Hurricane Allison (1995)
Hurricane Allison was the first named storm and first hurricane of the 1995 Atlantic hurricane season. It was an early season hurricane that delivered heavy rains and caused minor damage, primarily across Cuba, Florida and Georgia.
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS/NWS) | |
 Hurricane Allison at peak intensity in the Gulf of Mexico on June 4 | |
| Formed | June 2, 1995 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | June 11, 1995 |
| (Extratropical after June 6, 1995) | |
| Highest winds | 1-minute sustained: 75 mph (120 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 987 mbar (hPa); 29.15 inHg |
| Fatalities | 1 direct |
| Damage | $1.7 million (1995 USD) |
| Areas affected | Yucatán Peninsula, western Cuba, Florida, Georgia, Carolinas, Atlantic Canada |
| Part of the 1995 Atlantic hurricane season | |
The storm developed on June 2, less than 48 hours after the official start of the hurricane season. It strengthened into a tropical storm early on June 3 and into a hurricane on June 4 in the Gulf of Mexico. It would make landfall in the Big Bend area of Florida on June 5 before tracking northward as an extratropical system. One death was reported in Cuba. Allison's early formation heralded the start of what would eventually become a very active 1995 hurricane season.
Meteorological history
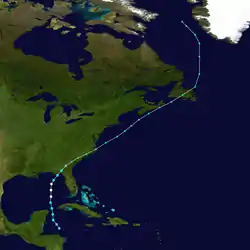
The origins of the system can be traced to a tropical wave that moved across the eastern Caribbean in the last week of May. The wave gradually organized itself as it entered the western Caribbean Sea on June 1. The circulation continued to close up on June 2 and that evening it was declared Tropical Depression One while east of Honduras.[1]
The depression was in an unusually low-shear environment for early June as it began tracking northward,[2] which allowed the system to strengthen into Tropical Storm Allison on the morning of June 3 as it tracked into the Yucatán Channel. Despite the fact that westerly wind shear began to increase, the warm water allowed Allison to gradually strengthen more that afternoon and evening.[3] Late that evening, while between the Yucatán Peninsula and Cuba, Allison developed a circular central dense overcast and became a high-end tropical storm.[4] As the storm emerged into the Gulf of Mexico, the warm waters allowed Allison to strengthen further and it was upgraded to a hurricane on the morning of June 4 while travelling almost due north.[1]
Allison remained somewhat disorganized, as no eye was visible, even when Reconnaissance flights confirmed that it was at hurricane intensity.[5] The storm maintained itself as a minimal hurricane throughout the day on June 4 before it began to turn to the northeast, in response to southwesterly shear. Late that evening, the storm began to weaken, dropping back to tropical storm intensity as it approached the Florida Big Bend area. The intensity leveled off on June 5 until it made landfall that morning. Allison made its first landfall at about 10:00 am EDT (1400 UTC) near Alligator Point, Florida as a high-end tropical storm with 70 mph (110 km/h) winds. It briefly re-emerged over Apalachee Bay and made another landfall near St. Marks, Florida about one hour later with 65 mph (100 km/h) winds.[1] Operationally, Allison was considered a hurricane until it made landfall,[6] and was considered the earliest hurricane landfall in the United States for some time.[7]
After making its final Florida landfall, Allison rapidly weakened. Tropical storm force winds continued over the eastern Florida Panhandle until late that afternoon, as the storm moved northward into Georgia. It weakened to a tropical depression on the evening of June 5 over southern Georgia.[1] Early on June 6, Allison began to transition into an extratropical storm as it interacted with a warm front to the northeast while tracking across the Carolinas.[1] The remnant low emerged into the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Cape Hatteras that evening. It then raced across the western Atlantic, crossing the easternmost part of Nova Scotia on June 8 and Newfoundland on June 9. It continued northward across the Labrador Sea, dissipating on June 11.[1]
Preparations
In anticipation of Allison, tropical cyclone warnings and watches were issued in Cuba, Mexico, and Florida. At 09:00 UTC on June 3, the government of Cuba issued a tropical storm warning for the extreme western portions of the country.[8] Six hours later, the Mexican government issued a tropical storm warning from Felipe Carrillo Puerto, Quintana Roo, to Tizimín, Yucatán.[9] As Allison moved northward, watches and warnings were posted in Florida, beginning with a tropical storm warning for Dry Tortugas at 21:00 UTC on June 3.[10] At 09:00 UTC on the following day, the National Hurricane Center issued a tropical storm watch from Anclote Key to Pensacola.[11] The tropical storm watch was upgraded to a hurricane warning six hours later, simultaneous to a new tropical storm warning being issued from south of Anclote Key to Bonita Beach.[12]
On June 4, Florida governor Lawton Chiles declared a state of emergency for northern and central Gulf Coast counties of the state.[13] Mandatory evacuations were ordered for portions of Citrus,[14] Franklin, Jefferson, Liberty, Taylor, and Wakulla counties.[13] Approximately 2,700 people evacuated from the Gulf Coast of Florida. Although no mandatory evacuation was issued in Bay County, 555 people sought shelter anyway.[14] Throughout the Big Bend region of Florida, several county offices, courthouses, schools, and universities – including Florida A&M University, Florida State University, and Tallahassee Community College – closed for at least a partial or full day on June 5.[15]
Impact
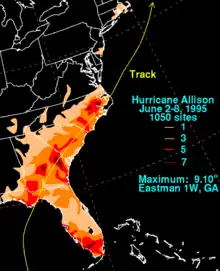
Winds to tropical storm-force were reported throughout the western part of Cuba, with a peak gust of 64 mph (102 km/h) in Havana. Heavy rainfall of up to 18 inches (450 mm) was also reported in the area.[1] 32 houses were damaged or destroyed due to flooding that resulted. One person was killed in western Cuba and three others were injured. The overall economic loss as a result of the storm was reported to be fairly minor.[16]
In Florida, Allison's dangerous winds knocked down power lines, leaving 48,000 residents without power and/or telephone services. Along the 150-mile (240 km) stretch of Florida's Big Bend, 65 seaside homes were flooded and there was extensive beach erosion as a result of the storm surge. Three hotels and a restaurant were damaged. In Apalachicola, three fishing boats were swamped; the storm closed a bridge linking Apalachicola with St. George Island. The highest storm surge in Florida was about 6 to 8 feet (1.8 to 2.5 m) in Wakulla and Dixie Counties, and 2 to 6 feet (0.6 to 1.8 m) to the east.[17] A tornado spawned by Allison touched down at Jacksonville Beach, causing minor damage when it downed power lines and flipped over vehicles. Minor crop damage was also reported. There were no deaths reported as a result of Allison in Florida. Damage was estimated at $860,000 in Florida, primarily as a result of the storm surge.[1]
Most of the damage in Georgia was as a result of several tornadoes related to Allison. The most significant of the tornadoes touched down in the town of St. Marys. An elementary school was destroyed and significant damage was also reported to several buildings at the Kings Bay Naval Submarine Base. Several other tornadoes also touched down but damage from them was minimal. Damage from the tornado was estimated at $800,000 (1995 USD).[1]
The remnants of Allison brought rainfall and elevated wind speeds to much of Atlantic Canada. The highest rainfall totals occurred in western Newfoundland, including a peak total of 5.2 inches (133 mm). Winds peaked at just under 42 mph (68 km/h) in Bonavista, while gusts reached just over 55 mph (89 km/h) at the same location. Little damage occurred in Canada.[18]
See also
References
- Richard Pasch (1996-01-26). "Preliminary Report: Hurricane Allison" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2016-11-29.
- Miles Lawrence (1995-06-02). "Tropical Depression One Discussion #1". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-11-15.
- Edward Rappaport (1995-06-03). "Tropical Storm Allison Discussion #4". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-11-15.
- Miles Lawrence (1995-06-04). "Tropical Storm Allison Discussion #6". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-11-15.
- Richard Pasch (1995-06-05). "Hurricane Allison Discussion #10". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-11-15.
- Lixion Avila (1995-06-05). "Hurricane Allison Advisory 1A". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2011-11-15.
- Steve Stone (1995-11-27). "Hampton Roads Escaped Unscathed in Busiest Hurricane Season Since 1933..." Virginian-Pilot. Archived from the original on 2004-12-23. Retrieved 2006-12-08.
- Lixon Avila (1995-06-03). "Tropical Depression One Advisory Number 3". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2019-11-21.
- Edward Rappaport (1995-06-03). "Tropical Storm Allison Advisory Number 4". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2019-11-21.
- Edward Rappaport (1995-06-03). "Tropical Storm Allison Advisory Number 5". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2019-11-21.
- Max Mayfield (1995-06-04). "Tropical Storm Allison Advisory Number 7". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2019-11-21.
- Max Mayfield (1995-06-04). "Hurricane Allison Advisory Number 8". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2019-11-21.
- "Hurricane Allison bears down on the Panhandle". Florida Today. Associated Press. 1995-06-05. p. 2A. Retrieved 2019-11-21 – via Newspapers.com.

- Chuck Murphy; Monica Davey; Amy Ellis; Lucy Morgan; Diane Rado; Jim Ross (1995-06-06). "Allison". Tampa Bay Times. p. 4A. Retrieved 2019-11-21 – via Newspapers.com.

- "What's Closed Today". Tallahassee Democrat. 1995-06-05. p. 1A. Retrieved 2019-11-21 – via Newspapers.com.

- http://www.11alive.com/weather/hurricane/hurricane_article.asp?storyid=34119%5B%5D
- National Climatic Data Center (1995). "NCDC: Event Details". NOAA. Retrieved 2006-12-19.
- "1995-Allison". Environment Canada. 2010-09-14. Archived from the original on 2018-11-18. Retrieved 2019-11-17.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hurricane Allison (1995). |
