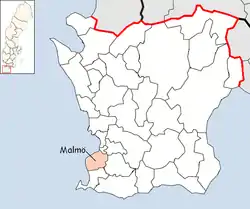
Malmö Municipality
Malmö Municipality (Swedish: Malmö kommun), or City of Malmö (Malmö stad), is a Swedish municipality in Skåne County, the southernmost of the counties of Sweden (and conterminous with the historical province (landskap) of Skåne).
Malmö Municipality | |
|---|---|
| Malmö kommun Malmö stad | |
.jpg.webp) Municipal building | |
 Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 55°35′N 13°2′E | |
| Country | Sweden |
| County | Skåne County |
| Seat | Malmö |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Katrin Stjernfeldt Jammeh (S) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 332.64 km2 (128.43 sq mi) |
| • Land | 156.87 km2 (60.57 sq mi) |
| • Water | 175.77 km2 (67.87 sq mi) |
| Area as of 1 January 2014. | |
| Population (31 December 2019)[2] | |
| • Total | 344,166 |
| • Density | 1,000/km2 (2,700/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | SE |
| Province | Skåne |
| Municipal code | 1280 |
| Website | www.malmo.se |
When the first Swedish local government acts were implemented in 1863, the Old City of Malmö was made one of the country's 88 city municipalities and the first city council was elected. The municipal territory has been augmented through mergers in 1911, 1915, 1931, 1935, 1952, 1967 and finally in 1971.

In 1971, the city was also converted into a municipality of unitary type, like all others in Sweden. Malmö Municipality, however, styles itself Malmö stad (City of Malmö) in all cases when it is legally possible. This is a decision taken by the municipal assembly. It is purely nominal and has no effect on the legal status of the municipality.
Localities
As of 2015, there were six urban areas (tätort or locality) and six smaller settlements (småorter) in the municipality.[3]
The localities are listed in the table according to the size of the population in 2018.[4] Note that a small part of Malmö (Arlöv) is situated in Burlöv Municipality.
| # | Locality | Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Malmö | 316,588 |
| 2 | Bunkeflostrand | 13,561 |
| 3 | Oxie | 13,165 |
| 4 | Tygelsjö | 3,455 |
| 5 | Vintrie | 803 |
| 6 | Skumparp | 253 |
City districts
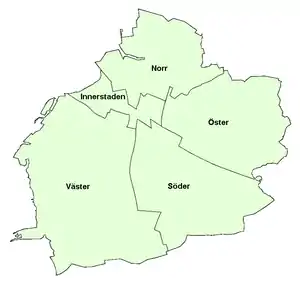
After a reform on 1 July 2013, Malmö Municipality is divided into five city districts (Swedish: stadsområde).[5][6] They manage public kindergartens, schools, and geriatric care within their geographical areas, and provide funds for local cultural and recreational activities.
There are 136 neighbourhoods.[7]
| Inhabitants as of 1 January 2013[8] | |
| Väster | 75,600 |
| Innerstaden | 67,900 |
| Norr | 62,100 |
| Söder | 56,300 |
| Öster | 44,300 |
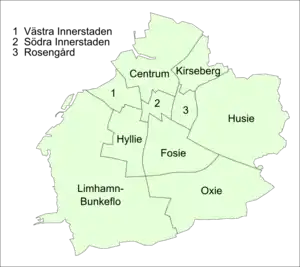
Before the reform on July 2013, Malmö Municipality was divided into ten city districts (Swedish: stadsdel) after the 1996 City District Reform (Swedish: stadsdelsreformen).
| City district | Population[9] | Area (hectare)[10] |
Density (people/km²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrum | 47,171 | 1,757 | 2,685 |
| Fosie | 43,889 | 1,243 | 3,531 |
| Limhamn-Bunkeflo | 42,646 | 5,147 | 829 |
| Södra Innerstaden | 34,671 | 302 | 11,480 |
| Västra Innerstaden | 33,191 | 465 | 7,138 |
| Hyllie | 32,998 | 901 | 3,662 |
| Rosengård | 23,563 | 332 | 7,097 |
| Husie | 20,769 | 2,948 | 705 |
| Kirseberg | 14,959 | 640 | 2,337 |
| Oxie | 12,453 | 2,306 | 540 |

Local government
The municipal legislative body of the municipality is the 61-member municipal assembly (kommunfullmäktige), elected by proportional representation for a four-year term. The assembly appoints the municipality's main governing bodies, the 11-member executive committee (kommunstyrelsen) and the 8 governing commissioners. The executive committee and the commissioners are headed by a municipal commissioner (kommunstyrelsens ordförande) or "mayor". The mayor is Katrin Stjernfeldt Jammeh of the Social Democratic Party.[11]
There are seven political parties represented in the council elected in 2018: Social Democratic Party (20 seats), Moderate Party (13), Sweden Democrats (11), Left Party (7), Liberals (4), Green Party (3) and Centre Party (3).[12]
International cooperation
Twin towns — Sister cities
As of 2019, Malmö has town twinning treaties or treaties of co-operation signed with 11 cities. Of these, cooperation is closest with Newcastle and Tallinn. The complete list of cities is the following (twinning year in parenthesis):[13]
 Vaasa (1940)
Vaasa (1940) Tangshan (1987)
Tangshan (1987) Varna (1987)
Varna (1987).svg.png.webp) Port Adelaide (1988)
Port Adelaide (1988) Florence (1989)
Florence (1989) Tallinn (1989)
Tallinn (1989) Szczecin (1990)
Szczecin (1990) Stralsund (1991)
Stralsund (1991) Province of Chieti co-operation treaty signed in 2001
Province of Chieti co-operation treaty signed in 2001 Newcastle co-operation treaty signed in 2003
Newcastle co-operation treaty signed in 2003 Kaliningrad co-operation treaty
Kaliningrad co-operation treaty
See also
References
- "Statistiska centralbyrån, Kommunarealer den 1 januari 2014" (in Swedish). Statistics Sweden. 2014-01-01. Archived from the original (Microsoft Excel) on 2016-09-27. Retrieved 2014-04-18.
- "Folkmängd i riket, län och kommuner 31 december 2019" (in Swedish). Statistics Sweden. February 20, 2020. Retrieved February 20, 2020.
- "Antal områden efter region, typ av område och vart 5:e år". Statistics Sweden (in Swedish). Retrieved 2019-07-23.
- "Folkmängd per tätort efter region och vart 5:e år" (in Swedish). Statistics Sweden. Retrieved 2019-07-23.
- "Nystart för ett bättre Malmö". Malmö Municipality (in Swedish). 27 June 2013. Archived from the original on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 17 January 2014.
- "Malmös karta har ritats om". Sydsvenskan (in Swedish). 1 July 2013. Retrieved 17 January 2014.
- "Befolkning per stadsområde, stadsdel, delområde 2007-2014". Malmö Municipality (in Swedish). 13 April 2015. Archived from the original on 2015-11-26. Retrieved 2015-11-26.
- "Malmö in brief" (PDF). Malmö Municipality. December 2013. Retrieved 17 January 2014.
- "Befolkningsbokslut Malmö 2012" (PDF). Malmö Municipality (in Swedish). 17 June 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- "Blad1 (Areal)". Malmö Municipality (in Swedish). Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- Source: Malmö City Council Archived 2007-09-29 at the Wayback Machine
- "Val till kommunfullmäktige i Malmö - Valda" (in Swedish). Valmyndigheten. 2018-09-19.
- "Vänorter" (in Swedish). Malmö stad. Retrieved 2019-07-22.