Rail transport in Mexico
Mexico has a freight railway system owned by the national government and operated by various entities under concessions (charters) granted by the national government. The railway system provides freight and passenger service throughout the country (the majority of the service is freight-oriented), connecting major industrial centers with ports and with rail connections at the United States border. Passenger rail services were limited to a number of tourist trains between 1997, when Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México suspended service, and 2008, when Ferrocarril Suburbano de la Zona Metropolitana de México inaugurated Mexico's first commuter rail service between Mexico City and the State of Mexico. This is not including the Mexico City Metro, which started service in 1969.

History
Construction
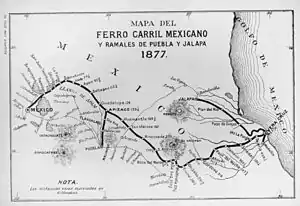


Mexico's rail history began in 1837, with the granting of a concession for a railroad to be built between Veracruz, on the Gulf of Mexico, and Mexico City. However, no railroad was built under that concession.
In 1857, Don Antonio Escandón secured the right to build a line from the port of Veracruz to Mexico City and on to the Pacific Ocean. Revolution and political instability stifled progress on the financing or construction of the line until 1864, when, under the regime of Emperor Maximilian, the Imperial Mexican Railway Company began construction of the line. Political upheaval continued to stifle progress, and the initial segment from Veracruz to Mexico City was inaugurated nine years later on January 1, 1873 by President Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada.
President Lerdo and his successor Porfirio Díaz encouraged further rail development through generous concessions that included government subsidies for construction. At the beginning of his first term Díaz inherited 398 miles (640.5 km) of railroads consisting almost exclusively of the British-owned Mexican Railway.[1] By the end of his second term in 1910, Mexico boasted 15,360 miles (24,720 km) of in-service track, mostly built by American, British and French investors.[2]
From a small start, the railway network expanded significantly, linking many parts of the country previously isolated. The Interoceanic Railway linked Mexico City to the port of Veracruz; the Monterrey and Mexican Railroad linked that northern city with the Gulf Coast port of Tampico; the Southern Pacific of Mexico linked west coast cities from Guaymas to Mazatlan; the Sonora Railway linked Nogales to the port of Guaymas; and the Mexican Central Railroad went north to the U.S. border at El Paso, Texas.[3] The British invested £7.4 million in railways during the decade of the 1880s, jumping to £53.4 million in 1910s. The decade-total of new investment in mining went from £1.3 million in 1880s to £11.6 million in 1910s. Investments in land and other properties rose from near zero in 1880s to £19.7 million in 1910s. The totals reached £135 million, almost as much as the United States.[4]
Growing nationalistic fervor in Mexico led the Díaz administration to bring the bulk of the nation's railroads under national control through a plan drafted by his Minister of Finance, José Yves Limantour. The plan, implemented in 1909, created a new government corporation, Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México (FNM), which would exercise control of the main trunk rail lines through a majority of share ownership.
Nationalization
The rail system deteriorated greatly from neglect during the period of the Mexican Revolution. Following the Revolution, the entirety of the Mexican rail system was nationalized between 1929 and 1937. In 1987 the government merged its five regional railroads into FNM. During the later period of national ownership, FNM suffered significant financial difficulties, running an operating deficit of $552 million (37 percent of its operating budget) in 1991. Competition from trucking and shipping decreased railroad's share of the total freight market to about 9 percent, or about half of rail's share a decade earlier.
Privatization
In 1995, the Mexican government announced that the FNM would be privatized and divided into four main systems. As part of the restructuring for privatization, FNM suspended passenger rail service in 1997.
.JPG.webp)
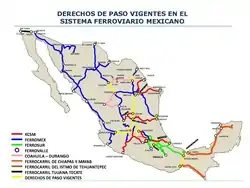
In 1996, Kansas City Southern (KCS), in a joint venture with Transportacion Maritima Mexicana (TMM), bought the Northeast Railroad concession that linked Mexico City, Monterrey, the Pacific port at Lázaro Cárdenas and the border crossing at Laredo. The company was initially called Transportación Ferroviaria Mexicana (TFM), but was renamed Kansas City Southern de México (KCSM) in 2005 when KCS bought out TMM's interests. KCS's systems in the United States and Mexico jointly form end-to-end rail system linking the heartlands of Mexico and the United States.
The Northwest Railroad concession, connecting Mexico City and Guadalajara with the Pacific port of Manzanillo and various crossings along the United States border was sold to a joint venture between Grupo Mexico and Union Pacific Railroad in 1998 during the presidency of Dr. Ernesto Zedillo (which later occupied the position of Director of the Board of Union Pacific). The company operates as Ferrocarril Mexicano or Ferromex. Ferromex's freight volumes have increased; it hauled a record 22,365 million tonne-km in the first 6 months of 2010. Also, Ferrosur, the railroad serving Mexico City and cities/ports southeast of Mexico City, hauled their own record 3,565 million tonne-kilometers.[5]
There were two southern concessions, merged in 2000 to form Ferrosur. Ferrosur operates the line between Mexico City and the Gulf of Mexico port of Veracruz. In 2005, Ferrosur was bought by Ferromex's parent company. KCSM challenged the acquisition and the merger failed to receive regulatory approval. However, in March 2011, a tribunal ruled in Grupo Mexico's favor, and the merger was permitted.[6]
The three major Mexican railroads jointly own Ferrocarril y Terminal del Valle de México (Ferrovalle) which operates railroads and terminals in and around Mexico City.
High-speed rail
In 2006, the Secretariat of Communications and Transport of Mexico proposed a high-speed rail link[7] that will transport its passengers from Mexico City to Guadalajara, Jalisco, with stops in the cities of Querétaro, Guanajuato, Leon and Irapuato; and a connected line running from the port city of Manzanillo to Aguascalientes. The train would travel at 300 km/h,[8] and would allow passengers to travel from Mexico City to Guadalajara in just 2 hours[8] at an affordable price (the same trip by road would last 7 hours). The network would also be connected to Monterrey, Chilpancingo, Cuernavaca, Toluca, Puebla, Tijuana, Hermosillo, Cordoba, Veracruz, Oaxaca, Colima, Zacatecas, Torreon, Chihuahua, Puebla, San Luis Potosi, Mexicali, Saltillo, and Acapulco by 2015.[7] The whole project was projected to cost 240 billion pesos, or about 25 billion dollars.[7] Mexican billionaire Carlos Slim expressed an interest in investing in high-speed rail.[9]
Revival of passenger service
President Enrique Peña Nieto proposed a return to services of intercity trains, the proposed projects are Mexico City-Toluca (construction began July 7, 2014), the Peninsular train (Yucatán-Mayan Riviera), Mexico-Querétaro high speed train starts construction October 2014 and will operate speeds up to 300 km/h (with expansion to Guadalajara) and Puebla-Tlaxcala-Mexico City. On November 3, 2014, China Railways Construction Corporation associated with Prodemex, Teya and GHP has won the contract to build the high Speed train Mexico City-Querétaro. The estimated cost will be close to 4 billion dollars, to be finished by the end of 2017 and will be fully operational by spring 2018. However, Mexico canceled [10] the contract four days later because of doubts over the bidding process. In 2015, Mexico opened a new tender, which was revoked again. Hence, Mexico could indemnify[11] China Railway Construction Corporation $1.31m.
President-elect Andrés Manuel López Obrador announced a US$7.4 billion plan to build a tourist and freight railway on the Yucatán Peninsula in September 2018. The project, named the Mayan Train, began construction in December 2018 and will connect Palenque to Cancún, but remains controversial with environmentalists and indigenous rights activists.[12][13]
Railways

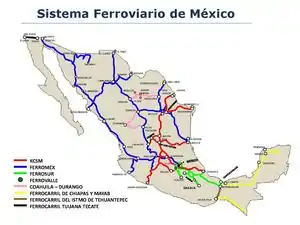
The major Class I freight railroads in Mexico include:
- Ferromex (FXE)
- Kansas City Southern de México (KCSM)
Short line railroads include:
- Baja California Railroad (BJRR)
- Ferrocarriles Chiapas-Mayab (FCCM)
- Ferrocarril y Terminal del Valle de México (Ferrovalle)
- Ferrosur (FSRR)
- Línea Coahuila Durango (LFCD)
- Ferrocarril Transístmico
Passenger rail lines include:
- Chihuahua al Pacífico, a tourist train running through the Copper Canyon.
- Tequila Express, a tourist train running from Guadalajara, Jalisco to a tequila distillery in Amatitán.
- Tren Suburbano (commuter rail system in the Mexico City metro area)
- Toluca–Mexico City commuter rail (under construction)
Mass transit
Urban rail transit systems in Mexico include four light rail or rapid transit systems: The Guadalajara light rail system, the Mexico City Metro, the Xochimilco Light Rail line (in Mexico City) and the Monterrey Metro. In 2017, a fifth light rail system opened in Puebla City.[14]
Museums
There are several rail museums in Mexico including: the Railway Museum in San Luis Potosi,[15] the Old Railway Station Museum in Aguascalientes, Aguascalientes; a former station along the Interoceanic Railway of Mexico in Cuautla, Morelos which serves as a museum; the Museo de las Ferrocarilles en Yucatán is in Mérida, Yucatán;[16] and the National Railway Museum in Puebla, Puebla.[17]
Railway links with adjacent countries
- United States – yes, freight only - same 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge
- Guatemala – yes – at Ciudad Tecún Umán, – break-of-gauge 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge / 914 mm (3 ft) (rebuilt as standard gauge in 2019[18])
See also
- List of Mexican railroads
- List of street railways in Mexico (all-time, historical list)
- Transportation in Mexico
References
- Bazant, Jan (1977). A Concise History of Mexico from Hidalgo to Cardenas 1805-1940. New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 111. ISBN 0-521-29173-9.
- Fred Wilbur Powell, the Railroads of Mexico, 1921
- Coatsworth, John H. Growth Against Development: The Economic Impact of Railroads in Porfirian Mexico. DeKalb: Northern Illinois University 1981.
- Tenenbaum, Barbara A. and James N. McElveen, "From speculative to substantive boom: the British in Mexico, 1821-1911." in Oliver Marshall, ed. English speaking communities in Latin America (Macmillan, 2000): 51-79, at p 69.
- "A record half". Railway Gazette International. London. September 9, 2010. Retrieved October 12, 2010.
- "Mexican Tribunal OKs Grupo Mexico Railroad merger". Reuters. March 28, 2011.
- Hawley, Chris (January 6, 2006). "Mexico reviving travel by train". Arizona Republic. Phoenix.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on May 1, 2011. Retrieved October 30, 2010.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Slim to invest in Santa Cruz" (Press release). Corporate Mexico. The America's Intelligence Wire. January 21, 2005.
- O‘Boyle & Graham, Michael & Dave (November 7, 2014). "Mexico scraps $3.75 bln China rail deal ahead of state visit". Reuters.
- "Mexico to pay China rail firm for cancelling project". BBC. May 22, 2015.
- Pskowski, Martha (February 22, 2019). "Mexico's 'Mayan Train' Is Bound for Controversy". CityLab. Retrieved February 23, 2019.
- Varillas, Adriana (November 23, 2018). "Everything you need to know about the Mayan Train project". El Universal. Retrieved February 23, 2019.
- "Puebla tram-train inaugurated". Metro Report International. January 25, 2017. Retrieved December 11, 2017.
- Ministry of Culture website
- Gorbman, Beryl (February 24, 2010). "Trains and The Merida Railway Museum". Retrieved May 10, 2011.
- Álvarez, Samantha; Minsk, Todd R. (March 2005). "Mexico's National Railway Museum". Journal of Transport History. 26 (1). Manchester University Press. p. 112. ISSN 0022-5266.
- https://www.puertochiapas.com.mx/news/362-railway-between-guatemala-and-mexico-connectivity-across-puerto-chiapas
Further reading
- Coatsworth, John H. "Indispensable railroads in a backward economy: the case of Mexico." Journal of Economic History 39.04 (1979) pp: 939-960. in JSTOR
- Coatsworth, John. "Railroads, landholding, and agrarian protest in the early porfiriato." Hispanic American Historical Review (1974) pp: 48-71. in JSTOR
- Knapp, Frank A. "Precursors of American investment in Mexican railroads." Pacific Historical Review (1952): 43-64. in JSTOR
- Lewis, Daniel. Iron Horse Imperialism: The Southern Pacific of Mexico, 1880-1950 (University of Arizona Press, 2007)
- Matthews, Michael. The Civilizing Machine: A Cultural History of Mexican Railroads, 1876-1910 (2014) excerpt
- Miller, Richard Ulric. "American railroad unions and the national railways of Mexico: An exercise in nineteenth‐century proletarian manifest destiny," Labor History 15.2 (1974) pp: 239-260.
- Powell, Fred Wilbur. The Railroads of Mexico (1921)
- Van Hoy, Teresa. A social history of Mexico's railroads: peons, prisoners, and priests (Rowman & Littlefield, 2008)
- Donovan, Frank and Kerr, John Leeds. Destination Topolobampo: The Kansas City, Mexico & Orient Railway (Golden West Books, 1968)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rail transport in Mexico. |
- The Mexican Railways
- History of Mexico's Railroads (in Spanish)
- The Railroads of Mexico by Fred Wilbur Powell on Google Books
- Ferrocarril Coahuila Durango
- Ferromex
- Ferrosur
- Kansas City Southern
- Ferrocarril Y Terminal Del Valle De Mexico
- Mexican government: Secretary of Communication & Transport
- Mexico Infrastructure and Rail Projects
- Union Pacific Railroad Company
- Kansas City Southern Railway Company
- Pictures of restored(non-operational) train station in Durango, Mexico
