Expressway Authority of Thailand
The Expressway Authority of Thailand (Thai: การทางพิเศษแห่งประเทศไทย) (EXAT) is a state enterprise under the Ministry of Transport.[1] It was founded in 1972, and operates Thailand's expressway (ทางพิเศษ thang phiset) system, which refers to (usually elevated) high-capacity controlled-access highways serving the Greater Bangkok area and some nearby provinces.
 | |
 Expressway in Bangkok | |
Native name | การทางพิเศษแห่งประเทศไทย |
|---|---|
Romanized name | kan thang phiset haeng prathet thai |
| Type | State enterprise |
| Industry | Greater Bangkok expressways |
| Founded | November 27, 1972 in Bangkok, Thailand |
| Headquarters | Bangkok , Thailand |
| Revenue | 16,060 million baht (2015) |
| Total assets | 180,696 million baht (2015) |
Number of employees | 4,701 regular, 625 temporary (2015) |
| Parent | Ministry of Transport |
| Website | www |
Expressway system
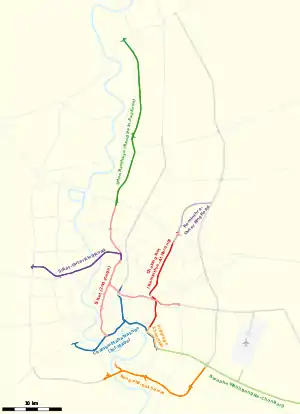
First opened in 1981, the system currently (2015) consists of seven expressways and four expressway links adding up to a total distance of 207.9 kilometres (129.2 mi), unchanged since FY2012.[2][3]:72 In 2013 the system served 594 million cars.[4]
The constituent expressway systems are (in order of completion):[5]
- Chaloem Maha Nakhon Expressway (first stage Expressway System)
- Si Rat Expressway (second stage Expressway System)
- Chalong Rat Expressway (Ramindra – At Narong Expressway)
- Burapha Withi Expressway (Bang Na Expressway)
- Udon Ratthaya Expressway (Bang Pa-in – Pak Kret Expressway)
- Third stage expressway System, S1 section (At Narong - Bang Na)
- Bang Phli–Suk Sawat Expressway (South Kanchanaphisek ring road)
- Ramindra–Outer Ring Road Expressway
- Si Rat–Outer Ring Road Expressway
Financials
Fiscal year 2015 (year ending 30 September 2015) revenues were 16,060 million baht on total assets of 180,696 million baht.[3]:4 It employed 4,701 regular and 625 temporary employees in FY2015.[3]:19 EXAT's top seven executives were remunerated 12.9 million baht total in FY2015.[3]:29
References
- "Expressway Authority of Thailand (EXAT)". Thailand Transport Portal (MOT). Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- EXAT Annual Report 2012
- Annual Report 2015; Expressway Authority of Thailand (PDF). Bangkok: Expressway Authority of Thailand (EXAT). 2015. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- "EXAT corporate social responsibility report" (PDF). Retrieved 10.11.2016. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - Expressway Authority of Thailand. "โครงข่ายทางพิเศษที่เปิดให้ใช้บริการ". Expressway Authority of Thailand website. Archived from the original on 7 October 2011. Retrieved 5 August 2011.