Sevier Desert
The Sevier Desert is a large arid section of central-west Utah, United States, and is located in the southeast of the Great Basin. It is bordered by deserts north, west, and south; its east border is along the mountain range and valley sequences at the perimeter of the Great Basin, with the large north-south Wasatch Range and its associated mountainous landforms. Its eastern border is specifically, the East Tintic, Gilson, and Canyon Mountains; also the massive Pahvant Range.
| Sevier Desert | |
|---|---|
 Gilson Mountains, Sevier River entering the east Sevier Desert at Leamington | |
 Sevier Desert | |
| Length | 105 mi (169 km) |
| Width | 60 mi (97 km) |
| Geography | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Utah |
| Counties | Juab and Millard |
| Borders on | Ferguson Desert-W Great Salt Lake Desert-NW & NNW Gilson & Canyon Mountains, and Pavant Range-E Escalante Desert-SW |
| Coordinates | 39.41661°N 112.66745°W |
| River | Sevier River |
| Lake | Sevier Lake |
The Sevier Desert contains the course of the Sevier River in a circuitous manner. It flows to Sevier Lake in the extreme southwest Sevier Desert. The Sevier River enters the east desert flowing west, immediately turning southwest, then west, to enter the north of Sevier Lake, which is mostly south-southwest trending.
The southeast section of the desert contains the Black Rock Desert volcanic field, with the notable Pahvant Butte, a formation from the time of Lake Bonneville. The volcanic field region is west of an agricultural four-city region from McCornick to Fillmore.[1]
The Little Sahara Recreation Area is located in the northeast of the desert.
Description

The desert is about 105-mi (169 km) long north-south, and about 60-mi (97 km) wide.[2] The desert covers a large section of the central-north Sevier River drainage (11,574 sq mi (29,980 km2)), and much of the east half of Millard County (6,828 sq mi (17,680 km2)). The Sevier Desert is named for the river, which is derived from "Río Severo" (wild river), a local name given by early Spanish explorers.[3]
In the north and northwest, the desert is composed of small mountain ranges, a few valleys, flatlands, and borders the south-southeast of the Great Salt Lake Desert. The Dugway Range and Dugway Valley on the Great Salt Lake Desert's perimeter, borders the Thomas Range, southeast. The Thomas Range and Drum Mountains lie due west of the Little Sahara Recreation Site. A large dissected flatland lies between drained southwesterly by Cherry Creek Wash. The region contains intermittent reservoirs, Hogback, Crater Bench, and Desert Mountain Reservoir. Also various springs, or wells. It is also the site of Fumarole Butte, 5,278 feet (1,609 m), about 10 miles (16 km) east[4] of the Drum Mountains.
Geographical layout
The west perimeter of the Sevier Desert has mostly a north-south border because of the House Range. The south desert perimeter is mostly east-west because the mountains on the south separate the Sevier from the Escalante Desert, an approximate triangle-shaped desert enclosed amongst mountain ranges, and the Escalante and Cedar Valleys. The east of the Sevier Desert contains the communities lying at the foothills of the mountain ranges. The Black Rock Desert volcanic field is located west of the cities. Pavant Valley lies at the west of the Pahvant Range, and west of the Canyon Mountains lies the Oak Creek Sinks adjacent east of the Sevier River, and west of Oak City.
The northeast perimeter of the desert lies at the southwest foothills of the East Tintic Mountains, noted for its mining. Tintic Valley, a small valley between the West Tintic Mountains feeds southwesterly into the Sevier Desert. Adjacent west of the West Tintics, lie two additional bordering mountain ranges, the southwest flank of the Sheeprock Mountains and the small, circular Simpson Mountains west.
In the west and southwest, west of the House Range, is the Ferguson Desert; the Confusion Range and Tule Valley lie between the House Range and the Ferguson Desert.
List of cities and landforms
The following is a list of communities or landforms associated with the north, south, east and west desert perimeters (approximate to mountain foothills, valleys, etc.).
|
West desert perimeter
|
East desert perimeter
|
|
North desert perimeter
|
South desert perimeter
|
Route access
Interstate 15 transits the southeast perimeter of the desert along mountain foothills. Utah State Route 257 transits north, then northeast through the center-east desert, from Black Rock, Utah to Oasis. U.S. 6 continues northeast from Oasis to Jericho and McIntyre, at the northeast perimeter of the desert. U.S. 6 is also the access route to the Little Sahara Recreation Area in the northeast.
References
- Utah DeLorme Atlas, pp. 34, 42.
- Utah DeLorme Atlas & Gazetteer, pp. 23, 31, 34, 41, 42.
- Van Cott, J. W., 1990, Utah Place Names, ISBN 0-87480-345-4
- Utah DeLorme Atlas, pp. 31 & 34.
- Utah Atlas & Gazetteer, DeLorme, 7th Ed, c. 2010, 64 pages.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sevier Desert. |
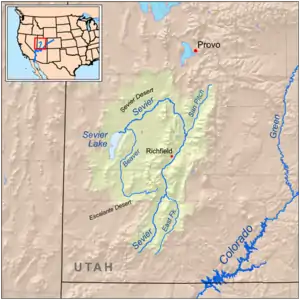 Sevier River watershed, (11,574 sq mi (29,980 km2))
Sevier River watershed, (11,574 sq mi (29,980 km2))