Seaton railway station (Cumbria)
Seaton railway station served the village of Seaton, near Workington in Cumberland (now in Cumbria), England.[7][8][9]
Seaton | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Seaton station, 1951. | |
| Location | Seaton, near Workington, Allerdale England |
| Coordinates | 54.6621°N 3.5234°W |
| Grid reference | NY018307 |
| Platforms | 2[1][2][3][4] |
| Other information | |
| Status | Disused |
| History | |
| Original company | Cleator and Workington Junction Railway |
| Key dates | |
| 4 January 1888 | Opened |
| July 1897 | Closed |
| February 1907 | Reopened |
| February 1922 | Closed to passengers[5] |
| 6 April 1962 | Closed completely[6] |
| 4 June 1992 | Line through the station closed[6] |
| Location | |
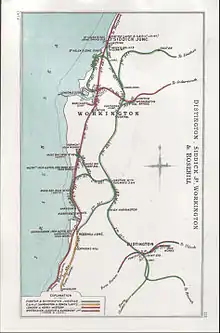
Cleator & Workington Junction Rly | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cumbrian Coast line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The station was opened by the Cleator and Workington Junction Railway (C&WJR) in 1888 on its new "Northern Extension" from Calva Junction on the northern edge of Workington to the Maryport and Carlisle Railway's Derwent Branch at Linefoot. The C&WJR built this 7-mile-30-chain long (11.9 km) line to connect the C&WJR with Carlisle and beyond. The line was double track from Workington to Seaton, then single to Linefoot Junction.
Most stations on C&WJR lines had heavy industrial neighbours, such as ironworks next to Cleator Moor West, or served primarily industrial workforces, such as Keekle Colliers' Platform. Seaton, however, was a fairly isolated country village.
History
The C&WJR was built in the late 1870s, being one of the fruits of the rapid industrialisation of West Cumberland in the second half of the nineteenth century, specifically being born as a reaction to oligopolistic behaviour by the London and North Western and Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railways.[10]
It was originally intended to drive the line northwards across country to meet the Caledonian Railway and cross into Scotland by the Solway Viaduct, but an accommodation was made with the LNWR leading to the intended northern extension being greatly watered down to three lines:
- a 1 mile 54 chains (2.7 km) link from Workington Central to Siddick Junction which opened in 1880
- a 30 chains (0.60 km) link from Cloffocks Junction to the CKPR line which opened in March 1885, and
- the "Northern Extension" through Seaton to Linefoot Junction.[11]
All lines in the area were primarily aimed at mineral traffic, notably iron ore, coal and limestone, none more so than the Northern Extension, which passed through open country. Passenger services were provided calling at Seaton, but they were so unsuccessful they petered out in 1922. The C&WJR earned the local name "The Track of the Ironmasters".[12]
The founding Act of Parliament of June 1878 confirmed the company's agreement with the Furness Railway that the latter would operate the line for one third of the receipts.[13]
All C&WJR's lines were heavily graded. Almost all of the first three miles of the Northern Extension from Calva Junction through Seaton was rising at 1 in 70.[14] This favoured loaded coal and coke trains.
The Northern Extension became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway at the Grouping of 1923.
Like any business tied to one or few industries, the C&WJR was particularly at the mercy of trade fluctuations and technological change. The Cumberland iron industry led the charge in the nineteenth century, but became less and less competitive as time passed and local ore became worked out and harder to win, taking the fortunes of the railway with it. The peak year was 1909, when the C&WJR handled 1,644,514 tons of freight.[15] Ominously for the line, that tonnage was down to just over 800,000 by 1922, bringing receipts of £83,349, compared with passenger fares totalling £6,570.[16]
The high water mark for tonnage on the C&WJR was 1909, the high water mark for progress was 1913, with the opening of the Harrington and Lowca line for passenger traffic. A chronology of the line's affairs from 1876 to 1992 has almost no entries before 1914 which fail to include "opened" or "commenced". After 1918 the position was reversed, when the litany of step-by-step closures and withdrawals was relieved only by a control cabin and a signalbox being erected at Harrington Junction in 1919.
Services
C&WJR passenger trains consisted of antiquated Furness stock hauled largely by elderly Furness engines[17][18] referred to as "rolling ruins" by one author after a footplate ride in 1949.[19]
No Sunday passenger service was ever provided on any C&WJR line.
The Northern Extension had three stations: Seaton, Great Broughton and Linefoot, the last being run jointly with the Maryport and Carlisle Railway (MCR). A passenger service was provided to Seaton over two periods: 1888 to 1897 and 1907 to 1922. The service in the first period appears to have been out and back over the 2 miles 19 chains (3.6 km) to Workington Central. This was reduced to Wednesdays and Saturdays only (Workington Market Days) from March 1891 and to Saturdays only from January 1894, being withdrawn completely in July 1897.[6][5]
The company tried again ten years later, with what appears to have been another daily out and back from Workington Central. From September 1908 this was extended, on Saturdays only, to Great Broughton and Linefoot Junction, making those outposts qualify as stations having had a publicly advertised passenger service. That experiment failed, as they disappeared from the timetable in December of that year, leaving Seaton as the only Northern extension station with a public passenger service.[20]
On 2 June 1913 a new public passenger service was opened from Lowca to Workington Central, aimed mainly but not exclusively at workers travelling to and from the remote Harrington No 10 Colliery and associated bi-products works on the clifftop at Lowca. One of these trains ran beyond Workington to Seaton and a second one did so on Saturday afternoons. Southbound ("Down") the early morning train started at Seaton and one other made an out and back trip from Seaton to Workington, rather than a through train.[21] All others plied between Lowca and Workington Central only. This remained the case in 1919.[22][23] The Lowca service continued to 1926, but the Seaton experiment ended altogether in February 1922.[24]
The W&CJR ran many workmen's trains. Three collieries were served by the Northern Extension - Camerton, Buckhill and Alice Pit. No source lists any station, halt or workmen's service to this last, which was at the northern end of the line near Linefoot Junction. The 1920 Working Time Table lists Alice Pit, but shows no booked services of any description.
Camerton Colliery Halt and Buckhill Colliery Halt both had workmen's services at some point,[25] but they are not mentioned in the May 1920 Working Time Table. Indeed, Camerton Colliery is not mentioned at all.[23]
The 1920 Working Time Table shows no Goods (as opposed to mineral) trains or "Through goods" trains booked to call or pass Seaton in either direction.[23]
Rundown and closure
The West Cumberland iron and steel industry was heavily dependent on supplies of coke from the Northumberland and Durham coalfields. The Northern Extension allowed "a large proportion" of this traffic to be routed away from Maryport and the coastal line. Likewise the short chord between Workington Bridge and Cloffocks Junction allowed Durham coke traffic to reach the furnaces via Cockermouth then the C&WJR.[26] These must have suffered a significant decline, as by 1920 there were just two booked mineral workings each way each weekday between Linefoot Junction and Workington through Seaton. There was also a daily booked mineral train from Workington to Buckhill Colliery which passed through Seaton. [23] It is therefore no surprise that the line north of Buckhill Colliery closed on 1 September 1921, leaving Seaton station "stranded" on what was effectively a long siding.[11]
Given this early decline it is remarkable that Seaton station remained open for goods traffic until 6 April 1962 and even more remarkable that the line through Seaton went on to outlive all other former C&WJR metals by some years. Buckhill Colliery's output and Seaton station's slender goods traffic appear to be the sole reasons for keeping the remnant of the Northern Extension open after 1922, though Camerton Colliery appears to have still been in production until 1931.[27] Buckhill Colliery closed in 1932,[28] though even here it is questionable how much rail borne coal traffic it generated after 1924 when an aerial ropeway was installed taking its coals over the Derwent to William Pit at Great Clifton.[29]
The branch's longevity came about because the Admiralty, attracted by a remote area with rail and sea access, chose part of the site of Buckhill Colliery and the surrounding area to build a rail-served armaments depot which opened in 1938 and closed in 1992, [30]taking the line with it. After the closure of the C&WJR south of Workington Central in 1965 all trains through Seaton to the armaments depot travelled south from Siddick Junction past Calva Junction, where they reversed towards Seaton.
Enthusiasts' specials
An enthusiasts' special passed through Seaton on 5 September 1954, travelling to the then limit of public railway at Buckhill, the only one to traverse the C&WJR using main line passenger stock.
The next such train to traverse any C&WJR metals was the "Solway Ranger" brakevan special on 7 May 1966, which repeated the run through Seaton to Buckhill, with a third and final such trip on 2 March 1968[31]
Afterlife
By 2015 the trackbed through Seaton was part of the West Cumbria Cycle Network.
| Preceding station | Disused railways | Following station | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workington Central Line and station closed |
Cleator and Workington Junction Railway Northern Extension |
Camerton Colliery Halt Line and station closed |
References
- Anderson 2002, p. 315.
- Robinson 2002, p. 15.
- Suggitt 2008, p. 70.
- Webb 1964a, p. 790.
- Butt 1995, p. 207.
- McGowan Gradon 2004, p. 68.
- McGowan Gradon 2004, pp. 6 & 63.
- Smith & Turner 2012, Map 26.
- Jowett 1989, Map 36.
- Anderson 2002, p. 309.
- McGowan Gradon 2004, p. 59.
- Anderson 2002, p. 313.
- Marshall 1981, p. 117.
- McGowan Gradon 2004, p. 64.
- McGowan Gradon 2004, p. 50.
- Suggitt 2008, p. 65.
- Anderson 2002, p. 314.
- McGowan Gradon 2004, pp. 40 & 42.
- McGowan Gradon 2004, p. 51.
- Bradshaw 1968, p. 477.
- Andrews 2001, p. 22.
- McGowan Gradon 2004, pp. 28-9.
- Haynes 1920, Tables.
- Bradshaw 1985, p. 595.
- Croughton, Kidner & Young 1982, pp. 55 & 53.
- McGowan Gradon 2004, p.11, Note 8.
- Camerton Colliery data, via Durham Mining Museum
- McGowan Gradon 2004, p. 56.
- Buckhill Colliery ropeway, via Durham Mining Museum
- McGowan Gradon 2004, pp. 58-59.
- McGowan Gradon 2004, pp. 60-1.
Sources
- Anderson, Paul (April 2002). Hawkins, Chris (ed.). "Dog in the Manger? The Track of the Ironmasters". British Railways Illustrated. Clophill: Irwell Press Ltd. 11 (7). ISSN 0961-8244.
- Andrews, Dr. Michael (May 2001). Peascod, Michael (ed.). "The Harrington & Lowca Light Railway". Cumbrian Railways. Pinner: Cumbrian Railways Association. 7 (2). ISSN 1466-6812.
- Bradshaw, George (1968) [April 1910]. April 1910 Railway Guide. Newton Abbot: David and Charles. ISBN 978-0-7153-4246-6. OCLC 30645.
- Bradshaw, George (1985) [July 1922]. Bradshaw's General Railway and Steam Navigation guide for Great Britain and Ireland: A reprint of the July 1922 issue. Newton Abbot: David and Charles. ISBN 978-0-7153-8708-5. OCLC 12500436.
- Butt, R. V. J. (1995). The Directory of Railway Stations: details every public and private passenger station, halt, platform and stopping place, past and present (1st ed.). Sparkford: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 978-1-85260-508-7. OCLC 60251199.
- Croughton, Godfrey; Kidner, R. W.; Young, Alan (1982). Private and Untimetabled Railway Stations, Halts and Stopping Places. The Oakwood Press. ISBN 978-0-85361-281-0. OCLC 10507501.
- Jowett, Alan (March 1989). Jowett's Railway Atlas of Great Britain and Ireland: From Pre-Grouping to the Present Day (1st ed.). Sparkford: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 978-1-85260-086-0. OCLC 22311137.
- Haynes, Jas. A. (April 1920). Cleator & Workington Junction Railway Working Time Table. Central Station, Workington: Cleator and Workington Junction Railway.
- McGowan Gradon, W. (2004) [1952]. The Track of the Ironmasters: A History of the Cleator and Workington Junction Railway. Grange-over-Sands: Cumbrian Railways Association. ISBN 978-0-9540232-2-5.
- Robinson, Peter W. (2002). Cumbria's Lost Railways. Catrine: Stenlake Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84033-205-6.
- Smith, Paul; Turner, Keith (2012). Railway Atlas Then and Now. Ian Allan Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7110-3695-6.
- Suggitt, Gordon (2008). Lost Railways of Cumbria (Railway Series). Newbury, Berkshire: Countryside Books. ISBN 978-1-84674-107-4.
- Webb, David R. (October 1964a). Cooke, B.W.C. (ed.). "Between the Solway and Sellafield: Part Two". The Railway Magazine. London: Tothill Press Limited. 110 (762). ISSN 0033-8923.
Further reading
- Conolly, W Philip (1998). British railways pre-grouping atlas and gazetteer (9th impression; 5th ed.). Shepperton: Ian Allan. ISBN 978-0-7110-0320-0. OCLC 221481275.
- Atterbury, Paul (2009). Along Lost Lines. Newton Abbot: David & Charles. ISBN 978-0-7153-2706-7.
- Bairstow, Martin (1995). Railways In The Lake District. Leeds: Martin Bairstow. ISBN 978-1-871944-11-2.
- Bowtell, Harold D. (1989). Rails through Lakeland: An Illustrated Journey of the Workington-Cockermouth-Keswick-Penrith Railway 1847–1972. Wyre: Silverling Publishing Ltd. ISBN 978-0-947971-26-7.
- Joy, David (1983). Lake Counties (Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain). Newton Abbot: David & Charles. ISBN 978-0-946537-02-0.
- Marshall, John (1981). Forgotten Railways: North West England. Newton Abbot: David & Charles. ISBN 978-0-7153-8003-1.
- Webb, David R. (September 1964b). Cooke, B.W.C. (ed.). "Between the Solway and Sellafield: Part One". The Railway Magazine. London: Tothill Press Limited. 110 (761). ISSN 0033-8923.
- Western, Robert (2001). The Cockermouth, Keswick and Penrith Railway. Usk: Oakwood Press. ISBN 978-0-85361-564-4. OL113.
External links
- Map of the CWJR with photos RAILSCOT
- Map of the WC&ER with photos RAILSCOT
- The station Rail Map Online
- The station on overlain OS maps surveyed from 1898 National Library of Scotland
- The closed station on a 1948 OS Map npe maps
- The station and line railwaycodes
- The railways of Cumbria Cumbrian Railways Association
- Photos of Cumbrian railways Cumbrian Railways Association
- The railways of Cumbria Railways_of_Cumbria
- Cumbrian Industrial History Cumbria Industrial History Society
- 5 September 1954, 7 May 1966 and 2 March 1968 railtours sixbellsjunction
- A video tour-de-force of the region's closed lines cumbriafilmarchive
- 1882 RCH Diagram showing the station, see page 173 of the pdf google
- Haematite earthminerals
- Coal and iron ore mining in Cleator Moor Haig Pit
- Photos of the C&WJR staff, tickets and timetables Harrington History
- Photos of Calva Jct to Buckhill Tim Harris
- Photos of Siddick Junction - Calva - Broughton Moor derbysulzers
- Cycle Network at Seaton visitcumbria

