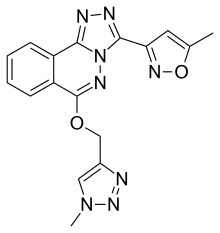
α5IA
α5IA (LS-193,268) is a nootropic drug invented in 2004 by a team working for Merck, Sharp and Dohme, which acts as a subtype-selective inverse agonist at the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAA receptor. It binds to the α1, α2, α3 and α5 subtypes.[1][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LS-193,268 |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H14N8O2 |
| Molar mass | 362.353 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Sternfeld F, Carling RW, Jelley RA, Ladduwahetty T, Merchant KJ, Moore KW, et al. (April 2004). "Selective, orally active gamma-aminobutyric acidA alpha5 receptor inverse agonists as cognition enhancers". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 47 (9): 2176–9. doi:10.1021/jm031076j. PMID 15084116.
- Street LJ, Sternfeld F, Jelley RA, Reeve AJ, Carling RW, Moore KW, et al. (July 2004). "Synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-heterocyclyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-(7,10-ethano)-1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-a]phthalazines and analogues as subtype-selective inverse agonists for the GABA(A)alpha5 benzodiazepine binding site". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 47 (14): 3642–57. doi:10.1021/jm0407613. PMID 15214791.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.