Verreaux's eagle
Verreaux's eagle (Aquila verreauxii) is a large, mostly African, bird of prey. It is also called the black eagle, especially in Southern Africa, leading to potential confusion with the Indian black eagle (Ictinaetus malayensis), which lives far to the east in Asia.[2] Verreaux's eagle lives in hilly and mountainous regions of southern and eastern Africa (extending marginally into Chad), and very locally in West Africa, the Arabian Peninsula and the southern Middle East. It is one of the most specialized species of accipitrid in the world, with its distribution and life history revolving around its favorite prey species, the rock hyraxes. When hyrax populations decline, the species have been shown to survive with mixed success on other prey, such as small antelopes, gamebirds, hares, monkeys and other assorted vertebrates. Despite a high degree of specialization, Verreaux's eagle has, from a conservation standpoint, been faring relatively well in historic times. One population of this species, in the Matobo Hills of Zimbabwe, is arguably the best studied eagle population in the world, having been subject to continuous detailed study since the late 1950s.[2][3] Like all eagles, this species belongs to the taxonomic order Accipitriformes (formerly included in Falconiformes) and the family Accipitridae, which may be referred to colloquially as accipitrids or raptors.
| Verreaux's eagle | |
|---|---|
%252C_Aquila_verreauxii%252C_at_Walter_Sisulu_National_Botanical_Garden%252C_Gauteng%252C_South_Africa_(28825027073).jpg.webp) | |
| At the Walter Sisulu National Botanical Garden in Roodepoort, South Africa | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Accipitriformes |
| Family: | Accipitridae |
| Genus: | Aquila |
| Species: | A. verreauxii |
| Binomial name | |
| Aquila verreauxii Lesson, 1830 | |
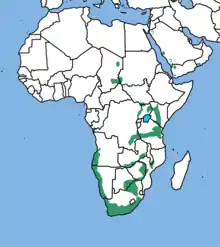 | |
| Range of Verreaux's eagle in green | |
Taxonomy

This species was first described by René Primevère Lesson in his 1830 publication, Centurie zoologique, ou choix d'animaux rares, nouveaux ou imparfaitement connus, as Aquila Verreauxii.[5] The species’ name commemorates the French naturalist Jules Verreaux, who visited southern Africa in the early 19th century and collected the type specimen for the French Academy of Sciences.[6][7]
Verreaux's eagle is part of a broad group of raptors called "booted eagles" which are defined by the feature that all included species have feathering over their tarsus, whereas most other accipitrids have bare legs. Included in this group are all species described as "hawk eagles" including the genera Spizaetus and Nisaetus, as well as assorted monotypical genera such as Oroaetus, Lophaetus, Stephanoaetus, Polemaetus, Lophotriorchis and Ictinaetus. The genus Aquila is distributed across every continent but for South America and Antarctica. Up to 20 species have been classified in the genus but the taxonomic placement of some of the traditionally included species has recently been questioned. Traditionally, the Aquila eagles have been grouped superficially as largish, mainly brownish or dark-colored booted eagles that vary little in transition from their juvenile to their adult plumages.
Genetic research has recently shown the Verreaux's eagle is included in a clade with its nearest relatives, the sister species Bonelli's eagle (A. fasciatus) and African hawk-eagle (A. spilogaster), as well as the more distant sister species pair, the wedge-tailed eagle (A. audax) and Gurney's eagle (A. gurneyi).[8] Closely related to this clade are the golden eagle and Cassin's hawk-eagle.[8] Some of the relationships within this group have long been suspected based on morphological similarities among the large-bodied species.[9] The identification of the smaller, much paler-bellied A. fasciatus and A. spilogaster as members of the clade was a surprise, given that they were previously included in the genus Hieraaetus.[3][10][11] Cassin's hawk-eagle has been assigned to both the Hieraaetus group and the Spizaetus/Nisaetus "hawk-eagle" group but is now known based on this genetic data to also nest within Aquila.[8]
Other largish Aquila species, the eastern imperial eagle (A. heliaca), the Spanish imperial eagle (A. adaberti), the tawny eagle (A. rapax) and the steppe eagles (A. nipalensis), are now thought to be separate, close-knit clade, which attained some characteristics similar to those of the prior clade via convergent evolution.[10][11] Genetically, the "spotted eagles" (C. pomarina, C. hasata & C. clanga), have been discovered to be more closely related to the long-crested eagle (Lophaetus occipitalis) and the black eagle,[10][12] and have been transferred to the genus Clanga.[8] The genus Hieraaetus, traditionally including the booted eagle (H. pennatus), little eagle (H. morphnoides) and Ayres's hawk-eagle (H. ayresii), consists of much smaller species, that are in fact the smallest birds called eagles outside of the unrelated Spilornis serpent-eagle genus. This genus has recently been eliminated by many authorities and is now occasionally also included in Aquila, although not all ornithological unions have followed this suit in this re-classification.[3][11][13] The small-bodied Wahlberg's eagle (H. wahlbergi) has been traditionally considered an Aquila species due to its lack of change from juvenile to adult plumage and brownish color but it is actually genetically aligned to the Hieraaetus lineage.[10][14]
Description


Verreaux's eagle is a very large eagle. It measures 75 to 96 cm (30 to 38 in) long from the bill to the tip of the tail, making it the sixth longest eagle in the world.[15] Males can weigh 3 to 4.2 kg (6.6 to 9.3 lb) and the larger females weigh 3.1 to 7 kg (6.8 to 15.4 lb). The average weight is approximately 4.19 kg (9.2 lb), based on the weights of 21 eagles of both sexes. Other reported mean body mass measurements of Verreaux's eagles were lower however, with seven unsexed birds averaging 3.32 kg (7.3 lb), while four unsexed eagles in an additional study averaged 3.72 kg (8.2 lb). In another group of weighed eagles, four females were found to average 4.6 kg (10 lb), which is more than a kilogram more than the average male, It is the seventh or eighth heaviest living eagle in the world. In average mass and overall weight range, if not linear measurements, the Verreaux's is very similar in size to its occasional competitor, the martial eagle, which is regularly titled the largest of the African eagles. It also rivals the martial and golden eagles as the largest extant member of the "booted eagle" clan.[15][16][17][18][19][20] It has a wingspan of 1.81 to 2.3 m (5 ft 11 in to 7 ft 7 in).[15][21] The wing chord of the male is 56.5 to 59.5 cm (22.2 to 23.4 in) and that of the female is 59 to 64 cm (23 to 25 in). Among other standard measurements in the Verreaux's eagles, both sexes measure 27.2 to 36 cm (10.7 to 14.2 in) in tail length and 9.5 to 11 cm (3.7 to 4.3 in) in tarsus length.[9][15] Other than the female's slight size advantage, adult males and females are physically indistinguishable from each other.[15] Adult Verreaux's eagles are mostly jet-black in color.[9] The yellow coloration of the cere (the bill is gun-metal grey), eye-ring and “eye-brows”, all stand out in contrast to the black plumage.[15] Even more prominent on flying birds when seen from above is the white on the back, rump and upper-tail coverts and part of the scapulars, which forms a V-shaped patch, although this feature is partially obscured in perched birds.[9] Adults also have conspicuous white windows on the wing quills at the carpal joint (at the base of the primaries) when seen flying both from above and below.[9][15] The bill is stout, the head is prominent on the relatively long neck and the legs are fully feathered.[15]

Juvenile and immature plumages differ markedly from the plumage of adults. They are overall a dark brown color.[22] Immatures have a strongly contrasting golden crown and a rufous or ginger nape and mantle. They have small white streaks on the forehead and black on their cheeks. The throat is dark streaked, the lower throat is pale brown and the upper-chest is brown.[15] The rest of the underside is brown but for a blackish-blotched rufous to cream-colored abdomen and lightly marked creamy thighs and legs. The feathers of the upper-tail and upper-wing coverts are brown with white streaks in young birds, while the other tail and wing quills are nearly black. The wing quills when seen from below in flight show considerable whitish mottling, with more extensive white than is typically seen in adult plumages. The immature has a dark brown iris and yellowish feet.[9] Black feathers increase from 2 to 5 years of age amongst a scattering of brown-tipped feathers, though the contrasting creamy trousers are maintained through the 3rd year. By the 4th year, they look dark grey-brown with a buff-patch on the nape and mottling of retained brownish feathers. At the end of the subadult phase at around 5 years of age, the plumage is practically indistinguishable from the adult.[23] Full adult plumage is probably attained in 5 to 6 years.[24]
The Verreaux's eagle is essentially unmistakable, especially in adulthood. No other black-colored raptor in its range approaches this species’ large size, nor possesses its distinctive patterns of white.[15] The golden eagle is of similar size or marginally larger size and the two species are the heaviest living Aquila species and measure only marginally less than the slightly lighter-weight Australasian wedge-tailed eagle in total wing and bill-to-tail length.[3] While the juvenile Verreaux's eagle is quite different from the adult's, its plumage is no less distinctive. No other accipitrid shares the mottled brownish body, blackish wings with large white patches or contrasting whitish, rufous and golden color around the head and neck. The flight profile of Verreaux's eagle is also distinctive: it is the only Aquila species other than the golden eagle to soar in a pronounced dihedral, with the wings held slightly above the back and primaries upturned at the tip to make a V shape. In the Bale Mountains of Ethiopia and possibly in some parts of the Arabian Peninsula and the southwestern edge of the Middle East, the ranges of the golden and Verreaux's eagles overlap, but the golden is a mostly brown bird and shares none of the Verreaux's black plumage. The immature golden eagle has white patches on its underwing as do Verreaux's, but they are less extensive than those of the latter species. The wing shape also differs from the golden's, as the Verreaux's eagle has very broad outer secondaries and a relatively narrow pinch at the base of the primaries, whereas the tapering of a golden eagle's wing is more gradual. The Verreaux's eagle wings have variously been described as paddle, spoon or leaf shaped.[9][15] Imperial eagles too have white markings on their wing coverts, but are different in flight profile (flatter winged) and overall coloration (dark brown).[15]

Voice

This species is largely silent, though is arguably a stronger vocalist than its close cousin, the golden eagle.[15] Chicking and chirruping sounds like that of a young turkey or francolin, pyuck, have been heard in various contexts, such as pairs being reunited. More striking sounds are loud, ringing whaeee-whaeee, heeeee-oh or keeooo-keeooo calls used as contact calls or during intruder chases. Various screams, barks, yelps and mews have been heard to be issued at potential mammalian predators.[9][15] The young emits feeble chirps at first, later more likely to cluck like the adults.[9]
Habitat and distribution

Verreaux's eagle has specific habitat requirements and is rare outside of its particular habitat type. It lives in kopjes, which are dry, rocky environments in anything from rocky hills to high mountains amongst cliffs, gorges and inselbergs often surrounded by savanna, thornbush and sub-desert.[15] It is often found in dry areas with less than 60 cm (24 in) of average annual rainfall.
It is highest ranging in elevation in Ethiopia and East Africa, where found up to 4,000 m (13,000 ft) above sea level.[9] Verreaux's eagle is found from the Marra Mountains[25] of Sudan southward through that country[26] to 16°N in Eritrea,[27] along the northern mountains of Somalia,[28] in much of Ethiopia (mostly the central, mountainous spine),[29] possibly some mountains in northeastern Uganda,[30] Kenya, easternmost Democratic Republic of the Congo and possibly Tanzania.[15]
Southeastern Africa is the heart of the Verreaux's eagle range: they are found in most mountain ranges in Malawi but for the Nyika Plateau, the Mafinga Hills and the Lulwe Hills,[31] in Zambia (especially the escarpments bordering Lake Kariba to the gorges below Victoria Falls), in Zimbabwe (especially east of the central plateau),[32]Mozambique, Swaziland,[33] Lesotho and down into South Africa, where they largely inhabit the Karoo, along the cliffs of the Great Escarpment, the Cape Fold Mountains and Cape Peninsula.[34][35][36] A somewhat more sparse distribution is known in Botswana, western Namibia and southwestern Angola (in the Serra da Chela).[37][38] Elsewhere in Africa, the Verreaux's eagle may be found but tends to be rare and only spottily seen, such as in eastern Mali, northeastern Chad,[39] the Aïr Mountains of Niger[40] and southwestern Cameroon (where known only as a vagrant).[41] In 1968, only a single record of Verreaux's eagle (from Jordan) was known from outside of Africa, but now it is known to be a rare breeder in the Middle East: from a handful of immature records and territorial adult behavior, breeding has been inferred in Lebanon,[42][43] Israel,[44] Oman,[45] Saudi Arabia[46] and Yemen.[47][48]
Dietary ecology

Two species comprise considerably more than half of (often more than 90% of) the Verreaux's eagle's diet: the Cape hyrax (Procavia capensis) and the yellow-spotted rock hyrax (Heterohyrax brucei). Few other accipitrids are as singularly specialized to hunt a single prey family as Verreaux's eagles, perhaps excluding the snail kite (Rostrhamus sociabilis) and the slender-billed kite (Helicolestes hamatus) with their specialization on Pomacea snails. Not even accipitrids named after their staple food are known to be as specialized, i.e. the bat hawk (Macheiramphus alcinus), palm-nut vulture (Gypohierax angolensis), lizard buzzard (Kaupifalco monogrammicus) and perhaps the rufous crab hawk (Buteogallus aequinoctialis). Certainly, the Verreaux's eagle has the most conservative diet of Aquila species, though the diet is more diverse in South Africa than in Zimbabwe.[49]
In the Matobo Hills of Zimbabwe, the two hyraxes comprised 1,448 out of 1,550 eagle prey items recorded at eyries just after the breeding season from 1995 to 2003.[50] In the same area, from 1957 to 1990, 98.1% of the diet was made up of rock hyrax.[2] In a sample size of 224 from 102 nests in Serengeti National Park in Tanzania, 99.1% of the remains were of hyrax.[51] Elsewhere in Tanzania, the diet is more mixed, with 53.7% of the remains from 24 nests made up of hyrax.[52] In a nest in South Africa, 89.1% of the remains from a sampling of 55 were of hyrax.[53] No detailed statistics are known but the hyrax are likely to the main prey in every population and have been mentioned to dominate the diet in Mozambique,[54] Malawi[31] and Botswana[55] Around 400 hyrax may be taken through the year by a pair with young.[15] The entire distribution of the species neatly corresponds with that of the two species of rock hyrax.[9] To date, there are no known instances of Verreaux's eagle hunting the two species of tree hyraxes.[49]
In the first 10 years of constant observation of the population from the Matobo Hills, only two kills were witnessed. However, enough hunting behavior has been ultimately observed to give a good idea how a Verreaux's eagle obtains its prey.[23] This species most often forages in low-level quartering flight, with the rock hyraxes chiefly caught after a rapid, somewhat twisting dive in the few seconds after the eagle surprises the hyrax. Like the golden eagle, Verreaux's eagle uses natural contours of the ground in rocky and mountainous habitats to increase the element of surprise, as hyraxes (appropriately considering their diverse range of predators) tend to be highly wary.[15][49] Verreaux's eagle have been known to hunt from a perch, though rarely.[9][56] Hunting hyrax cooperatively has been recorded, with one eagle of a pair flying past and distracting the prey while the other strikes from behind. Verreaux's eagle may knock hyraxes off cliffs and take arboreal prey from treetops, but it usually kills on the ground.[15] The daily estimate food requirements of this species are around 350 g (12 oz), nearly a third more than that of a golden eagle despite the latter's marginally heavier body weight.[23] Rock hyraxes are often difficult to observe for humans, other than a glimpse, but a Verreaux's eagle can fly out and then return to the nest with a kill in the matter of a few minutes.[23]
Of the two species regularly taken, the yellow-spotted rock hyrax can weigh from 1 to 3.63 kg (2.2 to 8.0 lb) with an average of 2.4 kg (5.3 lb), although specimens from Zimbabwe are noticeably heavier and larger than specimens from Serengeti National Park. Cape hyrax, weighing from 1.8 to 5.5 kg (4.0 to 12.1 lb) with average of around 3.14 kg (6.9 lb), can be even larger than the Verreaux's eagles themselves, so can be more difficult to kill. Yellow-spotted rock hyraxes are more often taken in the Matobo Hills, perhaps because of their smaller size or its more diurnal habits. Adult rock hyraxes are disproportionately selected, perhaps due to being out in the open more regularly. In Cape hyraxes, 1- to 2-year-old males are particularly vulnerable, since they are forced to disperse at sexual maturity. Juvenile hyraxes constituted from 11–33% of prey remains in the Western Cape while 18% of hyraxes killed were juveniles in Matobo Hills. Because of their greater weight, Cape hyraxes are frequently either consumed at the kill site (putting the eagle at risk of losing prey to competing predators or to attack by large mammalian carnivores) or are decapitated and brought to the nest or perch. Fewer skulls or jaws of Cape hyraxes than of yellow-spotted rock hyraxes have been found at nest sites.[57][58] However, the Cape hyrax has a wider distribution than the yellow-spotted and the Verreaux's eagle may hunt the Cape hyrax almost exclusively outside of the long band of eastern Africa where the smaller species is distributed.[49] In comparison to the golden eagle, Verreaux's eagle has a foot pad that about 20% wider, which may be an adaptation to taking the bulky and broad-backed rock hyrax.[59] The foot of the Verreaux's eagle is reportedly larger than a human hand.[60] In South Africa, where the Cape hyrax is the main prey species, the estimated mean size of prey taken to the nest is around 2.6 kg (5.7 lb), perhaps twice as heavy as prey taken by some nesting golden eagles.[59] However, the mean size of prey taken by Verreaux's eagle in the Matobo Hills, with more yellow-spotted rock hyrax, was around 1.82 kg (4.0 lb), around the same estimated weight as prey taken by golden eagles in Europe and smaller than the average estimated mass of prey taken to golden eagle nests in regions like Scotland or Mongolia.[3][61]
Other prey
.jpg.webp)
Verreaux's eagle are capable of taking diverse prey, but this is infrequent in areas with healthy rock hyrax populations. Cases where more diverse food is brought to the nest are usually either considered to be areas where rock hyrax populations have declined or areas where eagles occupy home ranges which included non-rocky habitat such as savanna, which are described by Valerie Gargett as “poor food areas” due to their lack of hyrax.[2][62] In such areas, about 80% of prey is mammalian.[9] Verreaux's eagles that are less specialized have diets and hunting capacities that are similar to those of the golden eagle, although the latter species often subsists on hares, rabbits, ground squirrels or grouse for about half or two-thirds of its diet, a portion still comprised by rock hyrax in the Verreaux's.[2][3] One study accumulated records of Verreaux's eagle preying on at least 100 prey species.[63] Other prey types recorded have included small (mainly juvenile) antelopes, hares, rabbits, meerkats (Suricata suricatta), other mongooses, monkeys, squirrels, cane rats, bushbabies and lambs (Ovis aries) and kids (Capra aegagrus hircus). Francolin (Francolinus ssp.) and guineafowl (Numina ssp.) as well as waterfowl, herons, egrets, bustards, pigeons, crows (Corvus ssp.), doves, chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) and a great sparrowhawk (Accipiter melanoleucus) have been among the recorded avian prey.[15][64] Avian prey ranging in size from 102.6 g (3.62 oz) alpine swift (Tachymarptis melba) to 7.26 kg (16.0 lb) adult male Denham's bustards (Neotis denhami).[16][65][66] In Tanzania, out of a sample size of 41 from 26 nests, 53.7% of remains were of hyraxes, 29.3% of francolins, guineafowl and chickens, 12.2% of antelopes, 2.4% of hares and rabbits and 2.4% of mongoose.[52] Tortoises made up 145 of 5748 from 73 sites (2.5%) in South Africa. Rarely, snakes and lizards may also be taken and even termites have been eaten by this species.[15][23]
In South Africa, the commonest foods were (in descending order of preference): Cape hyrax, Smith's red rock hare (Pronolagus rupertris), meerkat, mountain reedbuck (Redunca fulvorufula), goats and sheep, scrub hare (Lepus saxatilis), Cape francolin (Francolinus capensis), helmeted guineafowl (Numida meleagris), yellow mongoose (Cynictis penicillata) and Angulate tortoise (Chersina angulata).[15] In “poor food areas” of the Matobo Hills, three nests included 53.6% hyrax, 10.7% cane-rats, 7.1% monkeys, 7.1% mongoose and 3.6% antelope.[2] From 1997 to 2005 in the same area, non-hyrax prey (each representing less than 10 out of 1550 prey items at nests) included white-tailed mongoose (Ichneumia albicauda), steenbok (Raphicerus campestris), domestic goat, vervet monkey (Chlorocebus pygerythrus), Jameson's red rock hare (Pronolagus randensis), helmeted guineafowl, Swainson's francolin (Pternistis swainsonii), Natal francolin (Pternistis natalensis), southern red-billed hornbill (Tockus rufirostris), rock pigeon (Columba livia), white-necked raven (Corvus albicollis), leopard tortoise (Stigmochelys pardalis) and giant plated lizard (Gerrhosaurus validus).[50] In the Walter Sisulu National Botanical Garden of South Africa, the primary prey found around nests after a perceptible hyrax decline has become helmeted guineafowl and francolins, followed by cane rats, rabbits and dikdiks (Rhynchotragus ssp.).[62] Young baboons may also be hunted, even the large-bodied chacma baboons (Papio ursinus) which have issued a predator alarm call in response to the presence of Verreaux's eagles.[67] Carrion either fairly frequent or none at all.[2][56] A study of the taking of domestic lambs in the Karoo found only two cases of lambs being eaten by Verreaux's eagle and these were already dead when carried off. This contrasts with the golden eagle, which in some areas may eat many dead lambs and occasionally hunt lives ones.[3][68] Although any prey weighing over 4.5 kg (9.9 lb) is rarely taken, some ungulates hunted by Verreaux's eagles can be considerably larger.[15] Klipspringer (Oreotragus oreotragus) brought to the nest have weighed up to an estimated 12 kg (26 lb).[59] A Verreaux's eagle was observed to hunt and kill a mountain reedbuck lamb estimated to weigh 15 kg (33 lb).[69] The smallest known mammalian prey was a 97.6 g (3.44 oz) Cape gerbil (Gerbilliscus afra).[65][70]
Interspecies competition
.jpg.webp)
Although it is the most specialized predator of rock hyrax in the world, it does not have monopoly on this prey. Many wild predators are also attracted to rock hyraxes, which thus puts them in potential competition with the Verreaux's eagles. Amongst the other very large eagles which are widely found in sub-Saharan Africa, both the crowned eagle and the martial eagle may also locally favor rock hyraxes in their diets. However, these species have highly different habitat preferences and hunting techniques. The crowned eagle, a forest-dwelling species, is primarily a perch-hunter and can spend hours watching for prey activity from a prominent tree perch. The martial eagle is a dweller mainly of lightly wooded savanna and often hunts on the wing. soaring high and watching for prey activity with its superb vision, quite unlike the contour-hunting technique used by Verreaux's eagles. While the habitats of crowned and Verreaux's eagle keep them segregated enough to likely eliminate competition, confrontations between Verreaux's and martial eagles have been recorded. Although somewhat larger and more powerful, the martial eagle is relatively less nimble in the air and there is a case where a martial eagle was robbed of rock hyrax prey by a Verreaux's eagle.[15][23] Another case of kleptoparasitism by a Verreaux's eagle involved one stealing some carrion from a lammergeier (Gypaetus barbatus).[15] Verreaux's eagles occasionally prey on other large raptors including vultures, including white-headed vulture (Trigonoceps occipitalis), white-backed vulture (Gyps africanus) and Cape vulture (Gyps coprotheres), though the earlier cases probably refer to nestling or juvenile predation and the latter to nest defense on the part of the eagles.[49][63][71] An apparent predation attempt on a full grown juvenile Rüppell's griffon (Gyps rueppellii) was abortive.[72] A unique opportunity to study Verreaux's eagle living with its closest extant cousin, the golden eagle, has been afforded in the Bale Mountains of Ethiopia. The two species, with similar habitat preferences, were observed to defend their territories from one another exclusively, with many cases of goldens chasing Verreaux's eagles out of their respective territories in flight and only one of Verreaux's chasing the goldens. However, since the golden eagles prefer hares and Verreaux prefers rock hyraxes, they actually seem to have no deleterious effect on each other's breeding activities.[73] African hawk-eagles (Aquila spilogaster) may also take a few hyraxes, but are likely to avoid direct conflicts with their much larger cousins, so will tawny eagles (Aquila rapax).[23] Other predators of rock hyrax may include felids like African wildcats (Felis silvestris lybica), servals (Leptailurus serval), caracals (Caracal caracal) and leopards (Panthera pardus) as well as jackals (Canis ssp.), African rock pythons (Python sebae) and owls (mainly the large Verreaux's eagle-owl (Bubo lacteus) or possibly the Cape eagle-owl (B. capensis)). Neonate rock hyraxes may fall prey to mongooses and venomous snakes like Egyptian cobras (Naja haje) and puff adders (Bitis arietans).[74][75] Due to the formidable range of competitors it pays for Verreaux's eagle to be cautious from the moment it bears down on its prey. Cases where pirating has been attempted has involved diverse carnivores like caracals and jackals. In at least one case, a Verreaux's eagle was observed to be displaced off a rodent-kill (likely a cane-rat) by an Ethiopian wolf (Canis simensis).[76] As is often the case with reintroduced eagles (i.e. seen even in the huge harpy eagle (Harpia harpyja)), reintroduced Verreaux's eagle may lose their fear of other predators to their own detriment and one such bird fell victim to a caracal.[77] Cases where Verreaux's eagles have swooped at leopards are not likely competitive but are more likely to try to displace the cat from their territory, and such attacks have occasionally had fatal results for the birds.[9][78] This species is not normally aggressive to humans but may swoop uncomfortably close when the nest is being investigated.[9]
Behavior
Territoriality and movements
A rough estimated average of home range size in Verreaux's eagle is 10.9 km2 (4.2 sq mi).[23] Density of breeding pairs varies from 1 pair per 10.3 km2 (4.0 sq mi) in the Matobo Hills, Zimbabwe, 1 pair per 24 km2 (9.3 sq mi) in the Karoo, 1 pair per 25 km2 (9.7 sq mi) in East Africa, 1 pair per 28 km2 (11 sq mi) in the Bale Mountains of Ethiopia to a known maximum spacing of 1 pair per 35 to 65 km2 (14 to 25 sq mi) in the Magaliesberg and Drakensberg ranges.[2][49][79][80][81] The Matobo Hills reportedly has one of the greatest breeding densities known of any large eagle and territories are extremely stable through seasons and years. Such stable distributions are expected of long-lived raptors living in the tropics with a relatively stable food supply outside the seasonal variation of temperate zones.[82] While Matobo Hill home ranges ranged from 6 to 14 km2 (2.3 to 5.4 sq mi), most were observed to include about the same amount of kopje habitat (up to 5 km2 (1.9 sq mi)).[2] Populations fluctuate surprisingly little despite four-fold changes between peaks and troughs in hyrax numbers.[83] At troughs, eagles may temporarily disappear or switch to alternate prey. This is only especially marked in drought periods and on average occurs once every 20 years.[84] Some authors consider the Verreaux's eagle to be a partial migrant,[85] others describe it as sedentary.[86] This is more a matter of terminology than unclear behaviour, since this species is well known to behave like almost all raptors that breed in Sub-Saharan Africa. That is the young wander relatively widely once dispersed from their parent's territory but the adults generally remain sedentary on their home range for the remainder of their lives.[2]
Verreaux's eagle displays may potentially occur almost throughout the year. Frequently displays are in response to the presence of another soaring pair or after repelling a single intruder from the territory. They will also display if anxious about the nest when humans or other large mammals approach too closely.[23] The male's display often consists of him first flying up in an undulating flight with wings readily held spread or closed. Then, once at a great height, he plunges down as far as 305 m (1,001 ft) at a time, then quickly rises back up, sometimes swinging to and fro like the arms of a pendulum, at other times diving and rising along a straight line. These evolutions may be embellished with somersaults and sideways rolls at the peak before the descent.[9][23] Some displays involve pairs of eagles. A pair frequently circles or makes figures of eight over their territory. One bird may roll over and present claws in flight or the male may fly behind female with exaggeratedly upcurved wings.[15] It is now the prevalent thought that most displays in Aquila eagles are territorial, as they often occur along the boundary of a given home range rather than near the nest.[3] Displays with talon-grappling and tumbling are often aerial fights between territorial birds and occasionally the eagles may clasp and whirl downwards (one such fight reportedly resulting in the birds plunging into the sea).[9][15]
Breeding

In Zimbabwe, 60 pairs may nest in 620 km2 (240 sq mi), equivalent to 1 pair per 10.3 km2 (4.0 sq mi), but this is exceptional. In East Africa, one pair nests each 25 km2 (9.7 sq mi) and in South Africa sometimes as little as 1 pair per 10.2 to 15 km2 (3.9 to 5.8 sq mi), but nearer 60 km2 (23 sq mi) being more typical.[15] Verreaux's eagle may build from 1 to 3 nests, sometimes none over the course of a year. In the Matobo Hills, the average number of nests built per pair is 1.4.[23] Eagles nesting in the Karoo have much larger territories, though are subject to persecution and habitat change, more so than many other populations.[23] In the Matobos, the species is near the breeding population capacity level with almost unlimited nests that are rather unevenly distributed among available jumbles of rocky kopjes. In Kenya, nests are more scattered and Verreaux's eagle sometimes do not breed even where the habitat seems appropriate and there are good numbers of rock hyrax.[9] By virtue of location on a narrow ledge, nests tend to be much broader than deep and a relatively small for the size of the eagle.[9] The flattish nests, made out of green branches and lined with green leaves, are up to 1.8 m (71 in) across and 2 m (6.6 ft) deep. Though a nest depth of around 0.6 m (2.0 ft) is typical, one old nest was 4.1 m (13 ft) deep.[9][15] Typically nests are on cliffs, often in an overhung crevice or in a small cave, sometimes on an open ledge. The nest site is generally marked by a 'whitewash' which is formed by the birds' droppings.[87] Verreaux's is the most cliff dependent of all eagle species, in the late 1970s only 3 known nests were in trees.[23] Very rarely, they may nest in trees, such as Euphorbia or Acacia, often those growing out of a cliff crevice.[15] A handful of nests in South Africa have even been on electric pylons.[88] A new nest takes up to four months to construct, with some repair being typical upon each use. Both sexes participate in the nest construction, though the female usually takes the lead.[9] It may take several hundred feet of rope for a human to reach the nest.[9] Predation of young in the nest is either suspected or anecdotely reported as having been committed by African rock pythons, baboons and caracals. However, predation is believed to be normally quite rare, due to the combination of factors such as the inaccessibility of most nests by foot (thus cutting off all but the most nimble mammalian carnivores) and the bold defenses of the parent eagles.[2] Verreaux's eagle have reportedly dropped sticks on potential nest predators. This has been considered a form of tool-use, which is generally unknown in other raptorial birds and has been mostly reported in corvids and herons.[89]
Egg laying may occur from November to August in Sudan and Arabia, October to May in Ethiopia and Somalia, year around in East Africa (with a peak of June to December) and anywhere from April to November in Africa from Zambia southwards.[15] In an unusual behaviour for eagles, the males may bring food to females before egg laying and, more typically, males bring almost all food during the incubation stage.[2] Two eggs are generally laid, though a range of one to three is known. The eggs are rather elongated ovals and being chalky white sometimes with a bluish tinge or a few reddish-brown marking, measuring from 71 to 83.4 mm (2.80 to 3.28 in) in length and 56–62 mm (2.2–2.4 in) in width, with an average of 76.9 mm × 58.6 mm (3.03 in × 2.31 in).[9] The eggs are laid at three-day intervals starting in the middle of the day. Both sexes incubate, but the female takes the major share and tends to sit all night over them. Sometimes, the male may sit for 40-50% of the day with more shifts for him towards the end of incubation. These are close-sitters, which are not easily disturbed off the nest.[9] Incubation is 43 to 47 days. Hatching happens at about to 2–3 days apart, with about 24 hours from the first chipping of the egg's surface to complete hatching. One egg is sometimes infertile and the second egg tends to be about 10% smaller.[9] The Verreaux's eagle is considered an “obligate cainist”, that is the older sibling normally kills the younger one (in more than 90% of observed nests), by either starvation or direct attack. Aggression may continue for up to 70 days after hatching.[2][90] At one time no cases of two young successfully reaching the fledging stage were known, however a couple of cases of two healthy fledglings from a nest have been recorded.[9] Siblicide is regularly observed in raptorial birds, including unrelated families like owls and skuas and is common, even typical, in Aquila eagles. The behaviour is most commonly explained as a kind of insurance policy, with the second nestling existing both to act as a backup if the first egg or nestling perishes and to mitigate the stressful workload demanded of the parent raptors in feeding, brooding and defending the young.[90] The odds of survival for the second fledging are better in the golden eagle and other temperate-breeding Aquila eagles, possibly due to a shorter nesting stage in these species.[90] In roughly 20% of golden eagle nests and in some cases, such as prey-rich areas of North America, about half of the nests will successfully produce two fledglings.[3] In the Verreaux's eagle, no food is given to the hatchling in the first 36 hours, thereafter they are regularly fed.[2] Early in the fledging stage, the young is brooded up to 90% of the time. After 20 days, parents spend up to 20% of time with their eaglet around the nest, not brooding in daylight after 21 days. Feathers appear through the down at about 34 days, by 60 days feathers cover the down.[9] In Equatorial Africa, the eaglet fledges from the nest at 95–99 days, though sometimes as little as 90 days further south. In the golden eagle, the fledging stage is roughly 35 days shorter.[23] The young Verreaux's eagle takes its first flight and then returns to the nest for the first fortnight.[9] In the early fledging period, the male brings more food, later it is largely the female. At some point during the post-fledging stage, she ceases to roost with the young one and sits with the male at some distance, a behaviour that seems to vary from nest to nest in timing. After 45–50 days, food is caught by the parents but is likely eaten by themselves and not brought to the young. After leaving the nest, family parties may be together for up to 6 months. The eaglet grows stronger after the first month and accompanies the parents on hunting forays away from the nest. It often breeds every year, occasionally only on every other year.[9]
Population and status
.jpg.webp)
Verreaux's eagles’ nests are estimated to have a 40–50% success rate per year.[9] Success of nesting is significantly higher when hyrax are common: 0.56 young per year dropped to 0.28 young per year. In fact, in poor food areas no breeding attempt commonly occurred (66% did not attempt to breed) whereas 24% did not attempt to breed in better food areas. Frequency of breeding attempts is lower in wetter years. Near 90% attempted nesting in years with 300 mm (12 in) of rainfall whereas 45% attempted during years with roughly 1,000 mm (39 in) rainfall.[84] In the Matobo Hills, persistent intrusion by an unmated adult into a pair's nesting territory seemed to have an adverse effect on nesting success.[91]
The estimated average lifespan is 16 years.[9] Verreaux's eagle has a total population estimated very roughly to be somewhere in the tens of thousands in total. In northeastern South Africa, the local breeding population is estimated to include 240 pairs, while the western Cape region of the country may hold possibly more than 2,000 pairs.[34][81] Verreaux's eagle lives in kopje habitat, which is generally non-vulnerable to human destruction, unlike, say, the savanna inhabited by martial eagles or the forests inhabited by crowned eagles.[15] Unlike the other two big African eagles, they do not often partake of much carrion, so are at little risk of poisoning from carcass left out to control jackals.[15] Nonetheless, some people shoot at or otherwise persecute them when given the opportunity due to the largely mistaken belief that they are a threat to small livestock.[68]
Perhaps the greatest concern for the species is when rock hyraxes are locally hunted by humans for food and skins, leading to likely declines and requiring the eagles to either switch to other prey or have their nesting attempts fail. In Walter Sisulu National Botanical Garden in South Africa, despite an appreciable decline in rock hyrax populations, breeding data revealed few changes in the incubation period, nestling period and post-fledging dispersal period in two known pairs of the eagles.[62] At this same site, despite it being one of the most popular nature areas in metropolitan Johannesburg, high levels of human activity have had no apparent adverse effect on the eagles’ breeding behaviour (by contrast, when exposed to similar levels of disturbance, golden eagles have been shown to temporarily abandon their nests).[3][92] However, in South Africa, the overall number of pairs declined from 78 in 1980 (25 in reserves) to 27 in 1988 (with 19 in preserves).[15] In the Sisulu Botanical Garden, artificial feeding has been contemplated to maintain a breeding pair in the face of continuing declines of available wild prey.[92]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aquila verreauxii. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Aquila verreauxii. |
- BirdLife International (2016). "Aquila verreauxii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22696067A95221980. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22696067A95221980.en. Retrieved 23 December 2019.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Gargett, Valerie (1990). The Black Eagle: A Study. South Africa: Acorn Books and Russel Friedman Books. pp. 19, 30–31. ISBN 0-620-11915-2.
- Watson, Jeff (2010). The Golden Eagle. A&C Black. ISBN 978-1-4081-1420-9.
- Lesson, R. P. (1830). Centurie zoologique, ou, Choix d'animaux rares, nouveaux ou imparfaitement connus par R.P. Lesson. Chez F.G. Levrault, Paris. pp. 104–106.
- Kemp, A. C. (1994) IN del Hoyo, Elliott & Sargatal. eds. (1994). Handbook of the Birds of the World, vol. 2. ISBN 84-87334-15-6
- Gargett, p. 30.
- Mearns, Barbara; & Mearns, Richard. (1988). Biographies for Birdwatchers. The lives of those commemorated in Western Palaearctic bird names. Academic Press: London. ISBN 0-12-487422-3
- Lerner, H.; Christidis, L.; Gamauf, A.; Griffiths, C.; Haring, E.; Huddleston, C.J.; Kabra, S.; Kocum, A.; Krosby, M.; Kvaløy, K.; Mindell, D.; Rasmussen, P.; Røv, N.; Wadleigh, R.; Wink, M.; Gjershaug, J.O. (2017). "Phylogeny and new taxonomy of the Booted Eagles (Accipitriformes: Aquilinae)". Zootaxa. 4216 (4): 301–320. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4216.4.1.
- Eagles, Hawks and Falcons of the World by Leslie Brown & Dean Amadon. The Wellfleet Press (1986), ISBN 978-1555214722.
- Helbig, A.J., Kocum, A., Seibold, I. & Braun, M.J. "A multi-gene phylogeny of aquiline eagles (Aves: Accipitriformes) reveals extensive paraphyly at the genus level" (PDF). Elseveir. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 13, 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2013.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Lerner, H.R. & Mindell, D.P. "Phylogeny of eagles, Old World vultures, and other Accipitridae based on nuclear and mitochondrial DNA" (PDF). Elseveir. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- "Lophaetus pomarinus". The Peregrine Fund. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- "Aquila morphnoides". The Peregrine Fund. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- "Aquila wahlbergi". The Peregrine Fund. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- Raptors of the World by Ferguson-Lees, Christie, Franklin, Mead & Burton. Houghton Mifflin (2001), ISBN 0-618-12762-3.
- CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses, 2nd Edition by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (2008), ISBN 978-1-4200-6444-5.
- Brown, L. H., Gargett, V., & Steyn, P. (1977). Breeding success in some African eagles related to theories about sibling aggression and its effects. Ostrich, 48(3-4), 65-71.
- Mendelsohn, J. M., Kemp, A. C., Biggs, H. C., Biggs, R., & Brown, C. J. (1989). Wing areas, wing loadings and wing spans of 66 species of African raptors. Ostrich, 60(1), 35-42.
- Biggs, H.C., Kemp, A.C., Mendelsohn, H.P. & Mendelsohn, J.M. (1979). Weights of South African Raptors and Owls. Durban Museum Novitates, 12: 73-81.
- Brough, T. (1983). Average weights of birds. Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, Agricultural Science Service, Aviation Bird Unit, Worplesdon Laboratory.
- "Introduction". Black Eagle Project. Retrieved 2016-08-19.
- "Home- Wonderboom Urban Verreaux's Eagle". Wonderbloom Urban Verreaux's Eagle Monitoring Project 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- Brown, L. 1976. Eagles of the World. David and Charles, ISBN 0360003184.
- "Aquila verreauxii". The Peregrine Fund. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- W.W. Bowen, 1926. Catalogue of Sudan Birds. Khartoum, Sudan Government Museum of Natural History.
- Nikolaus, G. 1987. Distribution atlas of Sudan's birds with notes on habitat and status. Zoologisches Forschungsinstitut und Museum Alexander Koenig (Bonn) ISBN 3925382259.
- Smith, K. D. (1957). An annotated check list of the birds of Eritrea. Ibis, 99(2), 307-337.
- Birds of Somalia by John Miskell and John Ash (1998, Hardcover). John Ash. ISBN 1-873403-58-5.
- Ash, J. & Atkins, J. (2009) Birds of Ethiopia and Eritrea. Published by Christopher Helm, London.
- The Bird Atlas of Uganda: NHBS - Margaret Carswell, Derek Pomeroy and Jake Reynolds, British Ornithologists' Club, 2005.
- Dowsett-Lemaire, F. & Dowsett, R.J. The Birds of Malawi: An Atlas and Handbook. 2006, Tauraco Press and Aves, Liège, Belgium. 556 pages
- Irwin, M. P. S. 1981. The birds of Zimbabwe. Quest Publishing, Salisbury, Zimbabwe.
- Monadjem, A., and M. W. Rasmussen. 2008. Nest distribution and conservation status of eagles, selected hawks and owls in Swaziland. Gabar 18:1-22
- Tarboton, W.R. & Allan, D.G. 1984. The Status and conservation of Birds of Prey in the Transvaal. Pretoria: Transvaal Museum Monograph, No. 3.
- Jenkins, A.R., and A.J. van Zyl. 2005. Conservation status and community structure of cliff-nesting raptors and ravens on the Cape Peninsula, South Africa. Ostrich 76:175-184.
- Hockey, P.A.R.; Dean, W.R.J.; Ryan, P.G., eds. (2003). "Verreaux's Eagle. Black Eagle, Aquila verreauxii". Roberts – Birds of Southern Africa, VIIth Ed. Cape Town: The John Voelcker Bird Book Fund. pp. 531–532. ISBN 0620340517.
- Oatley, T.B., Oschadleus, H.D., Navarro, R.A. and Underhill, L.G. 1998. Review of ring recoveries of birds of prey in southern Africa: 1948-1998. Johannesburg: Endangered Wildlife Trust.
- Pinto, A. A. 1983. Ornithologia de Angola. Instituto de Investigacao Cientifica Tropical, Lisbon.
- Borrow N. & Demey R. 2001. Birds of western Africa. Christopher Helm, London.
- Newby, J., Grettenberger, J.& Watkins, J.(1987). The birds of the northern Aïr, Niger. Malimbus 9(1).
- Steinheimer, F. D., and S. Sammler. 2007. First record of Verreaux's Eagle Aquila verreauxii in Cameroon. Bulletin of the British Ornithologists' Club 127:167-168.
- Ramadan-Jaradi, G., T. Bara, and M. Ramadan-Jaradi. 2008. Revised checklist of the birds of Lebanon 1999-2007. Sandgrouse 30:22-69.
- Ramadan-Jaradi, G., S. P. Waterbury, and M. Ramadan-Jaradi. 2005. Ornithological observations from Lebanon during 2003-4. Sandgrouse 27:69-73.
- Shirihai, H. (1996) The Birds of Israel. Academic Press, London.
- Eriksen, H and Eriksen, J Birdlife in Oman. Al Roya Publishing, Muscat, Oman 1999.
- Jennings, M. C.; al Salama, M. I.; Felemban, H. M. 1988. Report on an ornithological survey of the Asir National Park, Saudi Arabia: 29 June to 18 July 1987. National Commission for Wildlife Conservation and Development, Riyadh.
- Porter, R.F., Christensen, S. and Schiermacker-Hansen, P. 1996. Poyser, London, UK
- Meinertzhagen 1954, Birds of Arabia. Edinburgh: Oliver & Boyd.
- Steyn, P. 1982. Birds of Prey of Southern Africa. David Philip, Cape Town.
- Chiweshe, N. 2007. Black Eagles and hyraxes -- the two flagship species in the conservation of wildlife in the Matobo Hills, Zimbabwe. Ostrich 78:381-386.
- Hoeck, H.N. 1982. Population dynamics, dispersal and genetic isolation in two species of Hyrax (Heterohyrax brucei and Procavia johnstoni) on habitat islands in the Serengeti. Zeitschrift fur Tierpsychologie, 59: 177-210.
- Rowe, E.G. 1947. The breeding biology of Aquila verreauxi, Lesson. Ibis, 89: 387-410; 576-606.
- Jenkins, A. 1984. Hunting behaviour and success of in a pair of Black Eagles. Ostrich, 55: 102-103.
- Parker, V. (2005). The atlas of the birds of central Mozambique. Endangered Wildlife Trust and the Avian Demography Unit.
- Penry, H. 1994. Bird Atlas of Botswana: NHBS, University of Natal Press- 319 pages.
- Maclean; 1993; p. 113
- Barry, R. E. and L. M. Barry. 1996. Species composition and age structure of remains of hyraxes (Hyracoidea: Procaviidae) at nests of black eagles. Journal of Mammalogy 77:702–707.
- Barry, R., & Mundy, P. 1998. Population dynamics of two species of hyraxes in the Matobo National Park, Zimbabwe. African Journal of Ecology, 36(3), 221-233.
- Munir Virani. "The Verreaux's Eagle- An Interview with Dr Rob Davies". African Raptors. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- Parry-Jones, J. 1997. Eagles & Birds of Prey: Eyewitness Books. Dorling Kindersley Limited, New York City. ISBN 978-0-7894-6618-1.
- Ellis, D.H., Tsengeg, P., Whitlock, P. & Ellis, M.H. 2000. Predators as prey at a Golden Eagle Aquila chrysaetos eyrie in Mongolia. Ibis, 142: 139 – 141.
- Kruger, T. L. (2010). Long term prospects for the persistence of breeding Verreaux's Eagles (Aquila verreauxii) at the Walter Sisulu National Botanical Garden, Johannesburg (Doctoral dissertation).
- Thompson, L. J., Clemence, L., Clemence, B., & Goosen, D. (2018). Nestling White-backed Vulture (Gyps africanus) eaten by a Verreaux’s Eagle (Aquila verreauxii) at a nest occupied for a record 21 years. Vulture News, 74(1), 24-30.
- Mortimer, J. 2009. Verreaux's Eagle preying on Grey Heron. Gabar 20:39.
- Boshoff, A. F., Palmer, N. G., Avery, G., Davies, R. A. G., & Jarvis, M. J. F. (1991). Biogeographical and topographical variation in the prey of the black eagle in the Cape Province, South Africa. Ostrich, 62(1-2), 59-72.
- Armstrong, A., & Avery, G. (2014). Taphonomy of Verreaux's Eagle (Aquila verreauxii) prey accumulations from the Cape Floral Region, South Africa: implications for archaeological interpretations. Journal of Archaeological Science, 52, 163-183.
- Zinner, D., & Peláez, F. (1999). Verreaux's eagles (Aquila verreauxi) as potential predators of hamadryas baboons (Papio hamadryas hamadryas) in Eritrea. American journal of primatology, 47(1), 61-66.
- Davies, R.A.G. 1999. "The extent, cost and control of livestock predation by eagles with a case study on black eagles (Aquila verreauxii) in Karoo". Journal of Raptor Research, 33: 67-72.
- Henwood, R.R., and W.W. Howells. 1990. "Mountain Reedbuck lamb as Black Eagle prey". Lammergeyer 41:48.
- Skinner, J. D., & Chimimba, C. T. (2005). The mammals of the southern African sub-region. Cambridge University Press.
- Mundy, P. J., Robertson, A. S., Komen, J., and O’Connell, T. J. 1986. Attacks by Black Eagles on vultures. Raptor Research 20: 61–64
- Thomsett, S., and Aldred, J. (2015). Attempted Verreaux’s Eagle predation on Rüppell’s Vulture and breeding observations at Lake Kwenia colony, Kenya. Vulture News 68: 59–63.
- Clouet, M. 1981. L'Aigle Royal Aquila chrysaetos dans les Pyrenees Francaises. Resultats de 5 ans d'observations. L'Oiseau et R.F.O., 51: 89-100.
- Estes, R. 1991. The Behavior Guide to African Mammals. Berkeley: The University of California Press.
- Olds, N., J. Shoshani. 1982. Mammalian Species Procavia capensis. American Society of Mammalogists, 171: 1-7.
- Sillero-Zubiri, C., & Gottelli, D. (1995). Diet and feeding behavior of Ethiopian wolves (Canis simensis). Journal of Mammalogy, 531-541.
- "The Breeding Cycle". Black Eagle Project. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- Norton, P.M., and S.R. Henley. 1985. Black Eagles "attacking" leopards. Bokmakierie 37:114-115.
- Allan, D.G. 1988. Breeding success, nest spacing and territory size of Black Eagles in the Magaliesberg, South Africa. Gabar 3: 76-81.
- Clouet, M., Barrau, C. & Goar, J.-L. 2000. The diurnal Afro-alpine raptor community of the Ethiopian Bale Highlands. Ostrich 71: 380-384.
- Davies. R.A.G. 1994. Black Eagle Aquila verreauxii predation on rock hyrax Procavia capensis and other prey in the Karoo. PhD thesis, University of Pretoria.
- Newton, I. 1979. Population Ecology of Raptors. Poyser, Berkhamsted.
- Davies, R.A.G. & Ferguson, J.W.H. 2000. The influence of predation by Black Eagles Aquila verreauxii on Rock Hyrax numbers in the arid Karoo. In: Chancellor RD & Meyburg, B-U. (Eds.) Raptors at risk. WWGBP, Hancock House, UK.
- Gargett, V., Gargett, E. & Damania, D. 1995. The influence of rainfall on Black Eagle breeding over 31 years in the Matobo Hills, Zimbabwe. Ostrich 66: 114-121.
- Bildstein, K.L. 2006. (Book) Migrating raptors of the world: their ecology and conservation. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, NY.
- Hartley, R. 1998. Raptor migration and conservation in Zimbabwe. Torgos 28:135-150.
- Kemp; 2001; p.78
- Griesel, R. 2004. Verreaux's Eagle nest sites in the southern Free State. Gabar 15:20-22.
- Dick, J. A., & Fenton, M. B. (1979). Tool-using by a black eagle.
- Simmons, R. 1988. Offspring quality and the evolution of cainism. Ibis, 130: 339-357.
- Gargett, V. 1977. A 13-year population study of the Black Eagles in the Matopos, Rhodesia, 1964-1976. Ostrich, 48: 17-27.
- Simmons, R., Rodrigues, L., Woodcock, L., Steyn, P. & Jenkins, A. 2007. City Limits: Can the Verreaux's Eagle survive urbanisation? Birds and Birding, pp. 43-45.
- 'Gordon Lindsay Maclean; 1993; Robert's Birds of Southern Africa; Sixth Edition; John Voelcker Bird Book Fund, p. 112-113
- 'Alan and Meg Kemp; 2001; Birds of Prey of Africa and its Islands; SASOL, p. 78
- 'Wonderboom Urban Verreaux's Eagle Project' http://www.blackeagleswb.com
External links
- (Verreaux's eagle = ) Black eagle Aquila verreauxii - Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
