Stevioside
Stevioside is a glycoside derived from the stevia plant, which can be used as a sweetener.[1] Evidence of benefit is lacking for long term effects on weight loss and heart disease risks.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
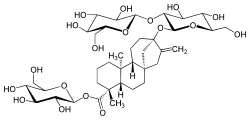
| IUPAC name
13-[(2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid β-D-glucopyranosyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.055.414 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C38H60O18 | |
| Molar mass | 804.8722 |
| Appearance | white powder |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Origin
Stevioside is the main sweetener with rebaudioside A, found in the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana, a plant originating in South America. Dried leaves, as well as aqueous extracts, have been used for decades as a sweetener in many countries, notably in Latin America and Asia (Japan, China).[3] Stevioside was discovered in 1931 by French chemists who gave it its name.[3] The sweetening power of stevioside was estimated to be about 300 times stronger than cane sugar.[3]
See also
References
- Ceunen S, Geuns JM (June 2013). "Steviol glycosides: chemical diversity, metabolism, and function". Journal of Natural Products. 76 (6): 1201–28. doi:10.1021/np400203b. PMID 23713723.
- Azad MB, Abou-Setta AM, Chauhan BF, Rabbani R, Lys J, Copstein L, et al. (July 2017). "Nonnutritive sweeteners and cardiometabolic health: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and prospective cohort studies". CMAJ. 189 (28): E929–E939. doi:10.1503/cmaj.161390. PMC 5515645. PMID 28716847.
- Scientific Committee on Food (17 June 1999). "Opinion On Stevioside as a Sweetener" (PDF). The European Commission.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.