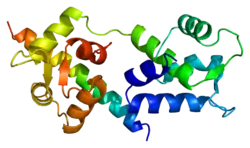
TNNI2
Troponin I, fast skeletal muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNNI2 gene.[5][6]
The TNNI2 gene is located at 11p15.5 in the human chromosomal genome, encoding the fast twitch skeletal muscle troponin I (fsTnI). fsTnI is a 21.3 kDa protein consisting of 182 amino acids including the first methionine with an isoelectric point (pI) of 8.74. It is the inhibitory subunit of the troponin complex in fast twitch skeletal muscle fibers.[7]
Gene evolution

Three homologous genes have evolved in vertebrates, encoding three muscle type-specific isoforms of TnI.[8][9][10] Sequence analysis, immunological distance, and examination of evolutionarily suppressed conformational states showed that the TnI genes have evolved in close linkage with the genes encoding troponin T (TnT), another subunit of the troponin complex.[10] The fast TnI-fast TnT gene pair represents the original TnI and TnT genes (Fig. 1). The three muscle fiber type-specific TnI-TnT gene pairs were likely originated from a TnI-like ancestor gene that presumably duplicated to form a closely linked fast TnI-like and fast TnT-like gene pair. A later duplication events resulted in emergences of a slow TnI-like and cardiac TnT-like gene pair that was further duplicated to give rise of the present-day slow TnI-cardiac TnT and cardiac TnI-slow TnT gene pairs. The seemingly scrambled ssTnI and cTnI gene pair is actually functionally related as they co-express and form troponin complex in the embryonic heart. The overlapping of enhancer elements of the TnT gene promoter with the upstream TnI gene structure may be a critical factor in the preservation of the close linkage of TnI and TnT gene pairs[11]
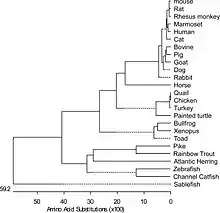
The phylogenetic tree in Fig. 2 summarizes the evolutionary lineage of fsTnI isoforms in vertebrate species.
Phylogenetic analysis of vertebrate TnI isoforms demonstrated that each of the muscle type-specific isoforms is more conserved across species than the three isoforms in one given species, indicating early diverged functions of the muscle fiber type-specific isoforms as well as the conservation of functions for each muscle fiber type.[12]
Tissue distribution
Fast skeletal muscle TnI was first cloned from a skeletal muscle cDNA library.[13] It is generally observed that fsTnI is exclusively expressed in fast twitch skeletal muscle fibers. More recent studies reported that subunits of fast skeletal muscle troponin (fsTnI, fsTnT, fsTnC) were expressed at significant levels in smooth muscle cells of mouse blood vessels,[14] bladder and bronchi.[15] Expression of fsTnI was also found in non-muscle cells, such as human corneal epithelial cells[16] and cartilage.[17][18] The function of fsTnI expressed in smooth muscle and non-muscle cells is unclear.
Protein structure and function
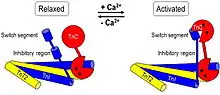
Crystallographic structure of fsTnI in troponin complex from chicken fast skeletal muscle showed an overall structure[19] similar to that of cardiac troponin.[20] The inhibitory region of fsTnI was resolved in skeletal troponin whereas it was invisible in the cardiac troponin crystal structure. Based on the crystal structure, a schematic illustration (Fig. 3) was proposed to show the conformational changes in troponin during muscle activation and relaxation.
Posttranslational modifications
Phosphorylation: Ser118 of fsTnI, equivalent to Ser150 in cTnI, was reported as a phosphorylation substrate of AMPK.[21] As AMPK is a key regulator of cellular energetics, phosphorylation of this site may provide an adaptive mechanism during energy deprivation in both skeletal and cardiac muscles.
S-glutathionylation: fsTnI was found to be S-glutathionylated at Cys133 in rodent fast-twitch skeletal muscle and in human type II muscle fibers after exercise, which increased Ca2+ sensitivity of the contractile apparatus.[22]
Clinical significance
A missense mutation R174Q, a nonsense mutation R156X, and three single residue deletions DE167, DK175 and DK176, all in the C-terminal actin-tropomyosin interacting domain, have been found in patients with distal arthrogryposis.[23][24][25][26]
Skeletal muscle TnI has been proposed as a sensitive and fast fiber-specific serum marker of skeletal muscle injury.[27][28] fsTnI concentration in increased peripheral blood when fast twitch fibers were damaged.[28]
Notes
References
- ENSG00000288219 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000130598, ENSG00000288219 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031097 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Tiso N, Rampoldi L, Pallavicini A, Zimbello R, Pandolfo D, Valle G, Lanfranchi G, Danieli GA (Jan 1997). "Fine mapping of five human skeletal muscle genes: alpha-tropomyosin, beta-tropomyosin, troponin-I slow-twitch, troponin-I fast-twitch, and troponin-C fast". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 230 (2): 347–50. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1996.5958. PMID 9016781.
- "Entrez Gene: TNNI2 troponin I type 2 (skeletal, fast)".
- Jin JP, Zhang Z, Bautista JA (2008-01-01). "Isoform diversity, regulation, and functional adaptation of troponin and calponin". Critical Reviews in Eukaryotic Gene Expression. 18 (2): 93–124. doi:10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v18.i2.10. PMID 18304026.
- Hastings KE (Feb 1997). "Molecular evolution of the vertebrate troponin I gene family". Cell Structure and Function. 22 (1): 205–11. doi:10.1247/csf.22.205. PMID 9113408.
- Perry SV (Jan 1999). "Troponin I: inhibitor or facilitator". Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 190 (1–2): 9–32. doi:10.1023/A:1006939307715. PMID 10098965. S2CID 23721684.
- Chong SM, Jin JP (May 2009). "To investigate protein evolution by detecting suppressed epitope structures". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 68 (5): 448–60. doi:10.1007/s00239-009-9202-0. PMC 2752406. PMID 19365646.
- Huang QQ, Jin JP (Dec 1999). "Preserved close linkage between the genes encoding troponin I and troponin T, reflecting an evolution of adapter proteins coupling the Ca(2+) signaling of contractility". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 49 (6): 780–8. doi:10.1007/pl00006600. PMID 10594179. S2CID 9839814.
- Jin JP, Chen A, Huang QQ (Jul 1998). "Three alternatively spliced mouse slow skeletal muscle troponin T isoforms: conserved primary structure and regulated expression during postnatal development". Gene. 214 (1–2): 121–9. doi:10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00214-5. PMID 9651500.
- Zhu L, Perez-Alvarado G, Wade R (Apr 1994). "Sequencing of a cDNA encoding the human fast-twitch skeletal muscle isoform of troponin I". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression. 1217 (3): 338–40. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(94)90297-6. PMID 8148383.
- Moran CM, Garriock RJ, Miller MK, Heimark RL, Gregorio CC, Krieg PA (Aug 2008). "Expression of the fast twitch troponin complex, fTnT, fTnI and fTnC, in vascular smooth muscle". Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton. 65 (8): 652–61. doi:10.1002/cm.20291. PMC 2570210. PMID 18548613.
- Ju Y, Li J, Xie C, Ritchlin CT, Xing L, Hilton MJ, Schwarz EM (Sep 2013). "Troponin T3 expression in skeletal and smooth muscle is required for growth and postnatal survival: characterization of Tnnt3(tm2a(KOMP)Wtsi) mice". Genesis. 51 (9): 667–75. doi:10.1002/dvg.22407. PMC 3787964. PMID 23775847.
- Kinoshita S, Adachi W, Sotozono C, Nishida K, Yokoi N, Quantock AJ, Okubo K (Sep 2001). "Characteristics of the human ocular surface epithelium". Progress in Retinal and Eye Research. 20 (5): 639–73. doi:10.1016/s1350-9462(01)00007-6. PMID 11470454. S2CID 25497205.
- Moses MA, Wiederschain D, Wu I, Fernandez CA, Ghazizadeh V, Lane WS, Flynn E, Sytkowski A, Tao T, Langer R (Mar 1999). "Troponin I is present in human cartilage and inhibits angiogenesis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (6): 2645–50. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.6.2645. PMC 15822. PMID 10077564.
- Li Q, Shen PY, Wu G, Chen XZ (Jan 2003). "Polycystin-2 interacts with troponin I, an angiogenesis inhibitor". Biochemistry. 42 (2): 450–7. doi:10.1021/bi0267792. PMID 12525172.
- PDB: 1YTZ; Vinogradova MV, Stone DB, Malanina GG, Karatzaferi C, Cooke R, Mendelson RA, Fletterick RJ (Apr 2005). "Ca(2+)-regulated structural changes in troponin". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 102 (14): 5038–43. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408882102. PMC 555973. PMID 15784741.
- Takeda S, Yamashita A, Maeda K, Maéda Y (Jul 2003). "Structure of the core domain of human cardiac troponin in the Ca(2+)-saturated form". Nature. 424 (6944): 35–41. doi:10.1038/nature01780. PMID 12840750. S2CID 2174019.
- Sancho Solis R, Ge Y, Walker JW (May 2011). "A preferred AMPK phosphorylation site adjacent to the inhibitory loop of cardiac and skeletal troponin I". Protein Science. 20 (5): 894–907. doi:10.1002/pro.623. PMC 3125873. PMID 21416543.
- Mollica JP, Dutka TL, Merry TL, Lamboley CR, McConell GK, McKenna MJ, Murphy RM, Lamb GD (Mar 2012). "S-glutathionylation of troponin I (fast) increases contractile apparatus Ca2+ sensitivity in fast-twitch muscle fibres of rats and humans" (PDF). The Journal of Physiology. 590 (Pt 6): 1443–63. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.224535. PMC 3382333. PMID 22250211.
- Sung SS, Brassington AM, Grannatt K, Rutherford A, Whitby FG, Krakowiak PA, Jorde LB, Carey JC, Bamshad M (Mar 2003). "Mutations in genes encoding fast-twitch contractile proteins cause distal arthrogryposis syndromes". American Journal of Human Genetics. 72 (3): 681–90. doi:10.1086/368294. PMC 1180243. PMID 12592607.
- Jiang M, Zhao X, Han W, Bian C, Li X, Wang G, Ao Y, Li Y, Yi D, Zhe Y, Lo WH, Zhang X, Li J (Sep 2006). "A novel deletion in TNNI2 causes distal arthrogryposis in a large Chinese family with marked variability of expression". Human Genetics. 120 (2): 238–42. doi:10.1007/s00439-006-0183-4. PMID 16802141. S2CID 6246993.
- Kimber E, Tajsharghi H, Kroksmark AK, Oldfors A, Tulinius M (Aug 2006). "A mutation in the fast skeletal muscle troponin I gene causes myopathy and distal arthrogryposis". Neurology. 67 (4): 597–601. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000230168.05328.f4. PMID 16924011. S2CID 72428621.
- Robinson P, Lipscomb S, Preston LC, Altin E, Watkins H, Ashley CC, Redwood CS (Mar 2007). "Mutations in fast skeletal troponin I, troponin T, and beta-tropomyosin that cause distal arthrogryposis all increase contractile function". FASEB Journal. 21 (3): 896–905. doi:10.1096/fj.06-6899com. PMID 17194691. S2CID 25491760.
- Simpson JA, Labugger R, Collier C, Brison RJ, Iscoe S, Van Eyk JE (Jun 2005). "Fast and slow skeletal troponin I in serum from patients with various skeletal muscle disorders: a pilot study". Clinical Chemistry. 51 (6): 966–72. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2004.042671. PMID 15833785.
- Chapman DW, Simpson JA, Iscoe S, Robins T, Nosaka K (Jan 2013). "Changes in serum fast and slow skeletal troponin I concentration following maximal eccentric contractions". Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport / Sports Medicine Australia. 16 (1): 82–5. doi:10.1016/j.jsams.2012.05.006. PMID 22795680.
Further reading
- Kinoshita S, Adachi W, Sotozono C, Nishida K, Yokoi N, Quantock AJ, Okubo K (Sep 2001). "Characteristics of the human ocular surface epithelium". Progress in Retinal and Eye Research. 20 (5): 639–73. doi:10.1016/S1350-9462(01)00007-6. PMID 11470454. S2CID 25497205.
- Wade R, Eddy R, Shows TB, Kedes L (Jul 1990). "cDNA sequence, tissue-specific expression, and chromosomal mapping of the human slow-twitch skeletal muscle isoform of troponin I". Genomics. 7 (3): 346–57. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(90)90168-T. PMID 2365354.
- Huang TS, Bylund DB, Stull JT, Krebs EG (Jun 1974). "The amino acid sequences of the phosphorylated sites in troponin-I from rabbit skeletal muscle". FEBS Letters. 42 (3): 249–52. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(74)80738-6. PMID 4369265. S2CID 40748797.
- Moir AJ, Ordidge M, Grand RJ, Trayer IP, Perry SV (Feb 1983). "Studies of the interaction of troponin I with proteins of the I-filament and calmodulin". The Biochemical Journal. 209 (2): 417–26. doi:10.1042/bj2090417. PMC 1154108. PMID 6847627.
- Grand RJ, Levine BA, Perry SV (Apr 1982). "Proton-magnetic-resonance studies on the interaction of rabbit skeletal-muscle troponin I with troponin C and actin". The Biochemical Journal. 203 (1): 61–8. doi:10.1042/bj2030061. PMC 1158193. PMID 7103951.
- Chong PC, Hodges RS (Oct 1982). "Photochemical cross-linking between rabbit skeletal troponin subunits. Troponin I-troponin T interactions". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 257 (19): 11667–72. PMID 7118902.
- Zhu L, Perez-Alvarado G, Wade R (Apr 1994). "Sequencing of a cDNA encoding the human fast-twitch skeletal muscle isoform of troponin I". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression. 1217 (3): 338–40. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(94)90297-6. PMID 8148383.
- Lanfranchi G, Muraro T, Caldara F, Pacchioni B, Pallavicini A, Pandolfo D, Toppo S, Trevisan S, Scarso S, Valle G (Jan 1996). "Identification of 4370 expressed sequence tags from a 3'-end-specific cDNA library of human skeletal muscle by DNA sequencing and filter hybridization". Genome Research. 6 (1): 35–42. doi:10.1101/gr.6.1.35. PMID 8681137.
- Jha PK, Leavis PC, Sarkar S (Dec 1996). "Interaction of deletion mutants of troponins I and T: COOH-terminal truncation of troponin T abolishes troponin I binding and reduces Ca2+ sensitivity of the reconstituted regulatory system". Biochemistry. 35 (51): 16573–80. doi:10.1021/bi9622433. PMID 8987992.
- Stefancsik R, Jha PK, Sarkar S (Feb 1998). "Identification and mutagenesis of a highly conserved domain in troponin T responsible for troponin I binding: potential role for coiled coil interaction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (3): 957–62. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.3.957. PMC 18637. PMID 9448267.
- Vassylyev DG, Takeda S, Wakatsuki S, Maeda K, Maéda Y (Apr 1998). "Crystal structure of troponin C in complex with troponin I fragment at 2.3-A resolution". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (9): 4847–52. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.9.4847. PMC 20176. PMID 9560191.
- Jha PK, Sarkar S (Sep 1998). "A recombinant monocysteine mutant (Ser to Cys-155) of fast skeletal troponin T: identification by cross-linking of a domain involved in a physiologically relevant interaction with troponins C and I". Biochemistry. 37 (35): 12253–60. doi:10.1021/bi980025z. PMID 9724539.
- Moses MA, Wiederschain D, Wu I, Fernandez CA, Ghazizadeh V, Lane WS, Flynn E, Sytkowski A, Tao T, Langer R (Mar 1999). "Troponin I is present in human cartilage and inhibits angiogenesis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (6): 2645–50. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.6.2645. PMC 15822. PMID 10077564.
- Mullen AJ, Barton PJ (Jan 2000). "Structural characterization of the human fast skeletal muscle troponin I gene (TNNI2)". Gene. 242 (1–2): 313–20. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00519-3. PMID 10721725.
- Sung SS, Brassington AM, Grannatt K, Rutherford A, Whitby FG, Krakowiak PA, Jorde LB, Carey JC, Bamshad M (Mar 2003). "Mutations in genes encoding fast-twitch contractile proteins cause distal arthrogryposis syndromes". American Journal of Human Genetics. 72 (3): 681–90. doi:10.1086/368294. PMC 1180243. PMID 12592607.
- Li Q, Liu Y, Shen PY, Dai XQ, Wang S, Smillie LB, Sandford R, Chen XZ (Jun 2003). "Troponin I binds polycystin-L and inhibits its calcium-induced channel activation". Biochemistry. 42 (24): 7618–25. doi:10.1021/bi034210a. PMID 12809519.
- Thijssen VL, Ausma J, Gorza L, van der Velden HM, Allessie MA, Van Gelder IC, Borgers M, van Eys GJ (Aug 2004). "Troponin I isoform expression in human and experimental atrial fibrillation". Circulation. 110 (7): 770–5. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000138849.03311.C6. PMID 15289369.