Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols
Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols (Chinese: 臺語方音符號; TPS: ㄉㄞˊ ㆣ丨ˋ ㄏㆲ 丨ㆬ ㄏㄨˊ ㄏㄜ˫) constitute a system of phonetic notation for the transcription of Taiwanese languages, especially Taiwanese Hokkien. The system was designed by Professor Chu Chao-hsiang, a member of National Languages Committee in Taiwan, in 1946.[1] The system is derived from Mandarin Phonetic Symbols by creating additional symbols for the sounds that do not appear in Mandarin phonology. It is one of the phonetic notation systems officially promoted by Taiwan's Ministry of Education.[2]
| Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols | |
|---|---|
| Type | |
| Creator | Chu Chao-hsiang, Taiwan NLC |
Time period | 1946 to the present, used as ruby characters in Taiwan |
Parent systems | Oracle Bone Script
|
Sister systems | Simplified Chinese, Kanji, Hanja, Chữ Nôm, Khitan large script, Khitan small script |
| Direction | Left-to-right |
| ISO 15924 | Bopo, 285 |
Unicode alias | Bopomofo |
| U+3100–U+312F, U+31A0–U+31BF | |
| Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 臺語方音符號 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 台语方音符号 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese romanization |
|---|
| Mandarin |
| Wu |
| Yue |
| Min |
| Gan |
| Hakka |
| Xiang |
| See also |

Symbols
There are 49 symbols used in standard Taiwanese Hokkien. Of these 49 symbols, 26 are from the original Mandarin Phonetic Symbols, while 23 are additional, created for Taiwanese languages.
| Initial symbols (21) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ㄅ | ㆠ | ㄆ | ㄇ | ㄉ | ㄊ | ㄋ | ㄌ | ㄍ | ㆣ | ㄎ | ㄫ | ㄏ | ㄐ | ㆢ | ㄑ | ㄒ | ㄗ | ㆡ | ㄘ | ㄙ | |||
| [p] | [b] | [pʰ] | [m] | [t] | [tʰ] | [n] | [l] | [k] | [g] | [kʰ] | [ŋ] | [h] | [t͡ɕ] | [d͡ʑ] | [t͡ɕʰ] | [ɕ] | [t͡s] | [d͡z] | [t͡sʰ] | [s] | |||
| Final symbols (24) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ㄚ | ㆩ | ㆦ | ㆧ | ㄜ | ㆤ | ㆥ | ㄞ | ㆮ | ㄠ | ㆯ | ㆰ | ㆱ | ㆬ | ㄢ | ㄣ | ㄤ | ㆲ | ㄥ | ㆭ | ㄧ | ㆪ | ㄨ | ㆫ |
| [a] | [ã] | [ɔ] | [ɔ̃] | [ə] | [e] | [ẽ] | [ai] | [ãĩ] | [au] | [ãũ] | [am] | [ɔm] | [m̩] | [an] | [ən] | [aŋ] | [ɔŋ] | [əŋ] | [ŋ̍] | [i] | [ĩ] | [u] | [ũ] |
- The symbols in blue do not exist in Mandarin phonology.
- Four voiceless consonants ㄅ, ㄉ, ㄍ, ㄏ may be written in small form to represent the unreleased coda, as in ㆴ [p̚ ], ㆵ [t̚ ], ㆶ [k̚ ], ㆷ [ʔ]. However, due to technical errors, the coda symbol for ㄍ was mistaken as ㄎ. Unicode encoded ㆻ (31BB) in its version 13.0, and added a note under ㆶ (31B6), indicating 31BB is preferred.[3]
- Some extra symbols are used in other Taiwanese dialects: ㄬ[ɲ], ㄛ [o], ㄝ [ɛ], ㆨ [ɨ].
Images
Images below are a collection of Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols:
![]()
![]()
- For Taiwanese Hokkien and Taiwanese Hakka:
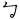 ,
, 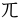 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 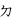 ,
,  ,
, 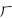
- For Taiwanese Hakka only:
 ,
, 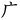
- For Taiwanese Hokkien only:
 ,
,  ,
, 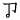 ,
, 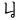 ,
, 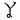 ,
,  ,
, 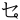 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 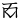 ,
, 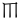 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
- For Standard Chinese only:
 ,
,  ,
, 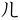 ,
, 
- For Taiwanese Hakka and Standard Chinese:
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
 represents [x] in Standard Chinese and [h] in Taiwanese Hokkien and Taiwanese Hakka.
represents [x] in Standard Chinese and [h] in Taiwanese Hokkien and Taiwanese Hakka. /
/ represent [ɛ]/[e] in Taiwanese Hokkien respectively, but they represent [e]/[ɛ] in Taiwanese Hakka.[4][5]
represent [ɛ]/[e] in Taiwanese Hokkien respectively, but they represent [e]/[ɛ] in Taiwanese Hakka.[4][5]- Vowel [ɨ] is represented with
 in Hokkien and
in Hokkien and  in Hakka.[5]
in Hakka.[5]
Etymology
| Initials | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Symbol | IPA | POJ | TL | BP | Notes | Example |
| Bilabial | ㄅ | p | p | b | Same value as in Mandarin | 邊 (ㄅㄧㄢ pian) | |
| ㆠ | b | b | bb | Derived from ㄅ as a voiced counterpart | 文 (ㆠㄨㄣˊ bûn) | ||
| ㄆ | pʰ | ph | p | Same value as in Mandarin | 波 (ㄆㄜ pho) | ||
| ㄇ | m | m | bbn | Same value as in Mandarin | 毛 (ㄇㆦ mo͘ ) | ||
| Alveolar | ㄉ | t | t | d | Same value as in Mandarin | 地 (ㄉㆤ˫ tē) | |
| ㄊ | tʰ | th | t | Same value as in Mandarin | 他 (ㄊㆩ thaⁿ) | ||
| ㄋ | n | n | ln | Same value as in Mandarin | 耐 (ㄋㄞ˫ nāi) | ||
| ㄌ | l | l | l | Same value as in Mandarin | 柳 (ㄌㄧㄨˋ liú) | ||
| Velar | ㄍ | k | k | g | Same value as in Mandarin | 求 (ㄍㄧㄨˊ kiû) | |
| ㆣ | g | g | gg | Derived from ㄍ as a voiced counterpart | 語 (ㆣㄧˋ gí) | ||
| ㄎ | kʰ | kh | k | Same value as in Mandarin | 去 (ㄎㄧ˪ khì) | ||
| ㄫ | ŋ | ng | ggn | Once appeared in old Mandarin | 雅 (ㄫㄚˋ ngá) | ||
| Glottal | ㄏ | h | h | h | Different value to Mandarin, in Mandarin [x] | 喜 (ㄏㄧˋ hí) | |
| Alveolo- palatal |
ㄐ | t͡ɕ | chi | tsi | zi | Same value as in Mandarin | 尖(ㄐㄧㆰ tsiam) |
| ㆢ | d͡ʑ | ji | zzi | Derived from ㄐ as a voiced counterpart | 入 (ㆢㄧㆴ. ji̍p) | ||
| ㄑ | t͡ɕʰ | chhi | tshi | ci | Same value as in Mandarin | 手 (ㄑㄧㄨˋ tshiú) | |
| ㄒ | ɕ | si | si | Same value as in Mandarin | 寫 (ㄒㄧㄚˋ siá) | ||
| Alveolar | ㄗ | t͡s | ch | ts | z | Same value as in Mandarin | 曾 (ㄗㄢ chan) |
| ㆡ | d͡z | j | zz | Derived from ㄗ as a voiced counterpart | 熱 (ㆡㄨㄚㆷ. jua̍h) | ||
| ㄘ | t͡sʰ | chh | tsh | c | Same value as in Mandarin | 出 (ㄘㄨㆵ chhut) | |
| ㄙ | s | s | s | Same value as in Mandarin | 衫 (ㄙㆩ saⁿ) | ||
| Rhymes and medials | |||||||
| Group | Symbol | IPA | POJ | TL | BP | Notes | Example |
| Vowels | ㄚ | a | a | a | Same value as in Mandarin | 查 (ㄘㄚ cha) | |
| ㆩ | ã | aⁿ | ann | na | Derived from ㄚ as a nasalized counterpart | 衫 (ㄙㆩ saⁿ) | |
| ㆦ | ɔ | o͘ | oo | oo | New symbol solely used in Taiwanese | 烏 (ㆦ o͘ ) | |
| ㆧ | ɔ̃ | oⁿ | onn | noo | Derived from ㆦ as a nasalized counterpart | 翁 (ㆧ oⁿ) | |
| ㄜ | ə | o | o | Different value from Mandarin, in Mandarin [ɰɤ]. May written as ㄛ and pronounced [o] in some dialects | 高 (ㄍㄜ ko) | ||
| ㆤ | e | e | e | New symbol solely used in Taiwanese | 禮 (ㄌㆤˋ lé) | ||
| ㆥ | ẽ | eⁿ | enn | ne | Derived from ㆤ as a nasalized counterpart | 生 (ㄙㆥ seⁿ) | |
| Diph- thongs |
ㄞ | ai | ai | ai | Same value as in Mandarin | ||
| ㆮ | ãĩ | aiⁿ | ainn | nai | Derived from ㄞ as a nasalized counterpart | ||
| ㄠ | au | au | ao | Same value as in Mandarin | 𠢕 (ㆣㄠˊ gâu) | ||
| ㆯ | ãũ | auⁿ | aunn | nao | Derived from ㄠ as a nasalized counterpart, rarely used | ||
| M finals |
ㆰ | am | am | am | A combination of ㄚ and ㄇ | 暗 (ㆰ˪ ām) | |
| ㆱ | ɔm | om | om | A combination of ㆦ and ㄇ, rarely used | 掩 (ㆱ om) | ||
| ㆬ | m̩ | m | m | Derived from ㄇ. May be used as a final bilabial nasal or a syllabic consonant | 姆 (ㆬˋ ḿ) | ||
| N finals |
ㄢ | an | an | an | Same value as in Mandarin | ||
| ㄣ | n | -n | -n | Only used in the finals ㄧㄣ, ㄨㄣ. ㄧㄣ has same value as in Mandarin. ㄨㄣ is pronounced as [un] unlike [wən] in Mandarin | 因 (ㄧㄣ in) | ||
| Ng finals |
ㄤ | aŋ | ang | ang | Same value as in Mandarin | 人 (ㄌㄤˊ lâng) | |
| ㆲ | ɔŋ | ong | ong | New symbol solely used in Taiwanese | 王 (ㆲˊ ông) | ||
| ㄥ | əŋ | -ng | -ng | Only used in the final ㄧㄥ. | 英 (ㄧㄥ eng) | ||
| ㆭ | ŋ̍ | ng | ng | Derived from ㄫ. May be used as a final velar nasal or a syllabic consonant | 酸 (ㄙㆭ sng) | ||
| Medial vowels |
ㄧ | i | i | i | Same value as in Mandarin | 衣 (ㄧ i) | |
| ㆪ | ĩ | iⁿ | inn | ni | Derived from ㄧ as a nasalized counterpart | 圓 (ㆪˊ îⁿ) | |
| ㄨ | u | u/o[lower-alpha 1] | u | u | Same value as in Mandarin | 污 (ㄨ u) | |
| ㆫ | ũ | uⁿ | unn | nu | Derived from ㄨ as a nasalized counterpart. Only used in the final ㄧㆫ [ĩũ] | 張 (ㄉㄧㆫ tiuⁿ) | |
- Written as ⟨o⟩ when followed by an ⟨a⟩ (ㄚ) or ⟨e⟩ (ㆤ), as in the finals ⟨oa⟩, ⟨oe⟩ and ⟨oai⟩ (ㄨㄞ). Written as ⟨u⟩ elsewhere.
Other features
Combined rhymes
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Example
| Audio File: | |
| Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols: | ㄒㄧㄢ ㄒㆪ ㄍㆲˋ, ㄏㄚㄍ̇ ㄒㄧㄥ ㄉㄧㆰ˫ ㄉㄧㆰ˫ ㄊㄧㆩ |
| IPA: | [ ɕɪɛn˧ ɕĩ˥ kɔŋ˥˩ hak̚˧ ɕiəŋ˥ tɪam˧ tɪam˧ tʰĩã˥ ] |
| Pe̍h-ōe-jī: | Sian-siⁿ kóng, ha̍k-seng tiām-tiām thiaⁿ. |
| Tâi-lô: | Sian-sinn kóng, ha̍k-sing tiām-tiām thiann. |
| Traditional Chinese: | 先生講、學生恬恬聽。 |
| Hanyu Pinyin: | Xiān shēng jiǎng, xué shēng tián tián tīng. |
| Translation: | A teacher is speaking. Students are quietly listening. |
Note: 恬恬 is Taiwanese Hokkien (台灣話). Synonyms would be 安靜 or 靜靜. 先生, in this context, means "teacher".
Unicode support
The Mandarin Phonetic Symbols were added to the Unicode Standard in October 1991 with the release of version 1.0. The Unicode block for Mandarin Phonetic Symbols is U+3100 ... U+312F.
| Bopomofo[1][2] Official Unicode Consortium code chart (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| U+310x | ㄅ | ㄆ | ㄇ | ㄈ | ㄉ | ㄊ | ㄋ | ㄌ | ㄍ | ㄎ | ㄏ | |||||
| U+311x | ㄐ | ㄑ | ㄒ | ㄓ | ㄔ | ㄕ | ㄖ | ㄗ | ㄘ | ㄙ | ㄚ | ㄛ | ㄜ | ㄝ | ㄞ | ㄟ |
| U+312x | ㄠ | ㄡ | ㄢ | ㄣ | ㄤ | ㄥ | ㄦ | ㄧ | ㄨ | ㄩ | ㄪ | ㄫ | ㄬ | ㄭ | ㄮ | ㄯ |
| Notes | ||||||||||||||||
The extended phonetic symbols were added to the Unicode Standard in September 1999 with the release of version 3.0. The Unicode block for the extended symbols is U+31A0 ... U+31BF. Four symbols for Cantonese and one for Minnan and Hakka coda were released in 2020 with the publication of version 13.0.[3] One can learn more information from the proposals.[6][7]
| Bopomofo Extended[1] Official Unicode Consortium code chart (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| U+31Ax | ㆠ | ㆡ | ㆢ | ㆣ | ㆤ | ㆥ | ㆦ | ㆧ | ㆨ | ㆩ | ㆪ | ㆫ | ㆬ | ㆭ | ㆮ | ㆯ |
| U+31Bx | ㆰ | ㆱ | ㆲ | ㆳ | ㆴ | ㆵ | ㆶ | ㆷ | ㆸ | ㆹ | ㆺ | ㆻ | ㆼ | ㆽ | ㆾ | ㆿ |
Notes
| ||||||||||||||||
Font Support
The Academia Sinica of Taiwan has released three sets of fonts for Taiwanese Hokkien: "吳守禮標楷台語注音字型", "吳守禮細明台語注音字型", "吳守禮台語注音字型".[8] When the above fonts are used (to Chinese characters), the Bopomofo Phonetic Symbols will automatically appear. For words with more than one pronunciation, user can choose "破音" fonts to find the desired pronunciation. The user manual can be downloaded here.[9]
See also
References
- 吳守禮, 吳昭新. "華、台語注音符號溯源".
- 方音符號系統(Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols) 臺語方音符號拼音方案使用手冊(閩南語音標系統) [Practical Manual for the Taiwanese Phonetic Symbols] (in Chinese). ROC Ministry of Education. 2001.
- Bopomofo Extended (Version 13.0). Unicode Version-Specific Code Charts. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- "Taiwanese Hakka Romanization System" (臺灣客家語拼音方案). 2009. Ministry of Education, Taiwan.
- "Hakka Romanization System" (客家語拼音方案使用手冊). 2012. Ministry of Education, Taiwan.
- Yang, B., & Chan, E. (2019). L2/19-177R Proposal to encode Cantonese Bopomofo Characters.
- Tung, B., Ko, B., Wei, S. (2018). L2/18-255 Proposal to fix glyphs in Bopomofo Extended block and encode one Bopomofo letter.
- 吳守禮台語注音字型。中央研究院。
- 中研院資訊所。(2013)。吳守禮台語注音字型說明。
External links
- 教育部方音符號系統
- 吳守禮, 吳昭新. "華、台語注音符號總表"
- 吳守禮, 吳昭新. "台語七種拼音法對照表"
- 吳昭新. "台語注音符號二式"