Negro National League (1933–1948)
The second Negro National League, founded in 1933 by businessman Gus Greenlee of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, was one of the several Negro leagues created during the time when professional organized baseball was segregated.
| Sport | Negro league baseball |
|---|---|
| Inaugural season | 1933 |
| Ceased | 1948 |
| No. of teams | ~18 |
| Country | United States |
| Most titles | Homestead Grays (10) |
| Classification | Major league |
League history
The second Negro National League was established in 1933 by Gus Greenlee, an African-American businessman of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, two years after the first Negro National League (NNL) had disbanded, after the start of the Great Depression.[1] The second NNL lasted until 1948, the year after Major League Baseball integrated. After that, its surviving teams merged into the Negro American League.[2]
Negro National League franchises
- Annual final standings: 1933, 1934, 1935, 1936, 1937, 1938, 1939, 1940, 1941, 1942, 1943, 1944, 1945, 1946, 1947, 1948
- Baltimore Black Sox (I) (1933)
- Brooklyn Royal Giants (1933)
- Cole's American Giants (1933–1935)
- Columbus Blue Birds / Akron Black Tyrites / Cleveland Giants (1933) – moved during season
- Indianapolis ABC's (II) / Detroit Stars (II) (1933) – moved to Detroit in April
- Nashville Elite Giants (1933–1934) / Columbus Elite Giants (1935) / Washington Elite Giants (1936–1937) / Baltimore Elite Giants (1938–1948)
- Pittsburgh Crawfords (1933–1938)
- Philadelphia Bacharach Giants (1934)
- Cleveland Red Sox (1934)
- Baltimore Black Sox (II) (1934)
- (Washington) Homestead Grays (1934–1948)
- †Newark Dodgers (1934–1935) / Newark Eagles (1936–1948)
- Philadelphia Stars (1934–1948)
- †Brooklyn Eagles (1935)
- New York Cubans (1935–1936; 1939–1948)
- New York Black Yankees (1936–1948)
- Washington Black Senators (1938)
†The Brooklyn Eagles and Newark Dodgers merged to form the Newark Eagles in 1936.
Member timeline
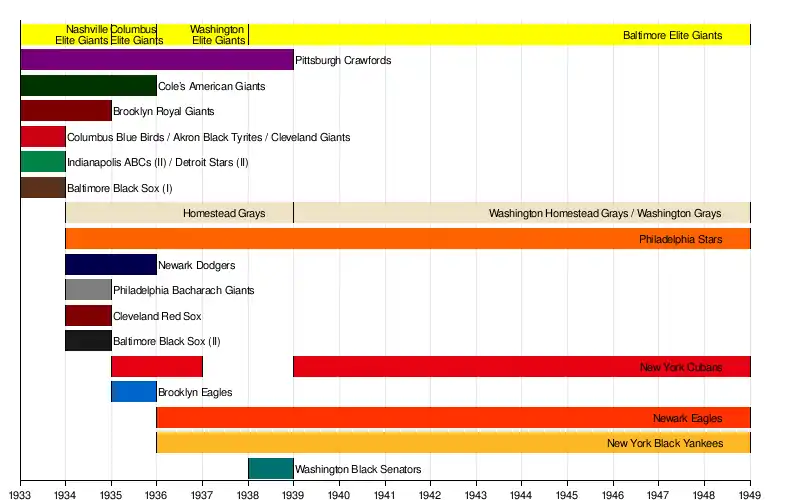
- 1933: Formation of NNL2 consisting of 7 teams — Baltimore Black Sox, Cole's American Giants, Columbus Blue Birds, Indianapolis ABCs (II) (moved to Detroit in April), Homestead Grays, Nashville Elite Giants and Pittsburgh Crawfords; Homestead was expelled early in the season for raiding Detroit's roster, Columbus was replaced mid-season by the Akron Black Tyrites who were then replaced by the Cleveland Giants.
- 1934: Dropped Cleveland Giants, Detroit Stars, Baltimore Black Sox (I); Added Philadelphia Bacharach Giants, Cleveland Red Sox, Philadelphia Stars and Baltimore Black Sox (II); Retained Homestead Grays as an associate team.
- 1935: Dropped Philadelphia Bacharach Giants, Baltimore Black Sox (II) and Cleveland Red Sox; Added Brooklyn Eagles, Homestead Grays, New York Cubans and Newark Dodgers.
- 1936: Dropped Cole's American Giants; Brooklyn and Newark merged.
- 1937: Dropped New York Cubans; Added New York Black Yankees.
- 1938: Added Washington Black Senators.
- 1939: Dropped Pittsburgh Crawfords and Washington Black Senators; Re-added New York Cubans.
- 1948: League disbanded after completion of season; All teams continued on with Baltimore, Philadelphia, Newark and New York Cubans joining the Negro American League for the 1949 season, while the Grays and Black Yankees playing independent of a league.
League champions
Pennant winners
From 1937 and 1938, 1940, and 1942 through 1946, the team in first place at the end of the season was declared the Pennant winner. Due to the unorthodox nature of the schedule (and little incentive to enforce it), some teams frequently played many more games than others did in any given season. This led to some disputed championships and two teams claiming the title. Generally, the team with the best winning percentage (with some minimum number of games played) was awarded the Pennant, but other times it was the team with the most victories. The "games behind" method of recording standings was uncommon in most black leagues.
- 1933 – Cole's Chicago American Giants (first half), Pittsburgh Crawfords (second half with better overall)†
- 1934 – Philadelphia Stars† won best half of season however Crawfords with better whole season record disputed title.
- 1935 – Pittsburgh Crawfords†
- 1936 – Pittsburgh Crawfords†
- 1937 – Homestead Grays
- 1938 – Homestead Grays
- 1939 – Baltimore Elite Giants*
- 1940 – Washington Homestead Grays
- 1941 – Washington Homestead Grays†
- 1942 – Washington Homestead Grays‡
- 1943 – Washington Homestead Grays‡
- 1944 – Washington Homestead Grays‡
- 1945 – Washington Homestead Grays‡
- 1946 – Newark Eagles‡
- 1947 – New York Cubans†‡
- 1948 – Washington Homestead Grays†‡
† – Pennant was decided via a split-season schedule with the winner of the first half of the season playing the winner of the second half of the season.
* – Pennant was decided via a 2-round play-off between the top four teams.
‡ – Pennant winner went on to play in the Negro World Series.
League play-offs
From 1925 through 1928, and again in 1930, the NNL split the season into two halves. The winner of the first half played the winner of the second half for the league Pennant. As mentioned above, disputes also occurred in the split season finishes.
- 1933 – Cole's American Giants (first half champions) tied Pittsburgh Crawfords (second half champions), 1 tie game
- 1934 – Philadelphia Stars (2nd half) beat Chicago American Giants (1st half), 4 games to 3 games, 1 tie
- 1935 – Pittsburgh Crawfords (1st half) beat New York Cubans (2nd half), 5 games to 2 games
- 1936 – Pittsburgh Crawfords (2nd half) over Washington Elite Giants (1st half), declared – no games played
- 1939 – 1st round: Washington Homestead Grays (1st place) beat Philadelphia Stars (4th place), 3 games to 2 games
- 1st round: Baltimore Elite Giants (3rd place) beat Newark Eagles (2nd place), 3 games to 1 game
- 2nd round: Baltimore Elite Giants (3rd place) beat Washington Homestead Grays, 3 games to 1 game, 1 tie
- 1941 – Washington Homestead Grays (1st half) beat New York Cubans (2nd half), 2 games to 0 games
- 1947 – New York Cubans (2nd half) over Newark Eagles (1st half)
- 1948 – Washington Homestead Grays (2nd half) over Baltimore Elite Giants (1st half)
Negro World Series
For the duration of the league, a Negro World Series took place seven times, from 1942 through 1948. The NNL Pennant winner met the champion of the rival Negro American League. Five out of the seven years, the Negro National League team (below in bold) prevailed.
- 1942 – Kansas City Monarchs beat Washington Homestead Grays, 4 games to 0 games
- 1943 – Washington Homestead Grays beat Birmingham Black Barons, 4 games to 3 games
- 1944 – Washington Homestead Grays beat Birmingham Black Barons, 4 games to 1 game
- 1945 – Cleveland Buckeyes beat Washington Homestead Grays, 4 games to 0 games
- 1946 – Newark Eagles beat Kansas City Monarchs, 4 games to 3 games
- 1947 – New York Cubans beat Cleveland Buckeyes, 4 games to 1 game
- 1948 – Washington Homestead Grays beat Birmingham Black Barons, 4 games to 1 game
References
- "Negro League Baseball Players Association: History" "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-12-20. Retrieved 2008-01-01.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). Accessed 9 February 2012.
- "Negro League History 101" http://www.negroleaguebaseball.com/history101.html. Accessed 9 February 2012.
Sources
- Holway, John B. (2001), The Complete Book of Baseball's Negro Leagues: The Other Half of Baseball History, Fern Park, Florida: Hastings House, ISBN 0-8038-2007-0