Regulatory sequence
A regulatory sequence is a segment of a nucleic acid molecule which is capable of increasing or decreasing the expression of specific genes within an organism. Regulation of gene expression is an essential feature of all living organisms and viruses.
Description
|
|
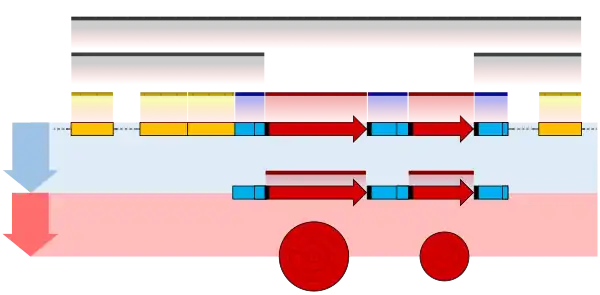
In DNA, regulation of gene expression normally happens at the level of RNA biosynthesis (transcription), and is accomplished through the sequence-specific binding of proteins (transcription factors) that activate or inhibit transcription. Transcription factors may act as activators, repressors, or both. Repressors often act by preventing RNA polymerase from forming a productive complex with the transcriptional initiation region (promoter), while activators facilitate formation of a productive complex. Furthermore, DNA motifs have been shown to be predictive of epigenomic modifications, suggesting that transcription factors play a role in regulating the epigenome.[2]
In RNA, regulation may occur at the level of protein biosynthesis (translation), RNA cleavage, RNA splicing, or transcriptional termination. Regulatory sequences are frequently associated with messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules, where they are used to control mRNA biogenesis or translation. A variety of biological molecules may bind to the RNA to accomplish this regulation, including proteins (e.g. translational repressors and splicing factors), other RNA molecules (e.g. miRNA) and small molecules, in the case of riboswitches.
Research to find all regulatory regions in the genomes of all sorts of organisms is under way.[3] Conserved non-coding sequences often contain regulatory regions, and so they are often the subject of these analyses.
Examples
- CAAT box
- CCAAT box
- Operator (biology)
- Pribnow box
- TATA box
- SECIS element, mRNA
- Polyadenylation signals, mRNA
- A-box
- Z-box
- C-box
- E-box
- G-box
Insulin gene
Regulatory sequences for the insulin gene are:[4]
- A5
- Z
- negative regulatory element (NRE)[5]
- C2
- E2
- A3
- cAMP response element
- A2
- CAAT enhancer binding (CEB)
- C1
- E1
- G1
See also
References
- Shafee, Thomas; Lowe, Rohan (2017). "Eukaryotic and prokaryotic gene structure". WikiJournal of Medicine. 4 (1). doi:10.15347/wjm/2017.002. ISSN 2002-4436.
- Whitaker JW, Zhao Chen, Wei Wang. (2014) Predicting the Human Epigenome from DNA Motifs. Nature Methods. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3065
- Stepanova et al., Bioinformatics, 21(9): 1789-96, year 2005. A comparative analysis of relative occurrence of transcription factor binding sites in vertebrate genomes and gene promoter areas
- Melloul et al., Diabetologica, 45, 309-326, year 2002. Regulation of insulin gene transcription
- Jang, Won Gu; Kim, Eun Jung; Park, Keun-Gyu; Park, Yong Bok; Choi, Hueng-Sik; Kim, Hye-Jin; Kim, Yong Deuk; Kim, Kyung-Sup; Lee, Ki-Up; Lee, In-Kyu (2007). "Glucocorticoid receptor mediated repression of human insulin gene expression is regulated by PGC-1α". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 352 (3): 716–721. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.11.074. PMID 17150186.