1999 Asturian regional election
The 1999 Asturian regional election was held on Sunday, 13 June 1999, to elect the 5th General Junta of the Principality of Asturias. All 45 seats in the General Junta were up for election. The election was held simultaneously with regional elections in twelve other autonomous communities and local elections all throughout Spain, as well as the 1999 European Parliament election.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 45 seats in the General Junta of the Principality of Asturias 23 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Registered | 979,618 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 623,242 (63.6%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
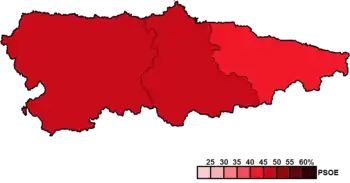 Constituency results map for the General Junta of the Principality of Asturias | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
An internal People's Party (PP) crisis starting in 1997 between the regional PP leadership and President Sergio Marqués resulted in a party split, with Marqués' government breaking away from the PP in 1998, maintaining the support of only 5 of the 21 PP deputies for the remainder of the legislature.
As a result of the ensuing political crisis, the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) of Vicente Álvarez Areces went on to win an absolute majority of seats, at the cost of the greatly weakened PP. United Left (IU) also suffered from the party crisis at the national level and lost half of its support, while Sergio Marqués' party, the Asturian Renewal Union (URAS), entered parliament with 3 seats.
Overview
Electoral system
The General Junta of the Principality of Asturias was the devolved, unicameral legislature of the autonomous community of Asturias, having legislative power in regional matters as defined by the Spanish Constitution and the Asturian Statute of Autonomy, as well as the ability to vote confidence in or withdraw it from a President of the Principality.[1] Voting for the General Junta was on the basis of universal suffrage, which comprised all nationals over eighteen, registered in Asturias and in full enjoyment of their political rights.
The 45 members of the General Junta of the Principality of Asturias were elected using the D'Hondt method and a closed list proportional representation, with a threshold of 3 percent of valid votes—which included blank ballots—being applied in each constituency. Parties not reaching the threshold were not taken into consideration for seat distribution. Additionally, the use of the D'Hondt method might result in an effective threshold over three percent, depending on the district magnitude.[2] Seats were allocated to constituencies, which were established by law as follows:
- Central District (comprising the municipalities of Aller, Avilés, Bimenes, Carreño, Caso, Castrillón, Corvera de Asturias, Gijón, Gozón, Illas, Las Regueras, Langreo, Laviana, Lena, Llanera, Mieres, Morcín, Noreña, Oviedo, Proaza, Quirós, Ribera de Arriba, Riosa, San Martín del Rey Aurelio, Santo Adriano, Sariego, Siero, Sobrescobio and Soto del Barco).
- Eastern District (comprising the municipalities of Amieva, Cabrales, Cabranes, Cangas de Onís, Caravia, Colunga, Llanes, Nava, Onís, Parres, Peñamellera Alta, Peñamellera Baja, Piloña, Ponga, Ribadedeva, Ribadesella and Villaviciosa).
- Western District (comprising the municipalities of Allande, Belmonte de Miranda, Boal, Candamo, Cangas del Narcea, Castropol, Coaña, Cudillero, Degaña, El Franco, Grado, Grandas de Salime, Ibias, Illano, Muros de Nalón, Navia, Pesoz, Pravia, Salas, San Martín de Oscos, Santa Eulalia de Oscos, San Tirso de Abres, Somiedo, Tapia de Casariego, Taramundi, Teverga, Tineo, Valdés, Vegadeo, Villanueva de Oscos, Villayón and Yernes y Tameza).
Each constituency was entitled to an initial minimum of two seats, with the remaining 39 allocated among the constituencies in proportion to their populations.[3]
The electoral law provided that parties, federations, coalitions and groupings of electors were allowed to present lists of candidates. However, groupings of electors were required to secure the signature of at least 1 percent of the electors registered in the constituency for which they sought election. Electors were barred from signing for more than one list of candidates. Concurrently, parties and federations intending to enter in coalition to take part jointly at an election were required to inform the relevant Electoral Commission within ten days of the election being called.[3][4][5]
Election date
The term of the General Junta of the Principality of Asturias expired four years after the date of its previous election. Elections to the General Junta were fixed for the fourth Sunday of May every four years. Legal amendments introduced in 1998 allowed for these to be held together with European Parliament elections, provided that they were scheduled for within a four month-timespan. The previous election was held on 28 May 1995, setting the election date for the General Junta concurrently with a European Parliament election on Sunday, 13 June 1999.[1][3][4][5]
After legal amendments earlier in 1999, the President of the Principality was granted the prerogative to dissolve the General Junta and call a snap election, provided that no motion of no confidence was in process, no nationwide election was due and some time requirements were met: namely, that dissolution did not occur either during the first legislative session or within the legislature's last year ahead of its scheduled expiry, nor before one year had elapsed since a previous dissolution under this procedure. In the event of an investiture process failing to elect a regional President within a two-month period from the first ballot, the General Junta was to be automatically dissolved and a fresh election called. Any snap election held as a result of these circumstances would not alter the period to the next ordinary election, with elected deputies merely serving out what remained of their four-year terms.[1]
Opinion polls
The table below lists voting intention estimates in reverse chronological order, showing the most recent first and using the dates when the survey fieldwork was done, as opposed to the date of publication. Where the fieldwork dates are unknown, the date of publication is given instead. The highest percentage figure in each polling survey is displayed with its background shaded in the leading party's colour. If a tie ensues, this is applied to the figures with the highest percentages. The "Lead" column on the right shows the percentage-point difference between the parties with the highest percentages in a given poll. When available, seat projections are also displayed below the voting estimates in a smaller font. 23 seats were required for an absolute majority in the General Junta of the Principality of Asturias.
| Polling firm/Commissioner | Fieldwork date | Sample size | Turnout | PAS | Lead | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999 regional election | 13 Jun 1999 | N/A | 63.6 | 32.3 15 |
46.0 24 |
9.0 3 |
2.6 0 |
7.1 3 |
13.7 |
| Eco Consulting/ABC[p 1] | 24 May–2 Jun 1999 | ? | ? | 38.1 18/19 |
34.6 19/20 |
14.4 5/6 |
4.8 1 |
4.6 1 |
3.5 |
| Demoscopia/El País[p 2] | 26 May–1 Jun 1999 | ? | 67 | 36.0 17 |
41.3 21 |
12.3 4 |
3.7 2 |
4.0 1 |
5.3 |
| Sigma Dos/El Mundo[p 3][p 4] | 19–26 May 1999 | 600 | ? | 39.6 19/20 |
41.2 20/22 |
8.4 3 |
2.7 0/1 |
3.6 1 |
1.6 |
| CIS[p 5][p 6][p 7] | 3–23 May 1999 | 1,057 | 67.6 | 31.9 15/16 |
39.3 19/20 |
13.6 5 |
4.6 1/2 |
8.4 3/4 |
7.4 |
| La Voz de Asturias[p 8] | 16 May 1999 | ? | ? | ? 17/19 |
? 17/19 |
? 6/7 |
? 1/2 |
? 1 |
Tie |
| El Comercio[p 9] | 19 Jul 1998 | ? | ? | 31.5 14 |
40.1 23 |
– | – | ? 2 |
8.6 |
| 1996 general election | 3 Mar 1996 | N/A | 75.9 | 41.0 | 39.9 | 15.5 | 1.7 | – | 1.1 |
| 1995 regional election | 28 May 1995 | N/A | 69.1 | 42.0 21 |
33.8 17 |
16.4 6 |
3.2 1 |
– | 8.2 |
Results
Overall
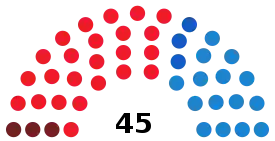 | ||||||
| Parties and coalitions | Popular vote | Seats | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | ±pp | Total | +/− | ||
| Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) | 284,972 | 46.00 | +12.17 | 24 | +7 | |
| People's Party (PP) | 200,164 | 32.31 | –9.69 | 15 | –6 | |
| United Left of Asturias (IU) | 55,747 | 9.00 | –7.42 | 3 | –3 | |
| Asturian Renewal Union (URAS) | 44,261 | 7.14 | New | 3 | +3 | |
| Asturianist Party (PAS) | 15,998 | 2.58 | –0.61 | 0 | –1 | |
| The Greens of Asturias (LV) | 3,343 | 0.54 | –0.15 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Andecha Astur (AA) | 2,206 | 0.36 | +0.06 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Asturian Left Bloc (BIA)1 | 1,366 | 0.22 | +0.05 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Centrist Union–Democratic and Social Centre (UC–CDS) | 737 | 0.12 | –1.66 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Asturian Council (Conceyu) | 496 | 0.08 | –0.05 | 0 | ±0 | |
| The Phalanx (FE) | 453 | 0.07 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Humanist Party (PH) | 23 | 0.00 | New | 0 | ±0 | |
| Blank ballots | 9,720 | 1.57 | +0.39 | |||
| Total | 619,486 | 45 | ±0 | |||
| Valid votes | 619,486 | 99.40 | –0.01 | |||
| Invalid votes | 3,756 | 0.60 | +0.01 | |||
| Votes cast / turnout | 623,242 | 63.62 | –5.43 | |||
| Abstentions | 356,376 | 36.38 | +5.43 | |||
| Registered voters | 979,618 | |||||
| Sources[6][7][8][9] | ||||||
Aftermath
| Investiture | |||
| Ballot → | 22 July 1999 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Required majority → | 23 out of 45 | ||
|
24 / 45 |
||
20 / 45 | |||
Absentees
|
1 / 45 | ||
| Sources[9] | |||
References
- Opinion poll sources
- "El tránsfuga Marqués abre el camino al PSOE". ABC (in Spanish). 7 June 1999.
- "El PSOE cobra la factura que los votantes pasan al PP". El País (in Spanish). 7 June 1999.
- "Asturias: El PSOE aprovecha la crisis". El Mundo (in Spanish). 29 May 1999.
- "ELECCIONES 13-J /BALANCE DE LAS ENCUESTAS". El Mundo (in Spanish). 6 June 1999.
- "Preelectoral elecciones autonómicas y municipales, 1999. Principado de Asturias (Estudio nº 2327. Mayo 1999)". CIS (in Spanish). 4 June 1999.
- "Estudio CIS nº 2327. Ficha técnica" (PDF). CIS (in Spanish). 4 June 1999.
- "Bono e Ibarra repiten y el PSOE recuperará Asturias". La Vanguardia (in Spanish). 5 June 1999.
- "Una encuesta atribuye un único escaño a Marqués en Asturias". ABC (in Spanish). 17 May 1999.
- "La sangría de votos del PP favorece a los socialistas". El País (in Spanish). 20 July 1998.
- Other
- "Statute of Autonomy for Asturias of 1981". Organic Law No. 7 of 30 December 1981. Official State Gazette (in Spanish). Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- Gallagher, Michael (30 July 2012). "Effective threshold in electoral systems". Trinity College, Dublin. Archived from the original on 30 July 2017. Retrieved 22 July 2017.
- "General Junta of the Principality of Asturias Elections System Law of 1986". Law No. 14 of 26 December 1986. Official Gazette of the Principality of Asturias (in Spanish). Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- "General Electoral System Organic Law of 1985". Organic Law No. 5 of 19 June 1985. Official State Gazette (in Spanish). Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- "Representation of the people Institutional Act". www.juntaelectoralcentral.es. Central Electoral Commission. Retrieved 16 June 2017.
- "General Junta of the Principality of Asturias election results, 13 June 1999" (PDF). www.juntaelectoralcentral.es (in Spanish). Electoral Commission of Asturias. 18 November 1999. Retrieved 8 December 2019.
- "Electoral Results. General Junta of the Principality of Asturias. 5th Legislature (1999–2003)". www.jgpa.es (in Spanish). General Junta of the Principality of Asturias. Retrieved 29 November 2019.
- "Electoral Results. 1999". www.sadei.es (in Spanish). SADEI. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
- "Elecciones a la Junta General (1983 - 2019)". Historia Electoral.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 27 September 2017.
.jpg.webp)
_(bis).jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
