Rapa Nui calendar
The Rapa Nui calendar was the indigenous lunisolar calendar of Easter Island. It is now obsolete.

Attestation
William J. Thomson, paymaster on the USS Mohican, spent twelve days on Easter Island from December 19 to 30, 1886. Among the data Thomson collected were the names of the nights of the lunar month and of the months of the year:[1]
- The natives reckoned their time, and in fact do so still by moons or months, commencing the year with August, which was, according to the traditions,the time when Hotu-Matua and his followers landed upon the island.
Months
Thomson recorded the months as follows:
Rapanui name Meaning Western equivalent, 1886–1887 Anekena August Hora-iti little summer September Hora-nui big summer October Tangarouri part of November Kotuti November and December Ruti December and January Koro January Tuaharo February Tetuupu March Tarahao April Vaitu-nui big winter May Vaitu-poto short winter June Maro or Temaro July
Days
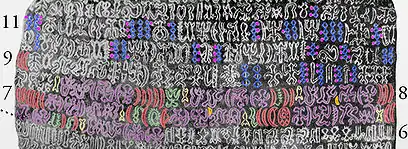
The month was divided in two, beginning with the new and full moon. Thomson recorded the calendar at the time of his visit to the island as follows. The new moon occurred on November 25 and again on the night of December 24;[2] Thompson records the crescent was first visible on November 26.
Rapanui name Meaning Western
equivalent, 1886Kokore tahi first kokore November 27 Kokore rua second kokore November 28 Kokore toru third kokore November 29 Kokore hâ fourth kokore November 30 Kokore rima fifth kokore December 1 Kokore ono sixth kokore December 2 Maharu first quarter December 3 Ohua December 4 Otua December 5 Ohotu December 6 Maure December 7 Ina-ira December 8 Rakau December 9 Omotohi full moon December 10 Kokore tahi first kokore December 11 Kokore rua second kokore December 12 Kokore toru third kokore December 13 Kokore hâ fourth kokore December 14 Kokore rima fifth kokore December 15 Tapume December 16 Matua December 17 Orongo first quarter [sic] December 18 Orongo taane December 19 Mauri nui December 20 Marui [sic] kero December 21 Omutu December 22 Tueo December 23 Oata new moon December 24 Oari December 25 Kokore tahi first kokore December 26
The three sources we have correspond with each other except for two intercalary days (in bold), and the night of the new moon in Englert, which seems to have been confused with one of these. Beginning with (o)ata, the night of the new moon, they are:
| day | Englert | Thomson | Métraux | day | Englert | Thomson | Métraux |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *1 | oata | oata | ata | *15 | omotohi | omotohi | motohi |
| 2 | ohiro | oari | ari | 16 | kokore tahi | kokore tahi | kokore tahi |
| 3 | kokore tahi | kokore tahi | kokore tahi | 17 | kokore rua | kokore rua | kokore rua |
| 4 | kokore rua | kokore rua | kokore rua | 18 | kokore toru | kokore toru | kokore toru |
| 5 | kokore toru | kokore toru | kokore toru | 19 | kokore hâ | kokore ha | kokore ha |
| 6 | kokore hâ | kokore ha | kokore ha | 20 | kokore rima | kokore rima | kokore rima |
| 7 | kokore rima | kokore rima | kokore rima | 21 | tapume | tapume | tapume |
| 8 | kokore ono | kokore ono | kokore ono | 22 | matua | matua | matua |
| *9 | maharu | maharu | maharu | *23 | orongo | orongo | rongo |
| 10 | ohua | ohua | hua | 24 | orongo taane | orongo tane | rongo tane |
| 11 | otua | otua | atua | 25 | mauri nui | mauri nui | mauri nui |
| x | — | ohotu | hotu | 26 | mauri karo | mauri kero | mauri kero |
| 12 | maure | maure | maure | 27 | omutu | omutu | mutu |
| 13 | ina-ira | ina-ira | ina-ira | 28 | tireo | tireo | tireo |
| 14 | rakau | rakau | rakau | x | — | — | hiro |
- *New moon, full moon, and first and last quarters.
The kokore are unnamed (though numbered) nights; tahi, rua, toru, haa, rima, ono are the numerals 1–6. The word kokore is cognate with Hawaiian ‘a‘ole "no" and Tahitian ‘aore "there is/are not"; here it may mean "without [a name], nameless".
Analysis
The calendar collected by Thomson is notable in that it contains thirteen months. All other authors mention only twelve, and Métraux and Barthel find fault with Thomson:
- Thomson translates Anakena as August and suggests that the year began at that time because Hotu-Matua landed at Anakena in that month, but my informants and Roussel (1869) give Anakena as July.[3]
- We are basing the substitution on the lists by Metraux and Englert (ME:51; HM:310), which are in agreement. Thomson's list is off by one month.[4]
However, Guy[5] calculated the dates of the new moon for years 1885 to 1887 and showed that Thomson's list fit the phases of the moon for 1886. He concluded that the ancient Rapanui used a lunisolar calendar with kotuti its embolismic month (AKA "leap month"), and that Thomson chanced to land on Easter Island in a year with a leap month.
The days hotu and hiro appear to be intercalary. A 28-day calendar month needs one to two intercalary days to keep in phase with the 29½-day lunar month. One of the rongorongo tablets may describe a rule for when to add these days.[6]
References
- THOMSON, William J. 1891, p546. "Te Pito te Henua, or Easter Island". Report of the United States National Museum for the Year Ending June 30, 1889. Annual Reports of the Smithsonian Institution for 1889. 447–552. Washington: Smithsonian Institution. (An online version is available [www.sacred-texts.com/pac/ei/ei61.htm here])
- Calculated here. Easter Island is about 109° (7.3 hours) west of Greenwich Mean Time, so the 09:55 UTC new moon of December 25 occurred at 2:38 AM local time, on the night of December 24.
- MÉTRAUX, Alfred. 1940, p52. "Ethnology of Easter Island." Bernice P. Bishop Museum Bulletin 160. Honolulu: Bernice P. Bishop Museum Press.
- BARTHEL, Thomas S. 1978, p48. The Eighth Land. Honolulu: the University Press of Hawaii.
- GUY, Jacques B.M. 1992. "À propos des mois de l'ancien calendrier pascuan" ("On the months of the old Easter Island calendar"), Journal de la Société des Océanistes 94/1:119–125
- GUY, Jacques B.M. 2001. "Le calendrier de la tablette Mamari", Bulletin du Centre d'Études sur l'Île de Pâques et la Polynésie 47:1–4.