Nissan MR engine
The MR is a family of straight-four all-aluminium automobile engines with variable valve timing co-developed by Renault and Nissan. Renault calls it the M engine. Other noteworthy features of this engine family include acoustically equal runner lengths and a tumble control valve for the intake manifold, a "silent" timing chain, mirror finished crankshaft and camshaft journals, and offset cylinder placement in an attempt for increased efficiency.
| Nissan MR engine | |
|---|---|
 MR20DE | |
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Nissan Motors & Renault |
| Production | 2004– |
| Layout | |
| Configuration | Inline 4 |
| Displacement | 1.6 L (1618 cc) 1.8 L (1797 cc) 2.0 L (1997 cc) |
| Cylinder bore | 79.7 mm (3.14 in) 84 mm (3.31 in) |
| Piston stroke | 81.1 mm (3.19 in) 90.1 mm (3.55 in) |
| Block material | Aluminum alloy |
| Head material | Aluminum alloy |
| Valvetrain | DOHC 4 valves x cyl. with VVT |
| Compression ratio | 9.5:1, 9.9:1 |
| Combustion | |
| Turbocharger | In some versions |
| Fuel system | Fuel injection Direct injection |
| Fuel type | Gasoline (all except M9R / M9T) Diesel (M9R / M9T) |
| Cooling system | Water-cooled |
| Output | |
| Power output | 188–300 bhp (191–304 PS; 140–224 kW) |
| Torque output | 240–285 N⋅m (177–210 lb⋅ft) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Nissan SR engine
Renault F-Type engine |
The MR engine family features 'under stress' manufacture, meaning while the block is being bored, a torque plate puts the block under stress. The block becomes temporarily distorted until the head is torqued onto it, at which point the block is pulled into the correct shape.
MR16DDT
The MR16DDT is a 1.6 L (1618 cc) DIG-T (Direct Injection Gasoline-Turbocharged) inline-four engine, with a bore x stroke of 79.7 mm × 81.1 mm (3.14 in × 3.19 in). It was first introduced in the Nissan Juke small SUV in the autumn of 2010. Output is 188 bhp (191 PS; 140 kW) and 240 N⋅m (177 lb⋅ft) of torque. The 2014 Juke NISMO RS FWD produced 215 bhp (218 PS; 160 kW) and 285 N⋅m (210 lb⋅ft). In 2015 Nissan Teana use 1.6 Turbo as replacement of the old 2.0 engine.

Some of the pertinent features of the MR16DDT are:
- Twin variable valve timing control (CVTCS on intake and exhaust valves)
- Turbo-charged and intercooled
- Compression ratio of 9.5:1
- Lightweight design and reduced frictions
Applications:
- 2011–present Nissan Juke 188 hp (191 PS; 140 kW)
- 2013-2015 Nissan Juke NISMO (V1 Engine) 197 hp (200 PS; 147 kW)
- 2014–present Nissan Juke NISMO RS FWD 215 PS (158 kW; 212 hp) and 285 N⋅m (210 lb⋅ft) of torque
- 2013–present Nissan Tiida (hatchback)/Nissan Pulsar/Nissan Sylphy
- 2012 Nissan Deltawing Race car (not production) (300 PS (221 kW; 296 hp) at 7400 rpm)
- 2013–present Renault Sport Clio (M5M) 200 PS (147 kW; 197 hp)/177 lb⋅ft (240 N⋅m)
- 2015–present Renault Sport Clio TROPHY (M5MT)215 PS (158 kW; 212 hp) and 210 lb⋅ft (285 N⋅m)
- 2013–present Renault Samsung SM5 TCE (M5M)
- 2015–present Nissan X-Trail (161 hp (120 kW; 163 PS))[1]
- 2015–present Nissan Teana L33 (190 PS (140 kW; 187 hp))
- 2015–present Renault Talisman TCE (150 PS (110 kW; 148 hp), 200 hp (149 kW; 203 PS))
- 2016–present Renault Samsung SM6 TCE (190 PS (140 kW; 187 hp))
- 2016–present Renault Mégane#Mégane GT (M5M B4)(205 PS (151 kW; 202 hp))
- 2017–present Nissan Sentra SR Turbo & NISMO (188 hp (140 kW; 191 PS))
- 2017–2018 Renault Kadjar TCe 160
MR18DE
The MR18DE is a 1.8 L (1798 cc) version, bore and stroke is 84 mm × 81.1 mm (3.31 in × 3.19 in). It produces 130 PS (96 kW; 128 hp).
In North America the output is 122 hp (91 kW; 124 PS) at 5500 rpm and 174 N⋅m (128 lb⋅ft) at 4800 rpm.
From July 6, 2006 this engine is also fitted to Nissan Livina Geniss for China version and the Nissan Grand Livina for Indonesia and Malaysia. Output is 126 PS (93 kW; 124 hp) at 5200 rpm and 174 N⋅m (128 lb⋅ft) at 4800 rpm.
For Brazil, this engine is fitted to the Tiida and Livina ranges, with Flex-fuel capability.
Applications:
- 2004–2012 Nissan Tiida/Versa
- 2006–2019 Nissan Grand Livina
- 2006–present Nissan Wingroad
- 2009-2014 Nissan Cube
MRA8DE

The MRA8DE is a 1.8 L (1797 cc) engine, different from the MR18DE as it has a twin variable valve timing system on both the intake and exhaust valves and uses a diamond-like carbon coating. Bore and stroke is 79.7 mm × 90.1 mm (3.14 in × 3.55 in). It produces 130 PS (96 kW; 128 hp) at 6000 rpm and 174 N⋅m (128 lb⋅ft) at 3600 rpm, and has a compression ratio of 9.9:1.
Applications:
- 2013–present Nissan Sylphy B17 (Asian)/Nissan Sentra (North America and Middle east)/Nissan Pulsar (Australasia)
MR18DDT (Renault TCe M5P)
The MR18DDT is a 1.8 L (1797 cc) engine, different from the MR18DE & MRA8DE as it has a turbocharged, twin variable valve timing system on both the intake and exhaust valves and uses a diamond-like carbon coating. Bore and stroke is 79.7 mm × 90.1 mm (3.14 in × 3.55 in). It produces 225–300 PS (165–221 kW; 222–296 hp) at 6000 rpm and 300–420 N⋅m (221–310 lb⋅ft) at 3600 rpm, and has a compression ratio of 9.0:1.
Applications:
- 2015–present Renault Espace V Energy TCe 225 EDC7
- 2017–present Renault Megane IV RS280 (Sport and Cup), Megane R.S. 300 Trophy
- 2017–present Alpine A110 (2017)
MR20DET

The MR20DET, a 2.0 L (1997 cc) engine, was the first MR series engine developed by Nissan as a replacement for the QR20DE. It is an undersquare engine, its bore and stroke being 84 mm × 90.1 mm (3.31 in × 3.55 in). It was first introduced in the Lafesta and Serena MPVs and Renault Samsung SM5 in early 2005. In November 2006, it entered Renault's lineup in the Clio III as the M4R, where it generates 278 PS (204 kW; 274 hp).
This engine is available with Nissan's XTRONIC CVT continuously variable transmission in several applications.
A detuned version, with 280 PS (206 kW; 276 hp) instead of 283 PS (208 kW; 279 hp), was added to the new Bluebird Sylphy in late 2006. In the new Nissan X-Trail, Qashqai and C-Platform Sentra, the MR20DE produces 296 PS (218 kW; 292 hp) at 5100 rpm and 420 N⋅m (310 lb⋅ft) of torque at 4800 rpm. Middle East version of the MR20DET engine that goes in the Nissan Qashqai produces 297 PS (218 kW; 293 hp) at 5200 rpm and 418 N⋅m (308 lb⋅ft) of torque at 4400 rpm.
Applications:
- 2005–present Nissan Serena
- 2005–present Renault Samsung SM5
- 2005–2012 Nissan Bluebird Sylphy
- 2006–present Renault Clio
- 2007–present Nissan X-Trail
- 2007–present Nissan Qashqai
- 2007–2012 Nissan Sentra
- 2007–2015 Renault Laguna
- 2008–2014 Nissan Teana(J32)
- 2008–present Renault Safrane
- 2008–2016 Renault Mégane(III)
- 2009–present Renault Scénic
- 2009–present Renault Fluence
- 2009–present Renault Samsung SM3
- 2009–present Renault Latitude
- 2013–present Nissan NV200
- 2013–present Nissan Sentra (Brazil only - Flex Fuel (gasoline and ethanol)
MR20DD (Renault M5R)

The MR20DD is a 2.0 L (1997 cc) engine developed by Nissan with direct injection and twin variable valve timing control. The MR20DD engine is "SU-LEV" certified in Japan, and produces 147 PS (108 kW; 145 hp) at 5600 rpm and 155 lb⋅ft (210 N⋅m) of torque at 4400 rpm.[2] Export models claim 137 hp (102 kW; 139 PS) at 5200 rpm and 147 lb⋅ft (199 N⋅m) at 4400 rpm.
The Australian & New Zealand markets Nissan Qashqai ST and Ti models use a variant of the MR20DD which achieves 106 kW (142 hp; 144 PS) at 6000 rpm and 200 N⋅m (148 lb⋅ft) at 4400 rpm.[3][4]
Applications:
- 2010–present Nissan Serena
- 2013–present Nissan X-Trail
- 2014–present Australian & New Zealand Markets Nissan Qashqai
- 2016-present Renault Kadjar (China)
- 2016-present Renault Koleos II
- 2017-present Renault Samsung QM6
- 2017-present Nissan Rogue Sport
MR20DD Hybrid
The MR20DD Hybrid is a 2.0 L (1997 cc) Hybrid engine developed by Nissan with direct injection and twin variable valve timing control. The MR20DD Hybrid engine is "SU-LEV" certified in Japan, and produces 144 PS (106 kW; 142 hp) at 6000 rpm and 147 lb⋅ft (199 N⋅m) of torque at 4400 rpm. with Synchronous Electric Motor produces 41 PS (30 kW; 40 hp) and 118 lb⋅ft (160 N⋅m) of torque and Lithium-Ion battery, for a combined power of 179 PS (132 kW; 177 hp).
Applications:
- 2013–present Nissan X-Trail Hybrid
MR20DD S-Hybrid
The MR20DD S-Hybrid is a 2.0 L (1997 cc) Hybrid engine developed by Nissan with direct injection and twin variable valve timing control. The MR20DD S-Hybrid engine is MHEV "SU-LEV" certified in Japan, and produces 150 PS (110 kW; 148 hp) at 6000 rpm and 147 lb⋅ft (199 N⋅m) of torque at 4400 rpm. with Synchronous Electric Motor and 48V battery.
Applications:
- 2012–present Nissan Serena S-Hybrid
M9 diesel
The M9R and M9T are a family of straight-four diesel engines co-developed by Nissan and Renault; the latter call them the M engines. Following Renault's designation plan, the last letter (M9R resp. M9T) is to indicate the swept volume of 2.0 l resp. 2.3 litres. Despite the similar names, the diesel engines are only loosely related to the MR gasoline engines.
Features of the diesel engines include a cast-iron block, aluminium alloy cylinder head with double overhead camshafts, 16-valve layout and a bushes timing chain. The M9T is directed to heavier vehicles like the Nissan Navara or the Renault Master. It features a bore and stroke of85 mm × 101.3 mm (3.35 in × 3.99 in) for a total displacement of 2,299 cc (2.3 L), balancer shafts,[5] typical speeds are 3500 rpm for maximum power and 1250 rpm for maximum torque.
Low output versions of the M9R for the Renault Trafic II at 66 and 85 kW (90 and 116 PS; 89 and 114 hp) had been replaced by the Renault R engine with the introduction of the Trafic III, while versions starting from 96 kW (131 PS; 129 hp) include VNT chargers. The top version of the Navara utilizes the M9T with twin-turbochargers and 140 kW (190 PS; 188 hp). During production period engines had been updated up to Euro 6 (in early 2017).
M9R
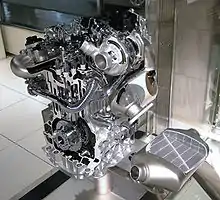
| Nissan M9R | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Nissan & Renault |
| Also called | 2.0 dCi |
| Production | 2006-present |
| Layout | |
| Configuration | Inline-four |
| Displacement | 2.0 L (1995 cc) |
| Cylinder bore | 84 mm (3.31 in) |
| Piston stroke | 90 mm (3.54 in) |
| Block material | Cast iron |
| Head material | Aluminium alloy |
| Valvetrain | DOHC 4 valves per cylinder |
| Compression ratio | 15.6:1 |
| Combustion | |
| Turbocharger | Yes |
| Fuel system | Common rail Direct Injection |
| Fuel type | Diesel |
| Cooling system | Water-cooled |
| Output | |
| Power output | 130–180 PS (96–132 kW; 130–180 hp) |
| Torque output | 320–400 N⋅m (240–300 lb⋅ft) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Renault F-Type engine |
| Successor | Renault R-Type engine |
The M9R is available in the 150 PS (110 kW; 148 hp) tune in Nissan Qashqai, Nissan X-Trail, Renault Mégane, Renault Koleos and Renault Laguna models. In this trim the engine achieves maximum power at 4000 rpm and maximum torque of 340 N⋅m (251 lb⋅ft) at 2000 rpm. A 175 PS (129 kW; 173 hp) form with particulate filter is available in Renault Laguna and Nissan X-Trail models. A 180 PS (132 kW; 178 hp) variant is also available on the Laguna GT. In both engines maximum power is achieved at 3750 rpm and maximum torque is available from 1750 rpm.
In order to reduce vibrations, balance shafts are included in some versions of the engine. The 2.0 dCi engine in all its versions complies with the Euro 4 and 5 standards for exhaust emissions. The 150 PS (110 kW; 148 hp) New Mégane and New Laguna respectively emitted 144 g (5.1 oz)/km and 154 g (5.4 oz)/km of CO2 and the 129 kW (175 PS; 173 hp) version of New Laguna 2.0 dCi emits 159 g (5.6 oz)/km of CO2; they all comply with the Euro 5 standards for exhaust emissions.
In 2011 the 96 and 110 kW (131 and 150 PS; 129 and 148 hp) M9R engines has been updated with an optional package to lower exhaust emissions (Euro5) and fuel consumption. These engines are tagged "2.0 Energy dCi 130" resp. "2.0 Energy dCi 150", typically maximum power is available at 3750 rpm and maximum torque at a minimum of 1750 rpm. The package comprises:
- Stop & Start
- Active thermal management
- Smart electrical management
- Variable capacity oil pump
The CO2 values were thus reduced to 118 g (4.2 oz)/km for the Laguna both the 2.0 Energy dCi 130 and 2.0 Energy dCi 150.
The engine is fitted to the following vehicles:
- 2007–2011 Nissan Qashqai
- 2007–2012 Nissan X-Trail
- 2005–2015 Renault Laguna
- 2006–2015 Renault Mégane
- 2007–present Renault Koleos
- 2006–2014 Renault Espace
- 2007–2010 Renault Vel Satis
- 2015 Nissan Teana
- 2006-2014 Vauxhall Vivaro Renault Trafic Nissan Primastar
- 2010–present Renault Latitude
- 2015–present Renault Espace V
M9T
| Renault M9T | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Mercedes-Benz & Renault–Nissan–Mitsubishi Alliance |
| Also called |
|
| Production | 2010– |
| Layout | |
| Configuration | Inline-four engine |
| Displacement | 2.3 L (2,298 cc) |
| Cylinder bore | 85 mm (3.35 in) |
| Piston stroke | 101.3 mm (3.99 in) |
| Block material | Aluminium alloy |
| Head material | Aluminium alloy |
| Valvetrain | DOHC |
| Compression ratio | 15.4:1 |
| Combustion | |
| Turbocharger |
|
| Fuel system | Common rail direct injection |
| Fuel type | Diesel |
| Cooling system | Water cooled |
| Output | |
| Power output | 75–140 kW (102–190 PS; 101–188 hp) |
| Torque output | 285–450 N⋅m (210–332 lb⋅ft) |
The M9T is a version specifically designed for light commercial vehicles that is manufactured by Renault in Cléon. It was introduced on the Renault Master and its badge engineered derivatives, initially with power ranging from 75 kW (101 hp) to 110 kW (150 hp), and torque ratings starting at 185 N⋅m (136 lbf⋅ft) up to 350 N⋅m (260 lbf⋅ft).[6][7] Later, it was also introduced to the Nissan Navara and the Mercedes-Benz X-Class.[8][9] Nissan calls it the YS23 while in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, it is named the OM699. The engines with lower power ratings feature a single fixed geometry turbocharger,[10] while the more powerful versions have a variable-geometry turbocharger or twin-turbochargers.[11] The engines are compliant with the Euro 6 emission regulations.[12]
Applications:
References
- "New Nissan X-Trail spec and engine details". March 5, 2014. Retrieved September 28, 2017.
- "NISSAN | Nissan Releases All-New Serena Minivan". Nissan-global.com. November 8, 2010. Archived from the original on August 10, 2017. Retrieved September 28, 2017.
- "All-New Nissan Qashqai Now on Sale in Audtralia". July 14, 2014. Retrieved September 28, 2017.
- Nissan Qashqai Specifications Retrieved September 28, 2017.
- http://www.powertrain.renault.com/application/storage/upload/filemanager/brochure/brochure_engine_new/Brochure_2000_dCi_MAJ_2014.pdf
- "Renault Launching New 2.3L Diesel". Green Car Congress. Retrieved 2020-08-06.
- "2011 Renault Master | Top Speed". 14 March 2012. Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- "2015 Nissan NP300 Navara - more details revealed". Paul Tan's Automotive News. 2014-07-29. Retrieved 2020-08-06.
- "2020 Mercedes-Benz X-Class Review | Top Gear". Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- "Renault presents the new 2.3 dCi diesel engine, designed and produced in Franc..." en.media.groupe.renault.com. Retrieved 2020-08-06.
- "2015 Nissan NP300 Navara - more details revealed". Paul Tan's Automotive News. 2014-07-29. Retrieved 2018-09-11.
- MATHIOUDAKIS, GoAutoMedia - BYRON. "Future Models - Nissan - Navara". GoAuto. Retrieved 2018-09-11.