Wide-gamut RGB color space
The wide-gamut RGB color space (or Adobe Wide Gamut RGB) is an RGB color space developed by Adobe Systems, that offers a large gamut by using pure spectral primary colors.[1] It is able to store a wider range of color values than sRGB or Adobe RGB color spaces. As a comparison, the wide-gamut RGB color space encompasses 77.6% of the visible colors specified by the CIELAB color space, while the standard Adobe RGB color space covers just 52.1%[2] and sRGB covers only 35.9%.[3]
When working in color spaces with such a large gamut, it is recommended to work in 16-bit per channel color depth to avoid posterization effects. This will occur more frequently in 8-bit per channel modes as the gradient steps are much larger.[4]
As with sRGB, the color component values in wide-gamut RGB are not proportional to the luminances. Similar to Adobe RGB, a gamma of 2.2 is assumed, without the linear segment near zero that is present in sRGB. The precise gamma value is 563/256, or 2.19921875.
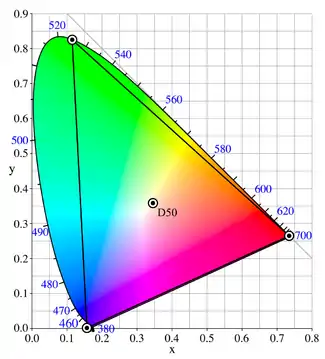
The white point corresponds to D50. The chromaticities of the primary colors and the white point are as follows:
| Color | CIE x | CIE y | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red | 0.7347 | 0.2653 | 700 nm |
| Green | 0.1152 | 0.8264 | 525 nm |
| Blue | 0.1566 | 0.0177 | 450 nm |
| White point | 0.3457 | 0.3585 |
References
- Pascale, Danny. "A Review of RGB Color Spaces ...from xyY to R'G'B'" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-02-12.
- Adobe RGB color space
- Rec. 709
- Rodney, Andrew. "The role of working spaces in Adobe applications" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-02-12.