Bata language
Bata (Gbwata) is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Nigeria in Adamawa State in the Numan, Song, Fufore and Mubi LGAs, and in Cameroon in North Province along the border with Nigeria. Dialects are Demsa, Garoua, Jirai, Kobotachi, Malabu, Ndeewe, Ribaw, Wadi, and Zumu (Jimo).[2] It is often considered the same language as Bacama.
| Bata | |
|---|---|
| Gbwata | |
| Native to | Nigeria, Cameroon |
| Region | Adamawa State, North Province |
Native speakers | (150,000 cited 1992)[2] |
Afro-Asiatic
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | bta – inclusive codeIndividual code: kso – Kofa (not a distinct language)[3] |
| Glottolog | bata1314 |
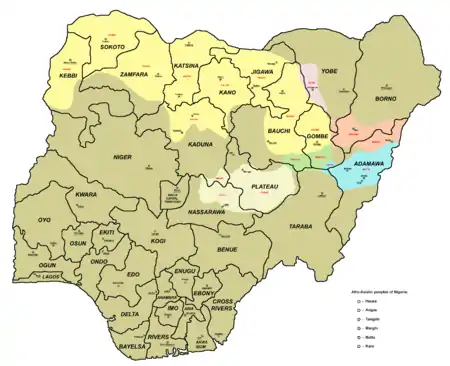 Ethnic territories of the Bata-speaking people (Batta) in Nigeria, in blue | |
Blench (2019) lists Bwatye (endonym: Ɓwaare; exonym: Bachama) as a closely related language variety. They are located in Adamawa State (Numan and Guyuk LGAs) and Kaduna State (northeast of Kaduna town).[4] It is also called Kwā ɓwàryē.[5]
Notes
- Hammarström (2015) Ethnologue 16/17/18th editions: a comprehensive review: online appendices
- Bata at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Kofa (not a distinct language)[1] at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) - Hammarström (2015) Ethnologue 16/17/18th editions: a comprehensive review: online appendices
- Blench, Roger (2019). An Atlas of Nigerian Languages (4th ed.). Cambridge: Kay Williamson Educational Foundation.
- Bata materials from Raymond Boyd
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.