Two- and four-stroke engines
Two-and-four stroke engines are engines that combine elements from both two-stroke and four-stroke engines. They usually incorporate two pistons.
M4+2 engine
The M4+2 engine , also known as the double-piston internal combustion engine, is a new type of internal combustion engine invented by a Polish patent holder Piotr Mężyk.[1]
The M4+2 engine took its name from a combination of the two working modes of the known engines, that is from the two-stroke engine and four-stroke engine. The two-stroke combustion engine is characterized by a simple construction and system of air load change, as well as bigger index of power output. Unfortunately, its filling ratio is worse than in four-stroke engine. The ecological index of two-stroke engine is also unfavorable. The system of valves of the four-stroke engine is its disadvantage. The cylinders of both modules of double-pistons engine have been joined along one axis with common cylinder head - in the form of the ring. The pistons are moved with different speed and with appropriate stage displacement. The two crankshafts are connected with a special transmission. The four-stroke crankshaft is rotated with twice a speed of two-stroke crankshaft. The engine is named double-piston because of its construction - double pistons and crankshafts. In the M4+2, the advantages of both engines being connected are obvious; the pistons of the engine working in one combustion cylinder are set oppositely to each other, but in different modes. Although the projects of connecting two stroke modes in one cylinder were tried already a long time ago in the opposed piston engine, the combination of the two different cycles had never been tried before. It turned out that the engine is not only able to work, but that the effects are very promising. The engine has a far greater efficiency over the break-even value known to combustion engines (about 35%) and closer to the one associated with steam turbines or electric engines (about 70%).

The other advantages are:
- more efficient power production (150 horsepower from 1000 cc of volume in the basic version)
- ability to use different fuel types (natural plant oils as well as petroleum)
- much better ecological effects – a huge reduction of carbon dioxide and other gas emission
- lower fuel consumption
- prolonged stroke expansion
- possibility to change the compression parameters without having to stop the engine
- simplicity of construction[2][3]
The idea was developed at the Silesian University of Technology, Poland, under the leadership of Adam Ciesiołkiewicz.[4] It was granted a patent number 195052 by the Polish Patent Office.[5] The work with the new combustion engine has been done by IZOLING P.W. Company in cooperation with Silesian University of Technology in Gliwice. Consultations with researchers from Technical University of Kraków also were held. So far, two working engine models have been made. The preliminary model is based on two existing engines (two-stroke motorbike engine and four-stroke small machine engine). This model confirms the concept of two- and four-stroke engines connection. The second model is the functional model. The new solution of combustion engine was presented during scientific conferences (KONES '2002, Seminary of bio - fuels 2003, etc.) and in mass media (journals, newspapers, TVP, radio). The hope to build modern and universal ecological engine with good technical parameters and low fuel consumption is connected with the double-piston internal combustion engine.
The M4+2 engine working cycle
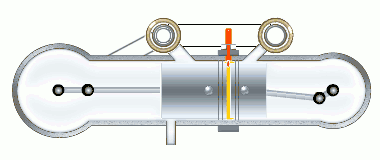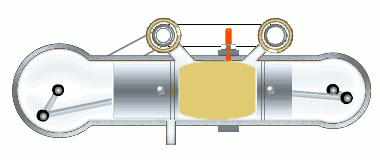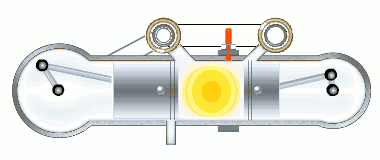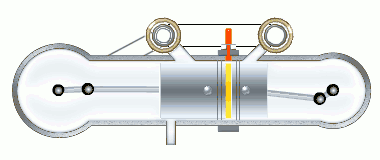
The stages of the working cycle:
- Gas exhaust
- Fresh air inlet (two stages)
- Medium compression
- Two-stage combustion
- Gas expansion
The filling process takes place at the overpressure phase, using a mechanical gas compressor and a throttle for the purpose of regulation.
The load change is assisted by a four-stroke piston, working as a dynamic boosting system and allowing the good scavenging of working space.
A possibility exists of changing the relative piston positions during the engine work, which gives the possibility of changing the compression ratio depending on the temporary level of the load. This suggests the possibility of different fuels for combustion (low-octane petrol, biofuels with high levels of vegetable components).
The working cycle is characterised by an almost constant combustion characteristic of the working space volume increasing during the expansion stage.[6][7]
The engine is characterized by:
- extended gas expansion and limited exhaust gas temperature on the outlet,
- the variability of the compression ratio and possibility of changing the compression ratio during the engine work depending on the temporary load,
- a beneficial changing of working space during the mixture compression with different crankshafts' polar location. That makes the pressure forming in cylinder possible (within reasonable limits)
- an almost constant characteristic of volume increasing during the expansion stage at different piston positions (it influences the steady power transport).
Calculations prove the new engine has more favorable parameters and work indicators:
- the increase of engine thermal efficiency (Although the mechanical efficiency is lesser than a conventional engine)
- higher total efficiency - efficiency characteristic is more favorable at medium load. It is comparable with the diesel engine efficiency so the exploitation of fuel consumption is relatively smaller
- the higher torque and the higher power output compared to the four-stroke SI engine with the same stroke volume
Ricardo 2x4 engine
The two-cycle modes are currently being researched at Ricardo Consulting Engineers in the UK. The concept consists in switching from one mode to the other depending on rpm value. The four-stroke engine is more efficient when running at full throttle, while the opposite is the case for the two-stroke engine. When a small car under heavy load runs at half speed, the engine automatically switches to the two-cycle mode, which is then more efficient. The research on this showed a 27% reduction in fuel consumption.[8][9]
Since the shaft of the four-stroke piston in the M4+2 engine always rotates twice as fast as the shaft of the two stroke piston, meaning the two-stroke part always runs at half speed, both parts work in optimal conditions regarding fuel consumption at all times. The same principles are involved as with having distinct engines, but the design of the M4+2 is much simpler.
See also
References
- Official site of the city of Myszków, Poland(Polish)
- Invenia New-generation various fuel forms internal combustion engine - a review from Spain
- BBS A review from Germany
- Journal abstract - Journal of KONES Internal Combustion Engines 2002 No. 1-2 ISSN 1231-4005, the official Polish educational site (Pdf)
- The Polish Patent Office newsletter (Polish, Pdf)
- The Academical Forum monthly A report published by a Polish academic monthly Forum Akademickie (Polish)
- An article on ndw.v.pl A report published by a Polish popular science magazine "Strefa NDW" (Polish)
- Engineer Online Stroke of genius The Engineer (UK magazine)
- Nonelectric Hybrid Engines Technology Review/MIT A novel hybrid engine could slash fuel consumption