Oiapoque
Oiapoque (Portuguese pronunciation: [ɔjɐˈpɔki]) is a municipality in the north of the state of Amapá, Brazil. Its population is 27,906[3] and its area is 22,625 square kilometres (8,736 sq mi).[4] Oiapoque is also a major river in the same state, forming the international border with French Guiana. The Oyapock River Bridge, connecting the village with Saint-Georges in French Guiana, was completed in 2011 but not opened to pedestrian or vehicle traffic until 2017.[5]
Oiapoque | |
|---|---|
| Município de Oiapoque | |
 A street in Oiapoque. | |
 Flag  Seal | |
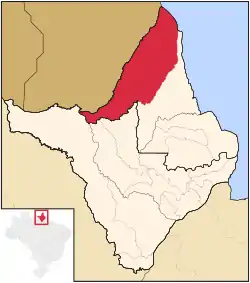 Location of Oiapoque in the State of Amapá | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 03°50′34″N 51°50′06″W | |
| Country | |
| Region | North |
| State | |
| Founded | 1945 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Maria Orlana (PSDB) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 22,625 km2 (8,736 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 3 m (10 ft) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 27,906 |
| • Density | 0.85/km2 (2.2/sq mi) |
| [1] | |
| Time zone | UTC-3 (UTC-3) |
| HDI (2000) | 0.738 – medium[2] |
| Website | oiapoque.com.br |
Lying on the northern coast of Brazil, Oiapoque is popularly considered the northernmost point of Brazil. The phrase do Oiapoque ao Chuí ("from Oiapoque to Chuí") means "all of Brazil."[6] However, there are more northerly points in Roraima state such as the municipality of Uiramutã. Oiapoque remains the northernmost coastal city of Brazil, and the northernmost city of Amapá. It occupies more than half of the north border of the state.
Early history
The Oiapoque River is said to have been found by Vicente Yáñez Pinzón in the first years of the 16th century. It has been called Japoc, Yapoc, Iapoco, and even Vicente Pinzón River. The name Oiapoque was officially used from 1900, when a territorial dispute between Brazil and France was resolved through Swiss diplomatic arbitration.
Clevelândia
At the beginning of the 20th century, the village of Oiapoque hosted a political and criminal concentration camp called Clevelândia. In 1922 an agricultural outpost called the Núcleo Colonial Cleveland was transformed into a camp during the presidency of Arthur Bernardes (1922–1926). Many Brazilian anarchist militants were sentenced to hard labour here. Of the 946 prisoners interned at Clevelândia between 1924 and 1927, 491 died. Many of the survivors returned to São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro permanently sickened with malaria.[7]
Geography
Oiapoque is bordered to the west by its long frontier with French Guiana. It is bordered to the north by the Atlantic Ocean. On its eastern and southern sides it borders the municipalities of Calçoene, Serra do Navio, Pedra Branca do Amapari, and Laranjal do Jari.[4] The municipality contains 24.15% of the 2,369,400 hectares (5,855,000 acres) Amapá State Forest, a sustainable use conservation unit established in 2006.[8]
Climate
Oiapoque has a tropical monsoon climate (Am) with moderate to little rainfall from August to November and heavy to very heavy rainfall in the remaining months.
| Climate data for Oiapoque | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 29.2 (84.6) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.8 (85.6) |
29.3 (84.7) |
29.5 (85.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
31.0 (87.8) |
31.9 (89.4) |
32.6 (90.7) |
33.0 (91.4) |
32.3 (90.1) |
30.3 (86.5) |
30.6 (87.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 25.4 (77.7) |
25.0 (77.0) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.8 (78.4) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.0 (78.8) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.3 (79.3) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.9 (78.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 21.6 (70.9) |
21.5 (70.7) |
21.6 (70.9) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
21.6 (70.9) |
21.0 (69.8) |
20.9 (69.6) |
20.5 (68.9) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.4 (68.7) |
21.2 (70.2) |
21.2 (70.2) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 395 (15.6) |
345 (13.6) |
396 (15.6) |
450 (17.7) |
537 (21.1) |
370 (14.6) |
193 (7.6) |
102 (4.0) |
48 (1.9) |
44 (1.7) |
116 (4.6) |
313 (12.3) |
3,309 (130.3) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[9] | |||||||||||||
References
- ESTIMATIVAS DAS POPULAÇÕES RESIDENTES, EM 1o DE JULHO DE 2008, SEGUNDO OS MUNICÍPIOS
- Archived 2013-06-26 at WebCite UNDP
- IBGE 2020
- "Oiapoque". Macapá: Amapá Digital. 2003. Retrieved 2014-12-04.
- Pacheco, John (2014). "Tráfego na ponte binacional em Oiapoque terá limitação de horários" (in Portuguese). G1 Amapá. Retrieved 2014-12-04.
- Pacheco, John (2014). "Oiapoque/Brazil". Lonely Planet. Archived from the original on 2014-12-08. Retrieved 2014-12-04.
- Romani, Carlo. "Clevelândia (Oiapoque): colônia penal ou campo de concentração?". Verve: revista semestral autogestionária do Nu-Sol (in Portuguese). Núcleo de Sociabilidade Libertária do Programa de Estudos Pós-Graduados em Ciências Sociais da PUC-SP. 2003 (3): 112–130. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- FES do Amapá (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-07-06
- "Climate: Oiapoque". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved August 14, 2020.