Solar eclipse of July 13, 2018
A partial solar eclipse occurred on July 13, 2018. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. Part of the Moon's shadow fell near the South Pole, so partial coverage of the Sun was visible in parts of southern Australia, such as Melbourne and Geelong in Victoria, Mount Gambier in South Australia, and Hobart and Launceston in Tasmania, with highest magnitude of about 0.1. The eclipse was also visible in Stewart Island in the far south of New Zealand.[1]
| Solar eclipse of July 13, 2018 | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) From Melbourne, Australia | |
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | -1.3542 |
| Magnitude | 0.3365 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 67.9°S 127.4°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 3:02:16 |
| References | |
| Saros | 117 (69 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9548 |
Partial Solar Eclipse on Friday the 13th
This is the first partial solar eclipse on Friday the 13th since December 1974 and the last until September 2080. The next solar eclipse on Friday 13 will be a total eclipse in June 2132.
Images

Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2018
Solar eclipses of 2018–2021
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
Note: Partial solar eclipses on February 15, 2018, and August 11, 2018, occurred during the previous semester series.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2018–2021 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 107 | 2017 July 23 | -2.14244 | 112 | 2018 January 17 | 1.78677 | |
117.jpg.webp) Partial from Melbourne, Australia | 2018 July 13 Partial |
-1.35423 | 122 Partial from Nakhodka, Russia | 2019 January 6 Partial |
1.14174 | |
127 La Serena, Chile | 2019 July 2 Total |
-0.64656 | 132.jpg.webp) Jaffna, Sri Lanka | 2019 December 26 Annular |
0.41351 | |
137 Beigang, Yunlin, Taiwan | 2020 June 21 Annular |
0.12090 | 142 Gorbea, Chile | 2020 December 14 Total |
-0.29394 | |
| 147 | 2021 June 10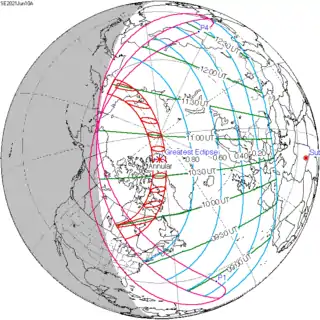 Annular |
0.91516 | 152 | 2021 December 4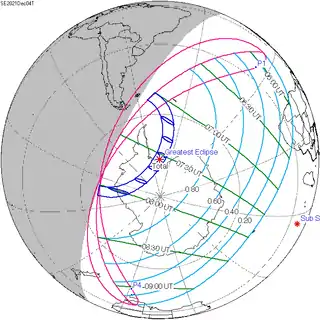 Total |
-0.95261 | |
| 157 | 2022 May 30 | 1.65174 | 162 | 2022 November 23 | -1.69875 | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 21 eclipse events, progressing from south to north between July 13, 2018 and July 12, 2094 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 12–13 | April 30-May 1 | February 16–17 | December 5–6 | September 22–23 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 July 13, 2018 |
 April 30, 2022 |
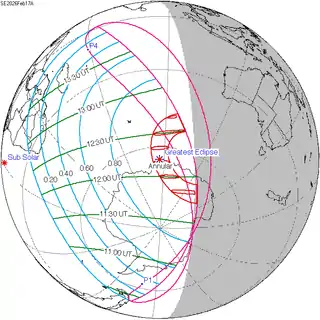 February 17, 2026 |
 December 5, 2029 |
 September 23, 2033 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 July 13, 2037 |
 April 30, 2041 |
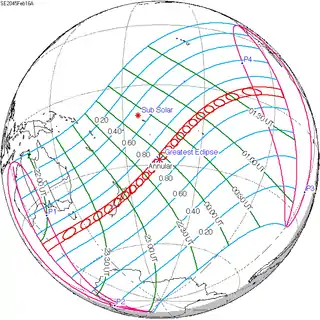 February 16, 2045 |
 December 5, 2048 |
 September 22, 2052 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
 July 12, 2056 |
 April 30, 2060 |
 February 17, 2064 |
 December 6, 2067 |
 September 23, 2071 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 July 13, 2075 |
 May 1, 2079 |
 February 16, 2083 |
 December 6, 2086 |
 September 23, 2090 |
| 157 | ||||
 July 12, 2094 | ||||
References
- "Partial Solar Eclipse on July 13, 2018". www.timeanddate.com. Retrieved July 13, 2018.
- van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2018 July 13. |
.jpg.webp)

