Flomoxef
It has been classified as second-generation[1] and fourth-generation.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
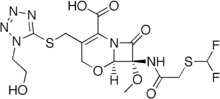
| Formula | C15H18F2N6O7S2 |
| Molar mass | 496.46 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 82.5 to 87.5 °C (180.5 to 189.5 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Flomoxef is an oxacephem antibiotic.
It was patented in 1982 and approved for medical use in 1988.[3]
References
- Masuda Z, Kurosaki Y, Ishino K, Yamauchi K, Sano S (April 2008). "Pharmacokinetic analysis of flomoxef in children undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass and modified ultrafiltration". Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 56 (4): 163–9. doi:10.1007/s11748-007-0208-5. PMID 18401677. S2CID 23845740.
- Ito M, Ishigami T (1991). "The meaning of the development of flomoxef and clinical experience in Japan". Infection. 19 Suppl 5: S253–7. doi:10.1007/bf01645536. PMID 1783441. S2CID 25339977.
- Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 496. ISBN 9783527607495.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.