Perforating arteries
The perforating arteries, usually three in number, are so named because they perforate the tendon of the Adductor magnus to reach the back of the thigh.
| Perforating arteries | |
|---|---|
 The arteries of the gluteal and posterior femoral regions. | |
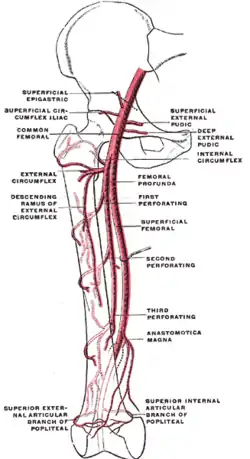 The profunda femoris artery, femoral artery and their major branches - right thigh, anterior view. (Perforating arteries labeled at right center.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Profunda femoris artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteriae perforantes |
| TA98 | A12.2.16.031 |
| TA2 | 4696 |
| FMA | 69460 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
They pass backward close to the linea aspera of the femur under cover of small tendinous arches in the muscle.
The first is given off above the Adductor brevis, the second in front of that muscle, and the third immediately below it.
First
The first perforating artery (a. perforans prima) passes posteriorly between the Pectineus and Adductor brevis (sometimes it perforates the latter); it then pierces the Adductor magnus close to the linea aspera.
It gives branches to the Adductores brevis and magnus, Biceps femoris, and Gluteus maximus, and anastomoses with the inferior gluteal, medial and lateral femoral circumflex and second perforating arteries.
Second
The second perforating artery (a. perforans secunda), larger than the first, pierces the tendons of the Adductores brevis and magnus, and divides into ascending and descending branches, which supply the posterior femoral muscles, anastomosing with the first and third perforating.
The second artery frequently arises in common with the first.
The nutrient artery of the femur is usually given off from the second perforating artery; when two nutrient arteries exist, they usually spring from the first and third perforating vessels.
Third/fourth
The third perforating artery (a. perforans tertia) is given off below the Adductor brevis; it pierces the Adductor magnus, and divides into branches which supply the posterior femoral muscles; anastomosing above with the higher perforating arteries, and below with the terminal branches of the profunda and the muscular branches of the popliteal.
The nutrient artery of the femur may arise from this branch.
The termination of the profunda artery, already described, is sometimes termed the fourth perforating artery of Elliott after the anatomist who first dissected its course.
Additional images
 Cross-section through the middle of the thigh.
Cross-section through the middle of the thigh.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 631 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)