Posterior lobe of cerebellum
The posterior lobe of cerebellum or neocerebellum, is the portion of the cerebellum below the primary fissure.[1]
| Posterior lobe of cerebellum | |
|---|---|
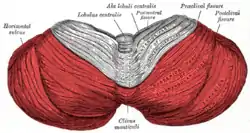 Superior view of an cerebellum. Posterior lobe shown in red. | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lobus posterior cerebelli |
| NeuroNames | 660 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_911 |
| TA98 | A14.1.07.201 |
| TA2 | 5795 |
| FMA | 72252 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
It is sometimes called the neocerebellum[2] since phylogenetically it is the newest part of the cerebellum. It plays an important role in fine motor coordination, specifically in the inhibition of involuntary movement via inhibitory neurotransmitters, especially GABA.[2]
The posterior lobe receives input mainly from the brainstem (i.e., reticular formation and inferior olivary nucleus) and cerebral cortex.[3]
It also has activation linked to happiness.[4]
Additional images
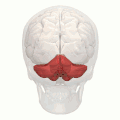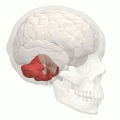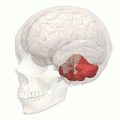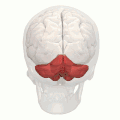 Animation. Posterior lobe shown in red.
Animation. Posterior lobe shown in red.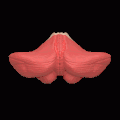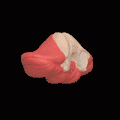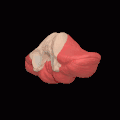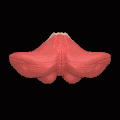 Close up animation. Posterior lobe shown in red.
Close up animation. Posterior lobe shown in red.
References
- "utah.edu".
- "The Cerebellum".
- Siegel, Allan Siegel, Hreday N. Sapru; case histories written by Heidi E. (2011). Essential neuroscience (2nd ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 190. ISBN 978-0-7817-8383-5.
- Schienle A, Scharmüller W (August 2013). "Cerebellar activity and connectivity during the experience of disgust and happiness". Neuroscience. 246: 375–81. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.04.048. PMID 23639880.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Posterior lobe of cerebellum. |
- Atlas image: n2a7p4 at the University of Michigan Health System
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.