TOI 700 d
TOI 700 d is an exoplanet, likely rocky, orbiting TOI 700, a red dwarf star 101.4 light-years away in the Dorado constellation. The exoplanet is the first Earth-sized exoplanet in the habitable zone discovered by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS).[3][4][5] It has been estimated that the planet receives about 86% the energy that the Earth receives from the Sun.[6] It was discovered in January 2020 by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS).
 Artist's impression of TOI 700 d | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Emily Gilbert |
| Discovery date | 3 January 2020 |
| Transit | |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| 0.163±0.015 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.110+0.140 −0.079[1] |
| 37.4260+0.0007 −0.0010 d | |
| Inclination | 89.73+0.15 −0.12 |
| Star | TOI 700 |
| Physical characteristics | |
Mean radius | 1.19±0.11R⊕[2] |
| Mass | 1.72+1.29 −0.63M⊕[2] |
Mean density | 5.61 g/cm3 |
| Temperature | 268.8+7.7 −7.6 K[1] |
Physical characteristics
Mass, radius and temperature
TOI 700 d is Earth-sized, an exoplanet that has a radius and mass similar to the Earth. It has an estimated mass of around 1.72 M⊕ and a radius of about 1.19 R⊕.[2] If it has an earthlike atmosphere, then it would be about 268.8 K (−4.3 °C; 24.2 °F).[1] A small chance of runaway greenhouse effect exists.
Host star
TOI 700 is a red dwarf of spectral class M that is about 40% the mass, about 40% the radius, and very roughly 50% of the temperature of the Sun.[5] The star is bright with low levels of stellar activity. Over the 11 sectors observed with TESS, the star does not show a single white-light flare. The low rotation rate is also an indicator of low stellar activity.[2]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 1.07+0.80 −0.43 M⊕ |
0.0637+0.0064 −0.0060 |
9.97701+0.00024 −0.00028 |
— | 89.67+0.23 −0.32° |
1.010+0.094 −0.087 R⊕ |
| c | 7.48+5.89 −3.30 M⊕ |
0.0925+0.0088 −0.0083 |
16.051098+0.000089 −0.000092 |
— | 88.90+0.08 −0.11° |
2.63+0.24 −0.23 R⊕ |
| d | 1.72+1.29 −0.63 M⊕ |
0.163±0.015 | 37.4260+0.0007 −0.0010 |
— | 89.73+0.15 −0.12° |
1.19±0.11 R⊕ |
Orbit
TOI 700 d orbits its host star every 37.4260 days.
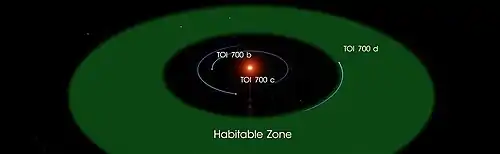
Proposed habitability
TOI 700 d orbits in the habitable zone of its host star TOI 700. The solar wind ram pressure and intensity of the interplanetary magnetic field are expected to be similar to the Earth's, therefore retention of planetary atmosphere is likely.[7][8]
Discovery
TOI 700 d was discovered by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) in early January 2020. This was the first Earth-sized exoplanet discovered by the TESS.[9]
See also
References
- Rodriguez, Joseph E.; Vanderburg, Andrew; Zieba, Sebastian; Kreidberg, Laura; Morley, Caroline V.; Kane, Stephen R.; Spencer, Alton; Quinn, Samuel N.; Eastman, Jason D.; Cloutier, Ryan; Huang, Chelsea X. (3 January 2020). "The First Habitable Zone Earth-Sized Planet From TESS II: Spitzer Confirms TOI-700 d". arXiv:2001.00954 [astro-ph.EP].
- Gilbert, Emily A.; Barclay, Thomas; Schlieder, Joshua E.; Quintana, Elisa V.; Hord, Benjamin J.; Kostov, Veselin B.; Lopez, Eric D.; Rowe, Jason F.; Hoffman, Kelsey; Walkowicz, Lucianne M.; Silverstein, Michele L. (3 January 2020). "The First Habitable Zone Earth-sized Planet from TESS. I: Validation of the TOI-700 System". arXiv:2001.00952 [astro-ph.EP].
- Andreolo, Claire; Cofield, Calla; Kazmierczak, Jeanette (6 January 2020). "NASA Planet Hunter Finds Earth-Size Habitable-Zone World". NASA. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- Garner, Rob (6 January 2020). "NASA Planet Hunter Finds Earth-Size Habitable-Zone World". NASA. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- Wall, Mike (6 January 2020). "NASA's TESS Planet Hunter Finds Its 1st Earth-Size World in 'Habitable Zone'". Space.com. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- "[VIDEO] TOI 700d : une planète de la taille de la Terre découverte dans une "zone habitable"". midilibre.fr (in French). Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- Cohen, O.; Garraffo, C.; Moschou, S.; Drake, J.; Alvarado-Gomez, J.; Glocer, A.; Fraschetti, F. (2020). "The Space Environment and Atmospheric Joule Heating of the Habitable Zone Exoplanet TOI700-d". arXiv:2005.11587 [astro-ph.SR].
- Dong, Chuanfei; Jin, Meng; Lingam, Manasvi (2020). "Atmospheric Escape from TOI-700 d: Venus vs. Earth Analogs". arXiv:2005.13190 [astro-ph.EP].
- https://www.space.com/nasa-tess-first-earth-size-habitable-exoplanet-toi-700d.html
External links
- TESS – Official WebSite
- ExoFOP TIC 150428135 TOI-700 in the Exoplanet Follow-up Observing Program website
- Gilbert, Emily A.; et al. (2020). "The First Habitable Zone Earth-sized Planet from TESS. I: Validation of the TOI-700 System". arXiv:2001.00952 [astro-ph.EP].
- Rodriguez, Joseph E.; et al. (2020). "The First Habitable Zone Earth-Sized Planet from TESS II: Spitzer Confirms TOI-700 D". arXiv:2001.00954 [astro-ph.EP].
- Suissa, Gabrielle; et al. (2020). "The First Habitable Zone Earth-sized Planet from TESS. III: Climate States and Characterization Prospects for TOI-700 D". arXiv:2001.00955 [astro-ph.EP].


_on_Jul_14_2020_aligned_to_stars.jpg.webp)