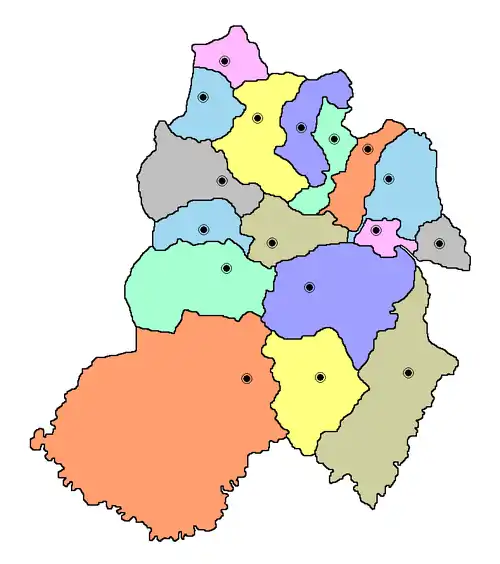
Paraguarí Department
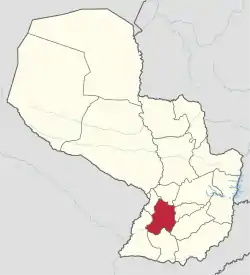
Paraguarí (Spanish pronunciation: [pa.ɾa.ɣwaˈɾi]; Guaraní: Paraguari) is a departamento in Paraguay. At the 2002 census it had a population of 221,932.[1] The capital is the city of Paraguarí.
Paraguarí | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 25°38′S 57°9′W | |
| Country | Paraguay |
| Capital | Paraguarí |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Miguel Jorge Cuevas (ANR) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 8,705 km2 (3,361 sq mi) |
| Population (2002) | |
| • Total | 221,932 |
| • Density | 25/km2 (66/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-04 (AST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-03 (ADT) |
| ISO 3166 code | PY-9 |
| Number of Districts | 17 |
History
The territory which forms this department is located in a valley formerly called "Yarigua'a" that was part of the mission of Jesuit priests in the era of colonization.
Numerous villages existed in this area, whose inhabitants were influenced by priests and chaplains responsible for directing agricultural and livestock activities.
Part of the territory was occupied also by the Dominican missionaries who were responsible for "Tavapy" with black people.
At the end of the 16th century, the Franciscan missionaries founded the city of Yaguarón with indigenous Guaraní.
The development of the new population was consolidated in the 17th century and civilians took shape in the 18th century. Foundations followed on which today form part of this department. In 1725 Carapeguá was founded, in 1733 Quiindy, 1766 saw the founding of Ybycuí, in 1769, Pirayú The current capital of the department, Paraguarí, was founded in 1775. Subsequently, Quyquyhó was founded in 1776, Ybytimí and Acahay in 1783 and was founded Caapucú in 1787.
During the government of Don Carlos Antonio López this territory benefited by the opening of railways in 1854. Once the Paraguayan War, the tracks reached Villarrica, which generated the founding of new cities like Cerro León, Escobar, Sapucai and General Bernardino Caballero.
Over time, people formed two lines, which were on the brink of the route and those who were along the railroad tracks. This situation contributed to the formation of two separate departments in 1906, Quiindy with the cities of Paraguarí and routes that was formed by the towns of Carapegua, Tavapy, General Bernardino Caballero, Escobar, Yaguarón, Pirayú, Ypacaraí and Itauguá, the latter two belonging to the department at present Central.
In 1945 the division policy changed, establishing the department of Paraguarí IX as it is currently.
Geography
Paraguarí is located in the south west of the Eastern Region, between 25°25′ and 26°30′ south and between 56°35′W and 57°40′W. Cordillera and Caaguazú departamentos are to the north; Misiones to the south; Guairá and Caazapá to the east; and Central and Ñeembucú to the west.

Paraguarí has a rich variety of soils in the landscape, elevated to the north and hills that are formed by landslides in the mountains of Senior. Towards the downtown area and south west owns land flat and undulating valley covered with vast grassland good for livestock.
In this department are the hills Mbatovi and Ybycuí. It also has smaller hills as the height of Pirayú, Azcurra, León, Paraguarí and Jhu.
The river tributaries flow into Tebicuary Paraguarí and rivers Tebicuarymí and the stream Mbuyapey bathe their coasts.
Another aspect is located in this area of the lake and the lagoon Ypo, seen, forming streams Ca'añabé, Aguai'y.
In the summer, the maximum temperature reached is 39 °C and the minimum in winter is 2 °C. The average annual temperature is 21 °C.
Districts
The department is divided into 17 districts:
Media and pathways
Previously, the main channel of communication was the rail Carlos Antonio López and the route I Mcal. Lopez has branches that extend into the cities of Piribebuy, Carapegua-Ybycuí, Caapucú-Mbuyapey and Mbuyapey-Ybycui. Currently, the railroad has stopped working.
Paraguarí has airstrips for small air machines.
As for the media radio, there are amplitude modulation stations such as Radio FM and 1000, radio Ybyty Rok, Pan American, Yaguarón, Oda, Mensajera, and Carapeguá Colmenar.
Economy
This department is rich in livestock production. Its inhabitants are principally engaged in raising cattle and pigs, on a smaller scale are breeding sheep, horses and goats.
Poultry production also occupies an important place in production, are raised chickens, geese, turkeys and guineas.
Agricultural production plays a less important and is geared primarily to supply its own inhabitants. The department has crops of rice, corn, onion, sweet orange, banana, sweet potato, sour orange, beans, tomatoes, pineapple, grapefruit, grapes, peas and potatoes.
The industries that are in Paraguarí are: sugar mill, cotton spinning mills, dairies, distilleries and sugar cane alcohol fuel.
Among the crafts, Carapeguá stands out with the production of a fabric called poyvi, also occurs ao po'i, encaje ju, hammocks and others.
Tourism

This department has places marked by a long history. The temple Yaguarón's altar was carved by hand by the Indians in 1775.
Their nature is very broad and has attractions such as Lake Ypoá and its tributaries, the numerous hills that allow the realization of adventure tourism, including the hill Yaguarón located at 180 meters. Above sea level. This hill is peculiarly marked by footprints imprinted in the rocks. The popular belief attributed the footsteps of St. Thomas in its passage through these lands.
It is also the Acahay hill with 672 meters which was declared Natural Monument and consists of an ancient volcano off.
The Eco Reserve Mbatoví is located in this department. This space has adventure tourism programs and is located at the foot of the hill of the same name.
The Museum Dr. Gaspar Rodriguez de Francia has an exhibition of objects belonging to proceed.
Getting there
Based on the country's capital, Asuncion, it should take Route I Mcal. Lopez, at approximately 51 km (from Asunción) is the city of Yaguarón. The capital of the department, Paraguarí, lies at an altitude of 66 meters.
From Asuncion, numerous public transport depart from the main bus terminal due to the capital of the department of Paraguarí with an affordable price.
See also
- List of high schools in Paraguarí
References
Bibliography
- Geography of Paraguay - Editorial Hispanic Paraguay SRL-1a. Edition 1999 - Asuncion Paraguay
- Geography of Paraguay Illustrated - ISBN 99925-68-04-6 - Distributed Arami SRL
- The Magic of our land. Alliance Foundation. Asuncion. 2007.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Paraguarí Department. |