Pfannenstiel incision
A Pfannenstiel incision /ˈfɑːnɪnʃtiːl/, Kerr incision, Pfannenstiel-Kerr incision[1] or pubic incision is a type of abdominal surgical incision that allows access to the abdomen. It is used for gynecologic and orthopedics surgeries,[2] and it is the most common method for performing Caesarian sections today. This incision is also used in Stoppa approach for orthopedics surgeries to treat pelvic fractures.[3]
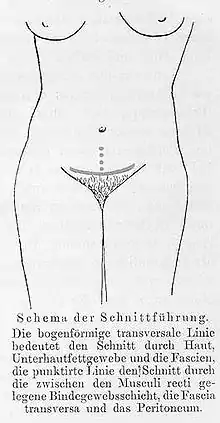
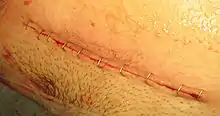
The Pfannenstiel incision offers a large view of the central pelvis but limits exposure to the lateral pelvis and upper abdomen, factors that limit the usefulness of this incision for gynecologic cancer surgery.[4]
This incision is commonly called the "bikini line incision". Some common reasons for this surgical access are obstetric delivery and hernia repair. It is often used in preference to other incision types for the sake of aesthetics, because the scar will be hidden by the pubic hair. The incision does not distort the belly button and heals faster than the traditional vertical incision.
The surgeon cuts on a generally horizontal (slightly curved) line just above the pubic symphysis. The skin and subcutaneous fat are lifted off the rectus muscle fascia, going towards the head. This allows access to the lower midline of the anterior abdominal wall fascia. The fascia is cut vertically to separate the rectus muscles and enter the abdomen. Though the skin is incised transversely, the fascia is still made in the midline.
Etymology and history
The name derives from the surname of Hermann Johannes Pfannenstiel (1862–1909), the German gynecologist who invented the technique in 1900.[5]
In the United Kingdom, the incision was popularized by Monroe Kerr, who first used it in 1911, so in English-speaking countries it is sometimes called the Kerr incision or the Pfannenstiel–Kerr incision. Kerr published the results in 1920, proposing that this method would cause less damage to the vascularized areas of the uterus than the classical operation. He claimed that it was better than the longitudinal uterine incision in terms of chances for scar rupture and injury to vessels.[6]
See also
References
- Vitale, Salvatore Giovanni; Marilli, Ilaria; Cignini, Pietro; Padula, Francesco; D’Emidio, Laura; Mangiafico, Lucia; Rapisarda, Agnese Maria Chiara; Gulino, Ferdinando Antonio; Cianci, Stefano (2014). "Comparison between modified Misgav-Ladach and Pfannenstiel-Kerr techniques for Cesarean section: review of literature". Journal of Prenatal Medicine. 8 (3–4): 36–41. ISSN 1971-3282. PMC 4510561. PMID 26265999.
- Hoffman, Barbara; Schorge, John; Schaffer, Joseph; Halvorson, Lisa; Bradshaw, Karen; Cunningham, F. (2012-04-12). Williams Gynecology, Second Edition. McGraw Hill Professional. ISBN 9780071716727.
- Wade R. Smith; Bruce H. Ziran; Steven J Morgan (12 June 2007). Fractures of the Pelvis and Acetabulum. CRC Press. pp. 180–. ISBN 978-1-4200-1638-3.
- Higgins RV, Hall J, Naumann RW, Gaupp FB, Talavera F, Barnes AD (February 7, 2014). "Abdominal Incisions and Sutures in Gynecologic Oncological Surgery". medscape.com. WebMD LLC. Retrieved 17 February 2014.
- Elsevier (2003). Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (30th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-0146-5.
- Powell, John (2001). "The Kerr Incision". Journal of Pelvic Surgery. 7 (3): 77–78. Retrieved 17 December 2016.