Pitcairn PA-3 Orowing
The Pitcairn PA-3 Orowing is an early Pitcairn biplane designed for light commercial use in the early 1920s when aircraft production rates did not meet demand for airmail, training, and passenger aircraft.[2]
| Pitcairn PA-3 Orowing | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 1926 Pitcairn PA-3 Orowing model on display at the EAA Airventure Museum | |
| Role | Biplane |
| National origin | United States of America |
| Manufacturer | Pitcairn Aircraft Company |
| Designer | Agnew E. Larson |
| First flight | 1926 |
| Introduction | 1926 |
| Number built | 35[1] |
Development
The Orowing was the first production aircraft from Pitcairn. Pitcairn purchased surplus Curtiss Oriole wings and mated them to production fuselages. The name "Orowing" is a mix of the PA-2 "Sesquiwing" and the Curtiss "Oriole". The initial production run also was powered by 250 surplus Curtiss OX-5 engines.[3]
Design
The three place Biplane was made of welded steel tube fuselage with an OX-5 engine. The aircraft featured dual controls for flight instruction. The wings were purchased from Curtiss and were the same design as a Curtiss Oriole.[4][5]
Operational history
Most Orrowing production was sold to Pitcairn Aviation for flight training and charters.
An Orowing flew in the 1926 Ford National Reliability Air Tour.[6]
Specifications (Pitcairn PA-3 Orowing)
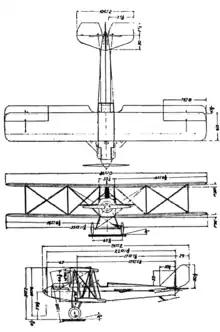
Data from The Pitcairn Aerowing[7]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Capacity: 2 passengers
- Length: 26 ft 2 in (7.98 m)
- Wingspan: 36 ft 0 in (10.97 m)
- Height: 2 ft 2 1⁄2 in (0.673 m)
- Wing area: 338.37 sq ft (31.436 m2)
- Airfoil: RAF 15 modified
- Empty weight: 1,345 lb (610 kg)
- Gross weight: 2,100 lb (953 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 30 US gal (25 imp gal; 110 L)
- Powerplant: 1 × Curtiss OX-5 , 90 hp (67 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed
Performance
- Maximum speed: 78 kn (90 mph, 140 km/h)
- Cruise speed: 70 kn (80 mph, 130 km/h)
- Stall speed: 39 kn (45 mph, 72 km/h)
- Range: 350 nmi (400 mi, 640 km)
- Endurance: 4 hr
- Service ceiling: 10,500 ft (3,200 m)
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pitcairn PA-3 Orowing. |
Notes
- "Harold Pitcairn". Retrieved 18 Jan 2011.
- William F. Trimble. High frontier: a history of aeronautics in Pennsylvania.
- Sport Aviation. November 1991. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Orowing". Retrieved 18 January 2011.
- Janet Rose Daly Bednarek, Michael H. Bednarek. Dreams of flight: general aviation in the United States.
- "Ford Air Tour" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-11. Retrieved 18 Jan 2011.
- Aviation November 22, 1926, pp. 882, 884.
Bibliography
- "The Pitcairn Orowing". Aviation. Vol. XXI no. 21. November 22, 1926. pp. 882, 884.