Complement component 5
Complement component 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C5 gene.[5]
Complement component 5 is involved in the complement system. It is cleaved into C5a and C5b:
- C5a plays an important role in chemotaxis.[6]
- C5b forms the first part of the complement membrane attack complex.
Deficiency is thought to cause Leiner's disease.
Function
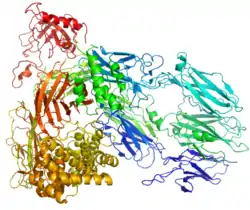
Complement component 5 is the fifth component of complement, which plays an important role in inflammatory and cell killing processes. This protein is composed of alpha and beta polypeptide chains that are linked by a disulfide bridge. An activation peptide, C5a, which is an anaphylatoxin that possesses potent spasmogenic and chemotactic activity, is derived from the alpha polypeptide via cleavage with a C5-convertase. The C5b macromolecular cleavage product can form a complex with the C6 complement component, and this complex is the basis for formation of the membrane attack complex, which includes additional complement components.[5]
Clinical significance
Mutations in this gene cause complement component 5 deficiency, a disease where patients show a propensity for severe recurrent infections. Defects in this gene have also been linked to a susceptibility to liver fibrosis and to rheumatoid arthritis.[5]
Therapeutic applications
The drug eculizumab (trade name Soliris) prevents cleavage of C5 into C5a and C5b.[7]
Complement system pathway

References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000106804 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026874 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "C5 complement C5 (Homo sapiens (human)) Gene ID: 727,". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. 29 November 2020. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- Immunology at MCG 1/phagocyt
- Dubois E, Cohen A (2009). "Eculizumab". Br J Clin Pharmacol. 68 (3): 318–319. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03491.x. PMC 2766470. PMID 19740388.
Further reading
- Tack BF, Morris SC, Prahl JW (1979). "Fifth component of human complement: purification from plasma and polypeptide chain structure". Biochemistry. 18 (8): 1490–7. doi:10.1021/bi00575a016. PMID 106884.
- Fernandez HN, Hugli TE (1978). "Primary structural analysis of the polypeptide portion of human C5a anaphylatoxin. Polypeptide sequence determination and assignment of the oligosaccharide attachment site in C5a". J. Biol. Chem. 253 (19): 6955–64. PMID 690134.
- DiScipio RG (1992). "Formation and structure of the C5b-7 complex of the lytic pathway of complement". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (24): 17087–94. PMID 1387399.
- Haviland DL, Haviland JC, Fleischer DT, et al. (1991). "Complete cDNA sequence of human complement pro-C5. Evidence of truncated transcripts derived from a single copy gene". J. Immunol. 146 (1): 362–8. PMID 1984448.
- Bohnsack JF, Mollison KW, Buko AM, et al. (1991). "Group B streptococci inactivate complement component C5a by enzymic cleavage at the C-terminus". Biochem. J. 273 (Pt 3): 635–40. doi:10.1042/bj2730635. PMC 1149811. PMID 1996961.
- Lundwall AB, Wetsel RA, Kristensen T, et al. (1985). "Isolation and sequence analysis of a cDNA clone encoding the fifth complement component". J. Biol. Chem. 260 (4): 2108–12. PMID 2579066.
- Zuiderweg ER, Fesik SW (1989). "Heteronuclear three-dimensional NMR spectroscopy of the inflammatory protein C5a". Biochemistry. 28 (6): 2387–91. doi:10.1021/bi00432a008. PMID 2730871.
- Zuiderweg ER, Nettesheim DG, Mollison KW, Carter GW (1989). "Tertiary structure of human complement component C5a in solution from nuclear magnetic resonance data". Biochemistry. 28 (1): 172–85. doi:10.1021/bi00427a025. PMID 2784981.
- Haefliger JA, Tschopp J, Vial N, Jenne DE (1989). "Complete primary structure and functional characterization of the sixth component of the human complement system. Identification of the C5b-binding domain in complement C6". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (30): 18041–51. PMID 2808363.
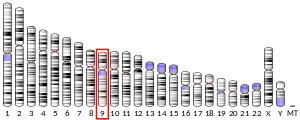
- Wetsel RA, Lemons RS, Le Beau MM, et al. (1988). "Molecular analysis of human complement component C5: localization of the structural gene to chromosome 9". Biochemistry. 27 (5): 1474–82. doi:10.1021/bi00405a012. PMID 3365401.
- Zuiderweg ER, Mollison KW, Henkin J, Carter GW (1988). "Sequence-specific assignments in the 1H NMR spectrum of the human inflammatory protein C5a". Biochemistry. 27 (10): 3568–80. doi:10.1021/bi00410a007. PMID 3408713.
- Stewart JL, Kolb WP, Sodetz JM (1987). "Evidence that C5b recognizes and mediates C8 incorporation into the cytolytic complex of complement". J. Immunol. 139 (6): 1960–4. PMID 3624872.
- Buhl AM, Osawa S, Johnson GL (1995). "Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation requires two signal inputs from the human anaphylatoxin C5a receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (34): 19828–32. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.34.19828. PMID 7649993.
- Babkina IN, Seregin SV, Daniliuk NK, et al. (1995). "[Chemico-enzymatic synthesis, cloning and expression of a gene for an analog of human anaphylatoxin C5a]". Bioorg. Khim. 21 (5): 359–64. PMID 7661861.
- Wang X, Fleischer DT, Whitehead WT, et al. (1995). "Inherited human complement C5 deficiency. Nonsense mutations in exons 1 (Gln1 to Stop) and 36 (Arg1458 to Stop) and compound heterozygosity in three African-American families". J. Immunol. 154 (10): 5464–71. PMID 7730648.
- Oppermann M, Götze O (1995). "Plasma clearance of the human C5a anaphylatoxin by binding to leucocyte C5a receptors". Immunology. 82 (4): 516–21. PMC 1414921. PMID 7835913.
- Süsal C, Kirschfink M, Kröpelin M, et al. (1994). "Complement activation by recombinant HIV-1 glycoprotein gp120". J. Immunol. 152 (12): 6028–34. PMID 7911492.
- Arribas J, Arizti P, Castaño JG (1994). "Antibodies against the C2 COOH-terminal region discriminate the active and latent forms of the multicatalytic proteinase complex". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (17): 12858–64. PMID 8175701.
- Süsal C, Kirschfink M, Kröpelin M, et al. (1996). "Identification of complement activation sites in human immunodeficiency virus type-1 glycoprotein gp120". Blood. 87 (6): 2329–36. doi:10.1182/blood.V87.6.2329.bloodjournal8762329. PMID 8630395.
- Ames RS, Li Y, Sarau HM, et al. (1996). "Molecular cloning and characterization of the human anaphylatoxin C3a receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (34): 20231–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.34.20231. PMID 8702752.
- Fredslund F, Laursen NS, Roversi P, et al. (2008). "Structure of and influence of a tick complement inhibitor on human complement component 5". Nat Immunol. 9 (7): 753–60. doi:10.1038/ni.1625. PMID 18536718. S2CID 205361576.
External links
- Complement+5 at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.