Renault 100 hp V-12
The Renault 100 hp aircraft engine from 1912 was a twelve-cylinder, air cooled 60° vee engine built by the French Renault company.
| Renault 100 hp | |
|---|---|
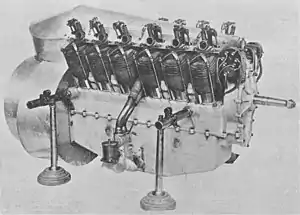 | |
| Renault 100 hp | |
| Type | Piston inline aero engine |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Renault |
| First run | c.1912[1] |
| Developed from | Renault 90 hp, Renault 60 hp |
| Developed into | Renault 80 hp, Renault 130 hp |
Design and development
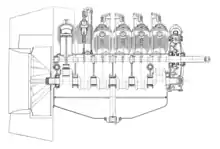
The Renault 100 hp V-12 engine was development from an earlier 90 hp Renault V-12. The main change was the increased bore size of 96 mm instead of 90 mm in the 90 hp engine. Otherwise the general design of the engine was left relatively unchanged, and like its predecessor its general construction was derivative of the air-cooled Renault V-8 engines of the time, such as the 60 hp V-8 type.
The V-12 engine had its two rows of cylinders angled at 60 degree to each other and had a cylinder bore of 96 mm and a stroke of 140 mm. The cylinders and cylinder heads were separate cast-iron pieces with cast fins for air-cooling. The cylinder head was tightened to the cylinder with a copper-asbestos washer, and then secured by a cross-shaped clamp which was bolted to the crankcase with four long studs.[2] Airflow for cooling the cylinders was generated with a fan driven from the rear end of the crankshaft. The fan was blowing air into the sheet metal enclosed chamber between the two rows of cylinders, which then left the enclosure through the narrow spaces between the cylinders, passing through the cylinder's cooling-fins.
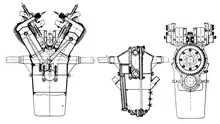
A single camshaft was situated between the two rows of cylinders and operates the inlet and exhaust valves of both cylinder rows, with each valve operated by a separate cam on the camshaft. The inlet and exhaust valves sat vertically opposed in a lateral pocket of the cylinder head on the side of the combustion chamber, with the inlet valve situated below the exhaust valve. The inlet valve was operated directly from the camshaft via a tappet, whereas the exhaust valve was operated via a push rod and a rocker lever. The propeller was mounted directly on the camshaft, which was driven from the crankshaft via reduction gearing consisting of spur gears.
The lower part of the crankcase served as an oil reservoir. A pressurized oil lubrication system was fed by a gear pump located on the lowest point of the crankcase. The oil pump was driven over a vertical shaft from the camshaft via helical gears.[3] The crankshaft was supported by five plain intermediate bearings and two outer ball bearings. Contrary to their V-8 predecessors, the V-12 engines had master-and-slave connecting rods instead of the side-by-side placement of the connecting rods on the same crank journal.[4] This design was kept on the later Renault 80 hp V-8 and Renault 130 hp V-12 aircraft engines. The pistons were made of steel and were fitted with three cast iron rings.
A dual carburetor was fitted on one side of the crankcase, with each barrel of the carburetor feeding one cylinder row.[4] Ignition was supplied by two Bosch magnetos, with each magneto separately serving one cylinder row. The two magnetos were mounted transversely on the top of camshaft on the propeller end. The drive shafts of the magnetos were joined together and driven from the camshaft via helical gears.[3]
The engine was said to produce up to 110 hp at 1800 rpm.[4]
Applications
- Astra C.M. hydroplane (concours de Saint-Malo 1912) [1][5]
- Sanchez-Besa biplane (concours de Saint-Malo 1912) [5]
Preserved engines
- A Renault V-12, serial number 42309, is on display at the Norwegian Aviation Museum [6]
Specifications (Renault 100 hp)

General characteristics
- Type: 12-cylinder, 60-degree Vee, air-cooled in-line piston engine
- Bore: 96 mm (3.780 in)
- Stroke: 140 mm (5.512 in)
- Length: 1,430 mm (56.3 in)
- Width: 820 mm (32.3 in)
- Height: 1,003 mm (39.5 in)
- Dry weight: 290 kg (639 lb)
Components
- Cooling system: Air-cooled
- Reduction gear: 0.5:1
Performance
- Power output: 100 hp at 1,800 rpm
References
Notes
- L'Aérophile. 1 October 1912. pp. 443-444
- Angle. 1921. p. 414
- Vorreiter. 1914. p. 82
- L'Aviation et l'automobilisme militaires : revue mensuelle des progrès scientifiques appliqués à la Défense nationale. March 1914. pp. 71-73
- L'Aérophile. 15 September 1912. pp. 418-419
- Europeana, https://www.europeana.eu/en/item/2022608/FMU_LMU_501795
- Huth. 1920. pp. 151-153
Bibliography
- Angle, Glenn Dale (1921). Airplane Engine Encyclopedia: An Alphabetically Arranged Compilation Of All Available Data On The World's Airplane Engines. Otterbein Press. p. 414. OL 23525261M.
- Vorreiter, Ansbert (1914). "5e Exposition Internationale de Locomotion Aerienne vom 5.-25. Dez. 1913". Zeitschrift für Flugtechnik und Motorluftschiffahrt, 5. Jahrgang, 1914 (in German). München und Berlin: R. Oldenbourg: 67–69, 82. OCLC 1606129.
- "Le nouveau 100 HP Renault". L'Aérophile, 1 October 1912 (in French). Paris. 1 October 1912. pp. 443-444.
- Mirguet, Henri (15 September 1912). "Les enseignements de Saint-Malo". L'Aérophile, 15 September 1912 (in French). Paris. pp. 418-419.
- Fouqueux (1914). "Les "Renault"". L'Aviation et l'automobilisme militaires : revue mensuelle des progrès scientifiques appliqués à la Défense nationale (in French). Paris. pp. 71-73.
- Huth, Fritz (1920). Motoren für Flugzeuge und Luftschiffe (in German) (3rd ed.). Berlin: R. C. Schmidt & co. OCLC 2116726.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Renault 100 hp. |
- Renault 100 hp V-12 engine installation (Gallica - BnF)
- Astra seaplane with Renault V-12 engine (Canada Aviation & Space Museum/Corbis via Getty Images)