Mazara del Vallo
Mazara del Vallo (Italian pronunciation: [madˈdzaːra del ˈvallo]; Sicilian: Mazzara) is a town and comune in the province of Trapani, southwestern Sicily, Italy. It lies mainly on the left bank at the mouth of the Mazaro river.
Mazara del Vallo
Mazzara | |
|---|---|
| Città di Mazara del Vallo | |
 Church of San Nicolò Regale. | |
 Coat of arms | |
.svg.png.webp) Mazara within the Province of Trapani | |
Location of Mazara del Vallo 
| |
 Mazara del Vallo Location of Mazara del Vallo in Italy 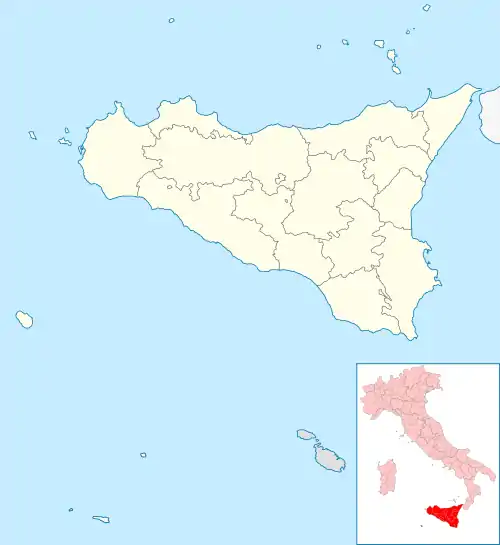 Mazara del Vallo Mazara del Vallo (Sicily) | |
| Coordinates: 37°39′N 12°35′E | |
| Country | Italy |
| Region | Sicily |
| Province | Trapani (TP) |
| Frazioni | Borgata Costiera, Mazara Due |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Salvatore Quinci (Civic list) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 275 km2 (106 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 8 m (26 ft) |
| Population (31 October 2017)[2] | |
| • Total | 51,534 |
| • Density | 190/km2 (490/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Mazaresi |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 91026 |
| Dialing code | 0923 |
| Patron saint | St. Vitus |
| Saint day | June 15 |
| Website | Official website |
It is an agricultural and fishing centre and its port gives shelter to the largest fishing fleet in Italy. Recently it has been a hotspot for migrants from North Africa which has led to controversy and crime increase.
History
Etymology and origins
Mazara was founded by the Phoenicians in the 9th century BC, with the name of Mazar (Tombstone). It then passed under the control of Greeks, Carthaginians, Romans, Vandals, Ostrogoths, Byzantines, before being occupied by the Arabs in the year 827 AD. During the Arab period, Sicily was divided into three different administrative regions, Val di Noto, Val Demone and Val di Mazara, making the city an important commercial harbour and centre of learning. The city centre, known as the Kasbah, retains Arab architectural influences.
In 1072, Mazara was conquered by Normans, headed by Roger I. During that period, in 1093, the Roman Catholic Diocese of Mazara del Vallo was instituted.
After the death of Emperor Frederick II, Sicily passed to the Angevins, then followed by the Spaniards of Aragon. The Aragon period (1282–1409) is characterized by a political, economic and demographic decline of Mazara. The city passed under the control of the House of Savoy in 1713, a reign which lasted only five years, being replaced by the Habsburg Empire (for 16 years) followed by the Bourbons. In 1860 the city was finally conquered by Giuseppe Garibaldi and the Mille, thus joining the then newly formed Kingdom of Italy.
The city was known as Mazzara del Vallo until the World War II period, following which the spelling was changed to Mazara del Vallo.
Today
Today Mazara is widely considered to be one of the most important fishing centres of Italy; tussles about fishing rights, especially with the North-African countries, figure large in the town's recent history, boat sequestrations being a common event. Currently the fishing business in the city seems to be withering, mainly because of the increasing lack of people willing to work on boats.
Mazara del Vallo is among the Italian cities with the highest percentages of immigrants; it is estimated that the city hosts at least 3,500 registered immigrants, mainly from nearby Tunisia but also the other countries of the Maghreb. They tend to live principally around the old Arab city centre (the Casbah). There exists a local school, managed by the Tunisian government, at which only Arabic and French are taught as languages. This has led to some controversy. Most of the local schools show openness to Arab culture, even providing Arabic language classes for both Italians and Arabs, and encouraging integration with the autochthonous students. The local city council also provides a seat reserved for a representative of Mazara's immigrant community.
Geography
Mazara borders with the municipalities of Campobello di Mazara, Castelvetrano, Marsala, Petrosino, and Salemi.[3] It counts the hamlets (frazioni) of Borgata Costiera and Mazara Due.
Main sights

Mazara made national news in March 1998, when a bronze statue called the Dancing Satyr (Satiro Danzante) was found off the port, at a depth of 500 metres (1,600 ft) in the Strait of Sicily by a local fishing boat. The statue is believed to have been sculpted by Greek artist Praxiteles and is now on display to the public in a dedicated museum in the city, after having been on show at the Chamber of Deputies of Rome, and in Aichi, Japan. After this event, the city quickly gained in terms of visiting tourists and a national advertising campaign was mounted with the slogan Mazara del Satiro.
Other attractions include the Norman Arc, that is the remains of the old Norman Castle built in 1073 and demolished in 1880, and a number of churches, including the Royal Saint Nicholas (San Nicolò Regale) Church, a rare example of Norman architecture built in 1124, the Seminary, built in 1710, which surrounds the main local piazza, Piazza della Repubblica, and St. Vitus on the Sea (San Vito a Mare) Church. In honour of St. Vitus, the official patronal saint as well as a native of Mazara del Vallo, the St. Vitus Feast (Lu Fistinu di Santu Vitu) is held every year.
Transportation
Mazara del Vallo is connected to the rest of Sicily by a regional train service (run by Trenitalia), a private bus service (only to Palermo), and by car, via the A29 highway (also known as Palermo-Mazara del Vallo). It is reachable from Trapani-Birgi Airport by an infrequent bus service or by taxi (€20 per person) and from Palermo by car or taxi.
During the summer period, Mazara is also connected via ferry to the island of Pantelleria and Hammamet, in Tunisia.
International relations
See also
References
- "Superficie di Comuni Province e Regioni italiane al 9 ottobre 2011". Istat. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- "Popolazione Residente al 1° Gennaio 2018". Istat. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- 39318 Mazara del Vallo on OpenStreetMap
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Mazzara del Vallo. |
 Mazara del Vallo travel guide from Wikivoyage
Mazara del Vallo travel guide from Wikivoyage- Official website