August 2017.
External links
- Current Space Demographics, compiled by William Harwood, CBS News Space Consultant, and Rob Navias, NASA.
.jpg.webp)