Methyl thiocyanate
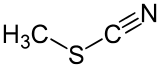
Methyl thiocyanate is an organic compound with the formula CH3SCN. It is a colourless liquid with an onion-like odor. It is produced by the methylation of thiocyanate salts. The compound is a precursor to the more useful isomer methyl isothiocyanate (CH3NCS).[4]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
methyl thiocyanate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
methyl thiocyanate | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.305 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | C047435 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H3NS | |
| Molar mass | 73.117 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.074 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −51 °C (−60 °F; 222 K) |
| Boiling point | 132 °C (270 °F; 405 K) (101.3 kP) |
| Slightly soluble[3] | |
| Solubility in Diethyl ether | Miscible[3] |
| Structure | |
| bent C-S-CN | |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R10, R23/24/25[1] |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S16, S26, S27, S28[1] |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 38 °C (100 °F; 311 K)[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Methyl isocyanate Methyl isothiocyanate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Safety
The LD50 is 60 mg/kg (rats, oral).
It is listed as an extremely hazardous substance by the United States's Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act.[5]
References
- "Chemblink chemical data". Retrieved June 29, 2011.
- "Chemical book page". Retrieved June 29, 2011.
- "United States chemical entree". Retrieved June 29, 2011.
- F. Romanowski, H. Klenk "Thiocyanates and Isothiocyanates, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_749
- 40 C.F.R.: Appendix A to Part 355—The List of Extremely Hazardous Substances and Their Threshold Planning Quantities (PDF) (July 1, 2008 ed.), Government Printing Office, archived from the original (PDF) on February 25, 2012, retrieved March 8, 2009
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
