Ghost-faced bat
The ghost-faced bat (Mormoops megalophylla) is a bat in the genus Mormoops. It occurs in Belize, Colombia, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Peru, Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela, and Texas in the United States.[1] Mormoops megalophylla is one of only two extant species within its genus, the other being the much smaller Mormoops blainvillii. These mammals are nocturnal and hunt using echolocation.
| Ghost-faced bat | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Mormoopidae |
| Genus: | Mormoops |
| Species: | M. megalophylla |
| Binomial name | |
| Mormoops megalophylla (Peters, 1864) | |
 | |
It gets its name from the unusual appearance of its face, which is due to the flaps of skin that hang from it, its poorly developed nose,[2] and "large, round ears that join across their forehead".[3]
Description
The ghost-faced bat is of medium size with a reddish-brown to dark-brown appearance. The reddish color becomes more prominent as the pelage ages. This particular bat undergoes molting, usually between June and September. On the dorsal side, molting starts on the shoulders and spreads over the back, whereas on the ventral side molting usually begins under the wings, on the neck and chin and then spreads down across the abdomen.[2]
The faces of these bats have a 'smashed-in' appearance. This odd appearance is the result of four combining factors; they do not have well-developed noses,[2] their foreheads rise abruptly from their noses,[3] their faces are composed of very thick dermis and muscle fibers, and they have large, round ears that seem to join across the forehead.
These bats maintain an unusually high body temperature, usually a few degrees higher than the ambient temperature. As a result, they are sensitive to temperatures under 10 °C and can only survive in these colder temperatures for a few hours before they succumb to hypothermia.
Biogeography
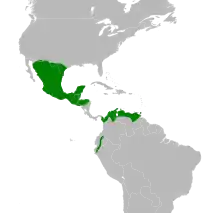
Ghost-faced bats are found in humid, arid, and semi-arid regions. They seem to prefer regions below 3000 m elevation. In the United States they have been found in southern Texas and Arizona. They have also been found in Mexico and through eastern Honduras and El Salvador. They appear to be absent in the countries of Nicaragua, Costa Rica, or Panama. Records of these bats then resume along the Caribbean coast of South America in countries such as Colombia, Venezuela, and Trinidad and Tobago. There are also records of them along the Pacific coasts in Colombia, Ecuador, and northern Peru.[2]
The earliest record of these bats is from the late Pleistocene era, when the bats appeared to have had a much broader geographical spread than they do today, with fossils found as far north as Florida. Fossils have also been found in many of the Caribbean islands such as Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, Bahamas, Trinidad and Tobago, and Aruba.
Ecology
Ghost-faced bats prefer warm climates. They tend to roost in large colonies but not in tight clusters, being very particular in that they roost about 15 cm apart from one another. When they leave their roosting spot (usually a cave, mine shaft, or tunnel) at night they fly in dense, fast-moving groups until they get to their feeding grounds where they disperse. These bats seem to prefer large-bodied moths as their main source of food. They are often found feeding over standing water. Because these bats tend to roost in larger colonies they are susceptible to parasites and rabies which have been known to wipe out entire colonies.[3]
Diet and feeding
The ghost-faced bat survives on a diet of small insects. They use echolocation to identify their food at night and are able to catch insects in the darkness with little or no additional light.
Reproduction and development
Very little is known about their reproduction and development. These bats only seem to carry one embryo at a time and are thought to give birth in the spring between March and June. Lactating females have also been observed between June and August.[2] Because pregnant females are so sensitive to changes in temperature, they appear to roost deeper in the caves than the rest of the colony. By roosting here these females and their young are in an area where ventilation is minimized and there is high heat retention.
References
- Davalos, L.; Molinari, J.; Mantilla-Meluk, H.; Medina, C.; Pineda, J.; Rodriguez, B. (2019). "Mormoops megalophylla". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T13878A22086060. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T13878A22086060.en.
- Rezsutek, Michael; Cameron, Guy N. (1993). "Mormoops megalophylla" (PDF). Mammalian Species. American Society of Mammalogists. 448 (448): 1–5. doi:10.2307/3504289. JSTOR 3504289.
- Steinway, M. (2000). "Mormoops megalophylla". Animal Diversity Web.
