Izu Islands
The Izu Islands (伊豆諸島, Izu-shotō), formerly the De Vries Archipelago,[1] are a group of volcanic islands stretching south and east from the Izu Peninsula of Honshū, Japan.[2] Administratively, they form two towns and six villages; all part of Tokyo Prefecture. The largest is Izu Ōshima, usually called simply Ōshima.
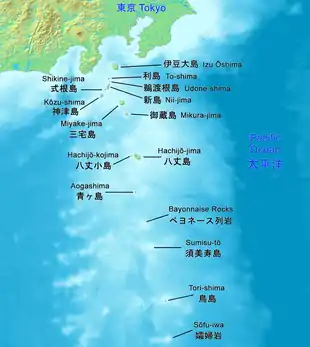
Although usually called the "Seven Islands of Izu" (伊豆七島, Izu Shichitō) in Japanese, there are in fact more than a dozen islands and islets. Nine among them are currently inhabited.
Geography


Right: A beach on Niijima

The Izu islands stretch south-east from the Izu Peninsula on Honshu and cover an area of approximately 301.56 km2 (116.43 sq mi). There are nine populated islands with a total population of 24,645 people (as of 2009) spread over 296.56 km2 (114.50 sq mi). The largest of them is Izu Oshima (8,346 inhabitants, 91.06 km2 (35.16 sq mi)), the smallest Toshima (292 inhabitants, 4.12 km2 (1.59 sq mi).)[3] Of the inhabited islands, seven are traditionally referred to as the "Izu Seven": Oshima, Toshima, Niijima, Kozujima, Miyakejima, Hachijojima, and Mikurajima, though Shikinejima and Aogashima are sometimes included as well. [3]
Each of the islands has its unique character: Oshima is noted for its active volcano Mt Mihara and camellias, Hachijojima for its former penal colony, Mikurajima for dolphin watching, Niijima for its numerous beaches, Kozujima for its white sandy shores, Hachijojima for its well-preserved unique culture, and Miyakejima for the 2001 volcanic eruption.[3]
During the Edo period, Nii-jima, Miyake-jima, and Hachijō-jima served as places of exile for criminals.
The subtropical Ogasawara Islands, which are also administratively part of Tokyo, lie further to the south. They form a far-flung archipelago of over thirty (30) islands some 1,000 km (621 mi) due south of Tokyo.
Islands
| Image | Name Kanji |
Area km² |
Pop. 2007 |
Peak m |
Peak Name | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Izu Ōshima 伊豆大島 | 91.06 | 8472 | 764 | Mihara | 34°44′N 139°24′E |
 | To-shima 利島 | 4.12 | 304 | 508 | Miyatsuka | 34°31′N 139°17′E |
| Udone-shima 鵜渡根島 | 0.4 | - 1) | 210 | 34°28′21″N 139°17′38″E | ||
 | Nii-jima (with Hanshima and Jinai-tō) 新島 | 23.87 | 2420 | 432 | Miyatsuka | 34°22′N 139°16′E |
| Shikine-jima 式根島 | 3.9 | 600 | 109 | Kambiki | 34°19.5′N 139°13′E | |
 | Kōzu-shima 神津島 | 18.48 | 1914 | 574 | Tenjō-zan | 34°13′N 139°9′E |
 | Miyake-jima 三宅島 | 55.44 | 2382 | 815 | Oyama | 34°5′N 139°32′E |
| Ōnohara-jima 大野原島 | 0.2 | - | 114 | Koyasu | 34°02′53″N 139°23′02″E | |
 | Mikura-jima 御蔵島 | 20.58 | 313 | 851 | Oyama | 33°52.5′N 139°36′E |
| Inamba-jima 藺灘波島 | 0.005 | - | 74 | 33°38′53″N 139°18′08″E | ||
| Hachijo Subprefecture | ||||||
| Hachijō-jima 八丈島 | 62.52 | 8363 | 854 | Nishiyama (Hachijō-Fuji) | 33°7′N 139°47′E | |
 | Hachijō-kojima 八丈小島 | 3.08 | - 2) | 616.8 | Taihei-zan | 33°7′31″N 139°41′18″E |
| Aogashima 青ヶ島 | 8.75 | 192 | 423 | Maruyama (Ō-Toppu) | 32°27′29″N 139°46′04″E | |
| Bayonnaise Rocks --- Myōjin-shō ベヨネース列岩 | 0.01 | - | 9.9 | 31°53′14″N 139°55′03″E | ||
 | Sumisu-tō 須美寿島 | 0.03 | - | 136 | 31°26′13″N 140°02′49″E | |
| Tori-shima 鳥島 | 4.79 | - 3) | 394 | Iō-zan | 30°28′48″N 140°18′22″E | |
| Sōfu-iwa 孀婦岩 | 0.0037 | - | 99 | 29°47′39″N 140°20′31″E | ||
1) Udone-shima was inhabited during the Meiji era.
2) Uninhabited since 1969 (then population 31, with a peak of 513)
3) Tori-shima, the largest of the uninhabited islands, had a population of 150 until 1902, when all were killed by a volcanic eruption. Since then, the island has been uninhabited.
Administrative divisions
The Izu Islands are divided into two towns (Oshima and Hachijojima) and six villages (remaining inhabited islands.) Three subprefectures are formed above the municipalities as branch offices of the metropolitan government.[3]
All the islands (more than a dozen in total) lie within the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park.[3] The four southernmost islands are not administrated under any town or village in Hachijō Subprefecture, but are unincorporated areas. Torishima is now uninhabited but is an important bird refuge.
Deserted islands between Aogashima and Ogasawara Islands, namely Bayonaise Rocks (Beyonēzu Retsugan), Smith Island (Sumisu-tō), Torishima, and Lot's Wife (Sōfu-iwa) do not belong to any municipality, because both Hachijō Town and Aogashima Village claim administrative rights. They are directly controlled by Hachijō Subprefecture instead.
- Ōshima Subprefecture
 Ōshima Town: Izu Ōshima
Ōshima Town: Izu Ōshima- Toshima Village: Toshima
- Niijima Village: Niijima, Shikinejima, and Udoneshima
- Kōzushima Village: Kōzushima
- Miyake Subprefecture
- Miyake Village: Miyakejima and Ōnoharajima
- Mikurajima Village: Mikurajima, Inambajima
- Hachijō Subprefecture
 Hachijō Town: Hachijōjima and Hachijōkojima
Hachijō Town: Hachijōjima and Hachijōkojima Aogashima Village: Aogashima
Aogashima Village: Aogashima- unincorporated: Bayonnaise Rocks (Beyonēzu Retsugan), Sumisu-tō, Torishima, and Sōfu-iwa
Demographics
Though the population on the Izu Islands has been dropping, the phase is less dramatic than on other isolated Japanese islands.[3]
| Year | Izu Islands | Isolated Japanese islands | Japan Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 38,707 | 923,062 | 94,301,623 |
| 1970 | 32,539 | 736,712 | 104,665,171 |
| 1980 | 31,902 | 630,536 | 117,060,396 |
| 1990 | 30,032 | 546,505 | 123,611,167 |
| 2000 | 28,756 | 472,312 | 126,925,843 |
| 2005 | 26,242 | 422,712 | 127,767,994 |
The divergent Hachijō language is spoken on the islands.
Infrastructure
The primary industries are fisheries, agriculture, and tourism. The most scenic spots on the islands are crowded with tourists during summers. Popular tourist activities include swimming, scuba diving, surfing, fishing, bird watching and trekking.[3]
Transportation between the islands, by cargo-passengers boats, jetfoils, and aircraft, is supported by harbours on all inhabited islands and five airports (small islands can be reached by helicopter).[3]
There are 5 airports, 15 harbors, and 19 fishing ports. Flights from Tokyo take 30 minutes, while boats take 7–10 hours and jetfoils make the route in about two hours. Transportation on the islands is considered important to the quality of life, which is why about 215 km (134 mi) of paved main roads have been constructed to serve various kinds of vehicles.[3]
There was no electricity on the islands before 1953, but by 1962 98% of the area was receiving electricity.[3]
Geology
The islands occupy the northern portion of the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Arc which extends to the Izu Peninsula and Mount Fuji on the Honshū mainland which are northern extensions of the Izu volcanic arc. The Izu arc ends there at a tectonic triple junction.
Volcanic activity is frequent in the area.[4] 31 people were killed when the research vessel Kaiyō Maru no 5 was destroyed during the 1953 eruption of Myōjin-shō. Volcanic activity, including the release of harmful gases, forced the evacuation of Miyake-jima in 2000. Residents were allowed to return permanently to the island in February 2005 but were required to carry gas masks in case of future volcanic emissions.[3]
To handle the various types of natural disasters threatening the region, including tsunamis, storm, floods, and volcanism, Tokyo metropolitan government has developed prevention and safety measures, including hazard maps and evacuation guidance, radios, signs, and a transport system for emergency supplies.[3]
Ecology
A chain of volcanic islands, the Izu Archipelago are oceanic islands that formed relatively recently (within a few million years) without any previous connection to mainland Japan. In contrast to isolated Pacific islands, such as Hawaii and the Galápagos, the Izu Islands are located near the mainland and have thus been frequently colonized by various species by overseas dispersal from the mainland or from adjacent islands. This make them interesting for the studies of ecological and evolutionary processes.[5]
Campanula (Bellflower) colonized the entire archipelago in a single event. Similarly, the Euhadra snails, endemic to Japan, populated the islands in a single event and all individuals on inhabited islands possess an identical haplotype. The Apodemus mice, on the other hand, colonized the islands from the mainland in two independent events.[5]
See also
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Izu-no-Shichi-Tō. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Izu Islands. |
References
- After Dutch explorer Maarten Gerritsz Vries, the first European to describe them in 1643. See "Izu Shotō" in Louis Frédéric, Japan Encyclopedia (Belknap, 2002), p. 412.
- Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Izu Shotō," Japan Encyclopedia, p. 412.
- Gotoh, H.; Maeno, Y.; Takezawa, T.; Murata, T.; Takahashi, N. (2010). "Infrastructure maintenance and disaster prevention measures on isolated Islands: the case of the Izu Islands near tokyo". In Favro, S.; Brebbia, C. A. (eds.). Island Sustainability. WIT transactions on ecology and the environment (Vol. 130). WIT Press. ISBN 978-1-84564-434-5.
- Volcanoes of the Izu, Volcano and Mariana Islands
- Kuriyama, Takeo; Brandley, Matthew C.; Katayama, Akira; Mori, Akira; Honda, Masanao; Hasegawa, Masami (2011). "A time-calibrated phylogenetic approach to assessing the phylogeography, colonization history and phenotypic evolution of snakes in the Japanese Izu Islands" (PDF). J. Biogeogr. 38: 259–271. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2010.02403.x.
- Teikoku's Complete Atlas of Japan, Teikoku-Shoin Co., Ltd. Tokyo 1990, ISBN 4-8071-0004-1
