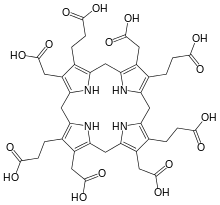
Uroporphyrinogen III
Uroporphyrinogen III is a tetrapyrrole, the first macrocyclic intermediate in the biosynthesis of heme, chlorophyll, vitamin B12, and siroheme. It is a colorless compound, like other porphyrinogens.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| MeSH | Uroporphyrinogen+III |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| C40H44N4O16 | |
| Molar mass | 836.795 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Structure
The molecular structure of uroporphyrinogen III can be described as a hexahydroporphine core, where each pyrrole ring has the hydrogen atoms on its two outermost carbons replaced by an acetic acid group (−CH
2−COOH, "A") and a propionic acid group (−CH
2−CH
2−COOH, "P"). The groups are attached in an asymmetric way: going around the macrocycle, the order is AP-AP-AP-PA.
Biosynthesis and metabolism
In the general porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, uroporphyrinogen III is derived from the linear tetrapyrrole preuroporphyrinogen (a substituted hydroxymethylbilane) by the action of the enzyme uroporphyrinogen-III cosynthase.[2][3]
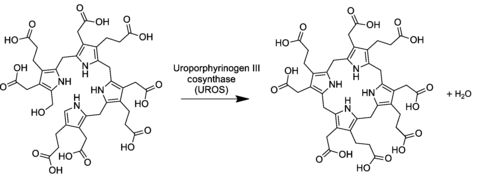
The conversion entails a reversal of the last pyrrole unit (thus swapping the acetic and propionic acid groups) and a condensation reaction that closes the macrocycle by eliminating the final hydroxyl −OH with a hydrogen atom of the first ring.
In the biosynthesis of hemes and chlorophylls, uroporphyrinogen III is converted into coproporphyrinogen III by the enzyme uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase. In the biosynthesis of sirohemes, uroporphyrinogen III is converted by two methyl transferases to dihydrosirohydrochlorin, which is subsequently oxidized sirohydrochlorin, a precursor to the siroheme prosthetic group.
Medical significance
If uroporphyrinogen-III synthase is not present or inactive, the hydroxymethylbilane will spontaneously cyclise into the structural isomer uroporphyrinogen I, which differs from the III isomer in that the acetic acid ("A") and propionic acid ("P") groups are arranged in a rotationally symmetric order, AP-AP-AP-AP. In this case, the next step produced coproporphyrinogen I, which accumulates — leading to the pathological condition congenital erythropoietic porphyria[3]
See also
References
- Dalton, J (1969). "Formation of the Macrocyclic Ring in Tetrapyrrole Biosynthesis". Nature. 223 (5211): 1151–1153. Bibcode:1969Natur.223.1151D. doi:10.1038/2231151a0. PMID 5810686.
- Paul R. Ortiz de Montellano (2008). "Hemes in Biology". Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470048672.wecb221. ISBN 978-0470048672.
- S. Sassa and A. Kappas (2000): "Molecular aspects of the inherited porphyrias". Journal of Internal Medicine, volume 247, issue 2, pages 169-178. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2796.2000.00618.x