General Carrera Lake
General Carrera Lake (Chilean part, officially renamed in 1959)[2] or Lake Buenos Aires (Argentine part) is a lake located in Patagonia and shared by Argentina and Chile. Both names are internationally accepted.
| General Carrera Lake | |
|---|---|
| Buenos Aires Lake Lake Buenos Aires | |
 | |
General Carrera Lake in the Aysén Region | |
 General Carrera Lake | |
| Location | Lago Buenos Aires Department, Santa Cruz Province, Argentina / General Carrera Province, Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region, Chile, in Patagonia |
| Coordinates | 46°26′15″S 71°42′54″W[1] |
| Type | Moraine dammed |
| Primary inflows | Soler, Los Antiguos, Jeinemeni, Ibáñez, San Martín, Delta |
| Primary outflows | Bertrand Lake and then Baker River (Pacific Ocean) Deseado River (Atlantic Ocean) |
| Basin countries | Argentina, Chile |
| Surface area | 1,850 km2 (710 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 586 m (1,923 ft) |
| Surface elevation | 217 m (712 ft) |
| Settlements | Chile Chico, Puerto Ingeniero Ibáñez, Puerto Guadal, Los Antiguos |
| References | [1] |
The lake is of glacial origin and is surrounded by the Andes mountain range. The lake drains to the Pacific Ocean on the west through the Baker River.
The weather in this area of Chile and Argentina is generally cold and humid. But the lake itself has a sunny microclimate, a weather pattern enjoyed by the few settlements along the lake, such as Puerto Guadal, Fachinal, Mallín Grande, Puerto Murta, Puerto Río Tranquilo, Puerto Sánchez, Puerto Ingeniero Ibáñez and Chile Chico in Chile, and Los Antiguos and Perito Moreno in Argentina.
The area near the coast of the lake was first inhabited by criollos and European immigrants between 1900 and 1925. In 1971 and 1991, eruptions of the Hudson Volcano severely affected the local economy, especially that of sheep farming. A car ferry operates between Puerto Ingeniero Ibáñez and Chile Chico in the Chilean sector of the lake. The lake is known as a trout and salmon fishing destination.
Area
The lake has a surface of 1,850 km2 (710 sq mi) of which 970 square kilometres (370 sq mi) are in the Chilean Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region, and 880 square kilometres (340 sq mi) in the Argentine Santa Cruz Province, making it the biggest lake in Chile, and the fourth largest in Argentina. In its western basin, Lake Gen. Carrera has 586 m (1,923 ft) maximum depth.[3]
Geology
The lake occupies a continental-scale graben formed by SWS-ENE normal faults that have resulted in down dropping the bottom of the lake to -350 meters below mean sea level.[4] Preservation of younger lithostratighraphic units within the graben form reverse stratigraphy with older units exposed at higher topographic elevations to the south. The graben channelled mountain glaciers which formed terminal moraine helping to modify the present-day shape of the lake. The tectonic activity that formed the depression can be inferred to subduction of the triple joint that has occurred over the past 20 million years, as indicated by ripple marks in volcaniclastic sediments observed along the southern shore line. There is some speculation on whether the tectonics and crustal heat flow in the lake area are influenced by the asthenospheric window that exists beneath the crust in this region of Patagonia.[5]
The Marble Caves, Marble Chapel and Marble Cathedral are unusual geological formations located on the shoreline midway along the lake's length. They represent a group of caverns, columns and tunnels formed in monoliths of marble. The Marble Caves have been formed by wave action over the last 6,200 years.[6]
Gallery
 SRTM-Topography of the Chilean zone
SRTM-Topography of the Chilean zone Boat near Chile Chico in Chile
Boat near Chile Chico in Chile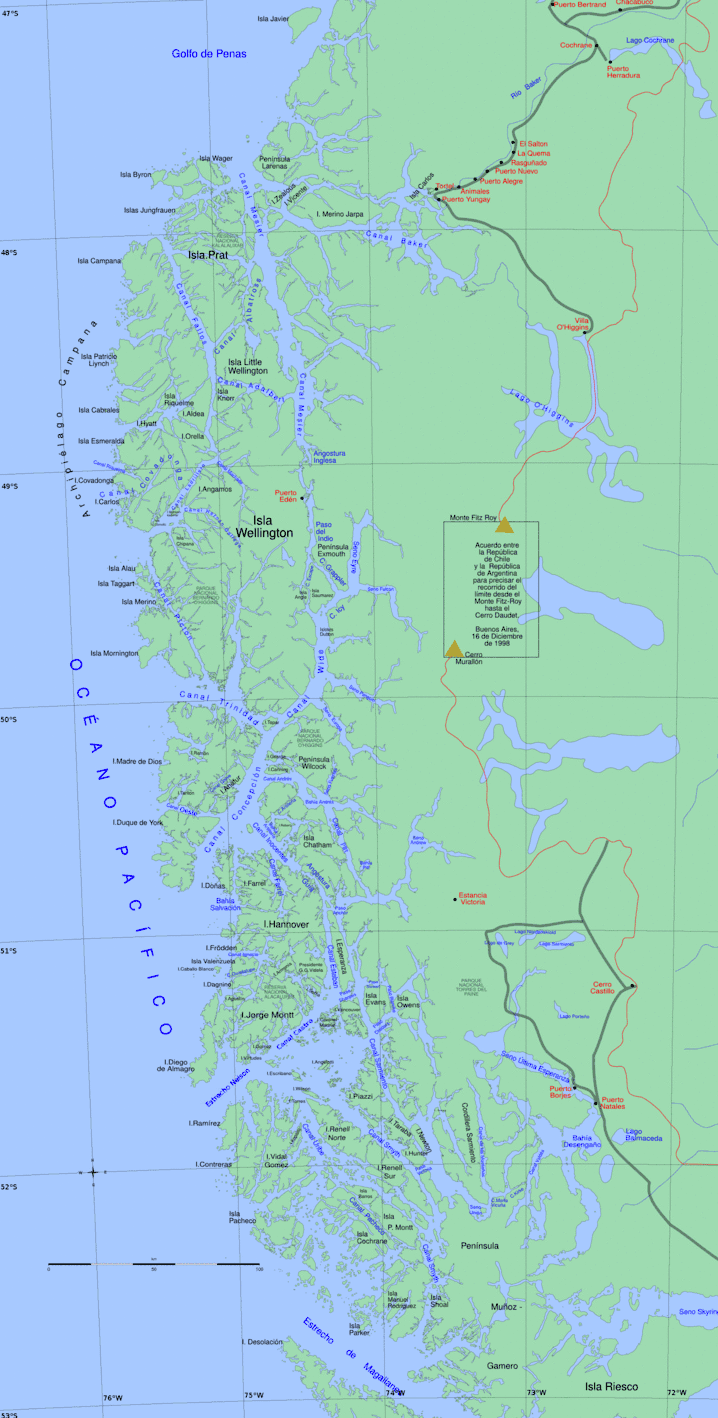 Map of the Chilean zone
Map of the Chilean zone
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to General Carrera Lake. |
- Earth Info, earth-info.nga.mil webpage: "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-05-04. Retrieved 2010-06-27.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Ley N.º 13.375: Crea y fija los limites de los departamentos de Palena, Aysén, Coyhaique y Chile Chico y las de sus respectivas comunas-subdelegaciones". Ministerio del Interior de Chile. 1959-09-09.
- Murdie et al. 1999, Geo-Marine Letters 18:315-320.
- B. Scalabrino, et.al., A morphotectonic analysis of central Patagonian Cordillera: Negative inversion of the Andean belt over a buried spreading center?, TECTONICS, VOL. 29, TC2010, doi:10.1029/2009TC002453, 2010
- Lagabrielle, Yves; Suárez, Manuel; Rossello, Eduardo A.; Hérail, Gérard; Martinod, Joseph; Régnier, Marc; de la Cruz, Rita (2004). "Neogene to Quaternary tectonic evolution of the Patagonian Andes at the latitude of the Chile Triple Junction". Tectonophysics. 385 (1–4): 211–241. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2004.04.023.
- "The Marble Caves (Cavernas de Mármol)". Wondermondo. 2012-01-10.
.png.webp)