Evans County, Georgia
Evans County is a county in the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2010 census, the population was 11,000.[1] The county seat is Claxton.[2] A bill creating the county was passed in the Georgia General Assembly on August 11, 1914, and later, on November 3, 1914, an amendment was ratified by a vote of the people which formally created the county.
Evans County | |
|---|---|
 Evans County Courthouse in Claxton | |
 Seal | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Georgia | |
 Georgia's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 32°10′N 81°53′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1914 |
| Named for | Clement A. Evans |
| Seat | Claxton |
| Largest city | Claxton |
| Area | |
| • Total | 187 sq mi (480 km2) |
| • Land | 183 sq mi (470 km2) |
| • Water | 4.0 sq mi (10 km2) 2.1%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2019) | 10,654 |
| • Density | 60/sq mi (20/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 12th |
| Website | www |
Evans County is located in an area known as the Magnolia Midlands within the Historic South region. The current Evans County Courthouse was created in 1923 and, in 1940, the people of Evans County elected their first female sheriff. Later, in the 1950s and 1960s, new growth came to the county with the building of Evans Memorial Hospital and the Claxton-Evans County Airport. In 2010, the population was 11,000; however, the 2012 Census Estimate showed a population of 10,689.
The county sits firmly within Georgia's coastal plain region and has predominantly sedimentary rock and red and yellow clays. The Canoochee River is the major body of water flowing through the county.
Manufacturing, educational, health and social services make up much of Evans County's diverse economy. Major employers in the county include Camellia Health and Rehabilitation, Claxton Poultry Company, Georgia Department of Corrections, Pinewood Christian Academy, and Valmont Newmark. The county is ranked 64 out of 71 Tier 1 counties with an 8% sales tax. Businesses in the county are 100% exempt on all classes of certain business inventory from property taxes.
History

On August 11, 1914, the Georgia General Assembly proposed a constitutional amendment to create Evans County from Bulloch and Tattnall counties. Georgia voters ratified the proposed amendment by a vote of 36,689 to 9,789[3] on November 3, 1914, which marks the official date of Evans County's creation. The county was named in honor of Clement A. Evans. Evans was a state senator from Stewart County, Georgia, a Brigadier General in the Confederate States Army, a Methodist minister, an historian and an author.[4]
The push to create Evans County came about for various reasons, most notably the desire to not have to travel so far to the court house; more office jobs; increase in businesses coming to the area, especially in regard to hotels and eating establishments and a belief that there was a minority in Reidsville, Georgia – the county seat in Tattnall County – which controlled the county.[4] Moreover, the entrance of the Savannah and Western Railroad into Tattnall County created a desire by landowners to have stations on their property; ultimately, these new stations led to the founding of the cities which would become part of Evans County: Bellville, Claxton, Daisy and Hagan.[5]
However, not everyone was for the creation of a new county. Some of the arguments against the creation of a new county included: the idea that the difficulties with distance to the courthouse were being overcome; also, the tax burden would override any benefits from new jobs.[4] Evans County was approved through the constitutional amendment process because of an earlier amendment from 1904 which limited the number of counties to 145. In order to get around this amendment, a new amendment was passed which allowed for the creation of Evans County.[6]
The current Evans County courthouse was completed in 1923. The courthouse is in Claxton and was designed in the neoclassical revival tradition by architect J.J. Baldwin.[4][6] Prior to the building of the current courthouse, all of the county's business was held in the White Building, a three-story edifice built by Mr. R. King White and later bought by Mrs. Ben Daniel. Mrs. Daniel's husband, Dr. Ben Daniel, used the building as his office.[4]
The first female elected sheriff in Evans County, and in Georgia, was Mrs. Josie Mae Rogers, who was appointed after the death of the late sheriff, her father Jesse C. Durrence on June 24, 1940. Later, she was elected sheriff by the people of the county.[7] Not long after, in July 1940, Camp Stewart – which would eventually become Fort Stewart – was created after the United States government bought up several tracts of land in various counties, including Evans County. In all, it is estimated that approximately 1,500 people were displaced by the creation of the camp.[8]
The late 1950s and the 1960s were a time of growth in Evans County, especially in regards to health care and transportation. Beginning in 1958, Dr. Curtis Gordon Hames began research on the Evans County Heart Study, which was funded by the National Institutes of Health; this study would continue until 1995 and resulted in 560 published papers on heart disease, genetics, cancer and other areas.[9] In 1964, the FAA approved a site for the construction of an airport in the county, just three miles (5 km) northeast of Claxton.[4] On December 7, 1967, after two decades of effort, Evans Memorial Hospital was opened.[4]
In November 1975, B.G. Tippins, a teacher at Claxton High School, worked with 15 students to build a Miller Lil' Rascal, a two-seat sporting biplane. This plane was the only one of its kind built.[11]
From 1980 to 1983 several buildings were placed on the National Register of Historic Places, including the courthouse and three homes.
On October 16, 2006, the Evans County Sheriff's Department was presented with seven bullet-proof vests by the Georgia Fraternal Order of Police.[12]
On June 3, 2008 Evans County commissioners unanimously passed a resolution to mark August 11 as Evans County Day.[13] Since that day there have been annual celebrations of the county's founding including the 2014 centennial celebration.
Geography
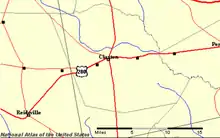
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 187 square miles (480 km2), of which 183 square miles (470 km2) is land and 4.0 square miles (10 km2) (2.1%) is water.[14] The major body of water is the Canoochee River which flows through Evans County. The Canoochee is a tributary of the Ogeechee River.
There are several ponds in Evans County. They include Cypress Pond; Dyess Pond; Beasley Pond; Bernard Smith Pond; I.W. DeLoach Ponds; Big Beasley Pond DeLoach Pond. Other bodies of water include Tippins Lake; Grice Creek; Billy Fork Creek; Thick Creek; Mill Branch; Barnard Mill; Rocky Branch; Scott Creek; Cedar Creek; and Dry Creek.[15]
The entirety of Evans County is located in the Canoochee River sub-basin of the Ogeechee River basin.[16]
Geology and terrain

Geologically, Evans County lies in the coastal plain region of Georgia, an area consisting mostly of sedimentary rocks.[17] The coastal plain is divided from the Piedmont by the Fall Line, which passes through Georgia from Augusta, Georgia in the east, then southwestward to Macon, Georgia, then to Columbus, Georgia and finally westward to Montgomery, Alabama.[18]
Yet, sedimentary rocks are not the only geological features to be found in Evans County. The county is mostly covered by thin sand and red and yellow clay.[19] As in Tattnall County along the Ohoopee River, the sand in Evans County that lies along the Canoochee River is white quartz of a medium to coarse grain.[19] There is exploitable medium-grain sand covering about 50 acres of land along the railroad above Bull Creek. The pure white sand along the Canoochee could be made into bottle glass, but is expensive to recover.[19]
Flora and fauna

Evans County is home to several protected species of flora and fauna. Among the flora in the county are the Georgia plume, Sarracenia flava, Sarracenia minor, beardtongue, Stewartia, loblolly-bay and sweetbay. Others include the purple honeycomb head, large-stem morning-glory, few-flower gay-feather, pond spice, Lobelia boykinii, hummingbird flower, and other plants. Protected animals in the area include the red-cockaded woodpecker, the indigo snake, Bachman's sparrow, the spotted turtle, Say's spiketail and the southern bald eagle, among other animals.[4][20]
Climate
Evans County is classified as a humid subtropical climate under the Köppen classification and has a mild climate, averaging 49.8 degrees in January and 82.7 degrees in July. The average annual rainfall is 48 inches and the county has a minimum altitude of 65 feet (20 m) above sea level and a maximum altitude of 228 feet (69 m) above sea level.[21] The county is 1.4 times below the U.S. average in historical area-adjusted tornado activity. From 1950 to 2004, only 2 injuries have been caused by tornadoes in the county; this occurred on March 29, 1974 when an F1 tornado hit the county, causing between $5,000 and $50,000 in damages.[15]
| City | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bellville[22] | 61 36 |
66 39 |
73 44 |
79 50 |
86 59 |
91 67 |
94 71 |
92 70 |
87 65 |
80 54 |
71 45 |
63 38 |
| Claxton[23] | 61 36 |
66 39 |
73 44 |
79 50 |
86 59 |
91 67 |
94 71 |
92 70 |
87 65 |
80 54 |
71 45 |
63 38 |
| Daisy[24] | 61 36 |
66 39 |
73 44 |
79 50 |
86 59 |
91 67 |
94 71 |
92 70 |
87 65 |
80 54 |
71 45 |
63 38 |
| Hagan[25] | 61 36 |
66 39 |
73 44 |
79 50 |
86 59 |
91 67 |
94 71 |
92 70 |
87 65 |
80 54 |
71 45 |
63 38 |
| Temperatures are given in °F format, with highs on top of lows | ||||||||||||
Adjacent counties
- Bulloch County – northeast
- Bryan County – east
- Liberty County – southeast
- Tattnall County – southwest
- Candler County – northwest
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1920 | 6,594 | — | |
| 1930 | 7,102 | 7.7% | |
| 1940 | 7,401 | 4.2% | |
| 1950 | 6,653 | −10.1% | |
| 1960 | 6,952 | 4.5% | |
| 1970 | 7,290 | 4.9% | |
| 1980 | 8,428 | 15.6% | |
| 1990 | 8,724 | 3.5% | |
| 2000 | 10,495 | 20.3% | |
| 2010 | 11,000 | 4.8% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 10,654 | [26] | −3.1% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[27] 1790–1960[28] 1900–1990[29] 1990–2000[30] 2010–2019[1] | |||
2000 census
As of the census[31] of 2010, there were 11,000 people, 4,033 households, and 2,805 families residing in the county. The population density was 60.2 people per square mile. There were 4,658 housing units. The racial makeup of the county was 66.4% White, 31% Black or African American, 0.4% Native American, 0.9% Asian, 0.3% Pacific Islander, and 1% from two or more races. 12.7% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 3,778 households, out of which 34.90% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 49.00% were married couples living together, 16.40% had a female householder with no husband present, and 29.10% were non-families. 25.00% of all households were made up of individuals, and 9.90% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.62 and the average family size was 3.10.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 27% under the age of 18, 10.20% from 18 to 24, 29.00% from 25 to 44, 20.70% from 45 to 64, and 12.60% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 34 years. For every 100 females there were 94.60 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.10 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $25,447, and the median income for a family was $31,074. Males had a median income of $26,959 versus $17,587 for females. The per capita income for the county was $27,657.[32] About 23.10% of families and 27.00% of the population were below the poverty line, including 36.20% of those under age 18 and 23.60% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 11,000 people, 4,033 households, and 2,805 families residing in the county.[33] The population density was 60.2 inhabitants per square mile (23.2/km2). There were 4,664 housing units at an average density of 25.5 per square mile (9.8/km2).[34] The racial makeup of the county was 58.8% white, 29.1% black or African American, 0.7% Asian, 0.2% Pacific islander, 0.2% American Indian, 10.0% from other races, and 1.1% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 13.1% of the population.[33] In terms of ancestry, 11.5% were Irish, 8.8% were German, 7.5% were English, and 6.4% were American.[35]
Of the 4,033 households, 36.1% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 46.5% were married couples living together, 17.4% had a female householder with no husband present, 30.4% were non-families, and 25.9% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.63 and the average family size was 3.16. The median age was 35.9 years.[33]
The median income for a household in the county was $40,796 and the median income for a family was $45,938. Males had a median income of $36,426 versus $28,282 for females. The per capita income for the county was $19,072. About 15.1% of families and 21.2% of the population were below the poverty line, including 32.0% of those under age 18 and 15.8% of those age 65 or over.[36]
Religion
Evans County is largely Protestant. The religious affiliation of the people of Evans County are:[15]
- Protestant: 87%
Other: 7%
Catholic: 6%
Evans County shares its Protestant heritage with the rest of Georgia and the Southern United States.
The largest denominations by number of adherents in 2002 were the Southern Baptist Convention with 2,043; the United Methodist Church with 1,620; and the Catholic Church with 286.[15]
Economy
Agriculture and industry

Evans County has a diverse economy, with manufacturing; educational, health and social services; retail trade; and construction providing the greatest employment in manufacturing. The Claxton-Evans County Industrial Park provides the strongest source of manufacturing, with the creation of concrete poles and galvanization of metals. Major employers in Evans County include Evans Memorial Hospital, Camellia Health and Rehabilitation, Claxton Poultry Company, Georgia Department of Corrections, Glenvue Nursing Home, JGI Incorporated Galaxy Food Center, McDonald's Restaurants, Nesmith Chevrolet Company, Pinewood Christian Academy, and Valmont Newmark.[37]
Outside of the cities, agriculture is important with corn and cotton being major crops. Other crops planted and harvested in Evans County include soybeans; wheat and vegetables; and land set aside for orchards.[15] The food industry is the most common industry for Evans Countians to work in.[15]
Local taxes
Evans County has an 8% total sales tax, including 4% state, 1% local option, 1% special purpose, and 1% educational.[38] Evans County is ranked 64 out of 71 Tier 1 counties in the state of Georgia.[39] Claxton and Evans County exempt 100% on all classes of certain business inventory from property taxes.[39]
Culture
People
Evans County is populated by many different ethnic groups.[31] Among these groups are Whites; Blacks or African Americans; Native Americans; Asians; Pacific Islanders; and Hispanics or Latinos. Foreign born Evans Countians are predominantly Mexican, followed by Filipinos; Guatemalans; Japanese; Indians; Germans; and Indonesians. The most common ancestries in Evans County include American; English; Irish; German; Scots-Irish; French; and Italian.[15] The combination of these ancestries and ethnicities has forged Evans County's character.
Evans Countians
Evans County has had a number of notable citizens. Joseph Kennedy was born in Claxton and went on to become the senator for the area and president pro tempore of the Georgia State Senate. Albert Parker and Ira S. Womble, Sr. both made Claxton and Evans County famous through their respective companies, The Claxton Bakery and The Georgia Fruitcake Company.[40][41] Cartha Deke DeLoach, a native Evans Countian, joined the FBI and worked alongside J. Edgar Hoover while Dr. Curtis Gordon Hames did a groundbreaking study on heart disease.[9] Two Evans County natives, Charles Gordon Edwards of Daisy, and William Washington Larsen of Hagan, went on to become United States Representatives.[42][43]
Customs

Evans County has held an annual rattlesnake roundup the second weekend of March since 1968, with the festival growing every year since then and moving from within Claxton to just outside the city in 2001; this festival has undergone a change and is now called the Claxton Rattlesnake and Wildlife Festival.[44][45] Another, more recent, annual event is the Cruisin' in the Country Bike Ride, began in 1995 as the Yuletide Ride. The event was changed from December to November the next year and expanded to include a 65-mile (105 km) route. Soon, the route became a complete century ride.[46]
Other events include the Martin Luther King Day parade, held every January; Christmas in Claxton, an event which occurs on the first Saturday in December and includes arts and crafts, food, and the Parade of Lights; barrel racing at the Richey Arena; and a tractor pull held on the first Saturday of each month at the Longneedle Farm Truck and Tractor Pull.[47] A Chicken Pickin' festival was held September 11, 2010.[48]
Cuisine

Evans County's cuisine includes a variety of different foods ranging from seafood, corn on the cob and chicken and dumplings to Brunswick stew, fried chicken and cornbread. Other well known and loved foods in the county include pecans, peaches and peanuts.[49] However, these are not the only foods enjoyed by Evans Countians. Because of the diversity within the county, the people of Evans County also frequent Mexican and Chinese restaurants.
Architecture

A number of buildings and homes in Evans County are on the National Register of Historic Places. In Claxton, there is the Dr. James W. Daniel House; the Evans County Courthouse; and the Mitchell J. Green Plantation.[50] In Hagan, there is the George W. DeLoach House.[50] And at Camp Oliver there is the Glisson Store (DOE).[50] Other places of interest include the Daisy Post Office and the train depot in Bellville.[51][52]
Evans County is also home to a number of antebellum houses that were built prior to the formation of the county. Many of these homes were built in the Plantation Plain style and include the A.D. Eason House; the Thomas A. Durrence House; and the Edwards-Strickland House.[53]
Infrastructure
Health care

Evans County has several medical facilities, including the Evans County Memorial Hospital;[54] the Jack Strickland Rehabilitation Wellness Center;[55] Northspring Assisted Living;[56] The Griffin House; the Camellia Health and Rehabilitation Center; The Evans County Health Department and Health and Well-Being Consultative Services.[57] There are approximately twelve doctors in the county, two dentists and two pharmacies.[57]
Education
Evans County has both public and private schools. Public education in Evans County is supervised by the Evans County School District. The current superintendent is Dr. Marty Waters.
All schools have been fully accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools as well as the Georgia Accrediting Commission.[58] There are currently 1,888 students and 122 teachers, a ratio of 15:1.[59] There are three public schools in Evans County: Claxton Elementary School; Claxton Middle School; and Claxton High School.
Pinewood Christian Academy is a co-educational private school in Bellville. Founded in 1970, the school has approximately 685 students and has a calendar year of 180 days with each school day lasting 7 hours.
Transportation

Transportation in Evans County is overseen by the Georgia Department of Transportation, a part of the executive branch of the state government. The major U.S. highways that run through Evans County are U.S. Route 25; U.S. Route 280; and U.S. Route 301. State highways running through Evans County are State Route 30; State Route 73; State Route 129; State Route 169; and State Route 292. Georgia Central Railway provides transportation for industrial customers in the county.[21]
Air travel in Evans County is provided by the Claxton-Evans County Airport. The site for the airport was approved by the FAA in 1964 and it was activated in 1971; the airport is three miles (5 km) northeast of Claxton, Georgia.[4] It is operated by the city of Claxton. It has a 5,000-foot (1,500 m) runway, hangars, pilot control lighting, and a Precision Approach Path Indicator.[60] The Claxton-Evans County Airport has an elevation of 112 ft (34.1 m).
Major highways
| Road | Route Description |
|---|---|
| Starting at the intersection of US 17/SR 25 in Brunswick, US 25 goes northwest to Jesup then northeast to Ludowici. It then stays at a general north route through the cities of Statesboro, Millen, Waynesboro and finally Augusta, where it crosses the Savannah River into South Carolina. The overall majority of the route is 4-lane. | |
| US 280 begins in Georgia at the state's border with Alabama in Columbus. There it is paired with State Route 520 and U.S. Route 27. It maintains this designation as it passes through Fort Benning. US 280 continues east, where it passes through Plains and becomes cosigned State Route 30 in Americus. It maintains this designation until the route's terminus in Blichton. | |
| US 301 uses SR 4/SR 15 from Florida to Folkston, SR 23 from Folkston to Glennville, and SR 73 from Glennville to South Carolina. US 1/US 23/SR 4/SR 15/SR 121 split to the northwest at a junction north of Folkston, leaving only US 301 and SR 23 to head north across US 82/SR 520 at Nahunta to Jesup. There US 84 and SR 38 continue northeast, while US 25/US 301/SR 23 turn northwest with SR 57. | |
| US 280/SR 30 meet the southern terminus of SR 56 (Shepards Bridge Road) before curving to the northeast. Almost immediately after the end of the curve is the northern terminus SR 147 (Tattnall Street). About 1,000 feet (300 m) later is an intersection with SR 23/SR 57/SR 121 (Main Street). In Bellville, is an intersection with SR 169 (Smith Street). At North Ralph Street, SR 129 joins the concurrency. At South River Street, SR 129 departs from the concurrency to the south. In Daisy, they meet the northern terminus of former SR 250 (now known as Ellerbee Avenue). | |
| SR 23 and SR 57 split off to the northwest at Glennville. SR 73 begins there, taking US 25 and US 301 north from Glennville across US 280/SR 30 at Claxton and I-16/SR 404 to Statesboro. | |
| State Route 129 (SR 129) is a 20.0-mile-long (32.2 km) state highway that runs southeast-to-northwest through portions of Evans, Tattnall, and Candler counties in the east-central part of the U.S. state of Georgia. It connects the towns of Claxton and Metter. | |
| State Route 169 (SR 169) is a 55.4-mile-long (89.2 km) state highway that runs south-to-north through portions of Wayne, Appling, Tattnall, and Evans counties in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Georgia. | |
| East of Lyons Georgia State Route 292 intersects with SR 86. Just past SR 86, the route crosses the Ohoopee River, where it enters Tattnall County. Farther to the southeast, in the city of Collins, is an intersection with SR 23/SR 57/SR 121. The route continues east through Manassas and enters the city of Bellville. There, it intersects SR 169. Just east of Bellville, SR 292 meets its eastern terminus, an intersection with US 280/SR 30. | |
Energy use and production
Evans County's electricity generation and consumption are provided through a variety of means. Natural gas is also available in large quantities. Evans Countians consumes 269,420 gallons of water a day out of a plant capacity of 3,720,000 gallons a day. There is an elevated storage capacity of 700,000 gallons.[60] The energy produced and consumed is available through the Claxton-Evans County Industrial Park.[61]
Law and government
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 68.0% 2,888 | 31.2% 1,324 | 0.8% 35 |
| 2016 | 66.5% 2,404 | 31.3% 1,130 | 2.2% 79 |
| 2012 | 63.6% 2,268 | 35.6% 1,268 | 0.8% 29 |
| 2008 | 63.9% 2,462 | 35.6% 1,374 | 0.5% 20 |
| 2004 | 65.2% 2,291 | 34.5% 1,213 | 0.3% 12 |
| 2000 | 59.8% 1,841 | 39.5% 1,217 | 0.7% 22 |
| 1996 | 47.5% 1,206 | 44.0% 1,117 | 8.5% 215 |
| 1992 | 42.0% 1,244 | 41.6% 1,230 | 16.4% 486 |
| 1988 | 62.0% 1,707 | 37.2% 1,023 | 0.8% 23 |
| 1984 | 57.3% 1,601 | 42.7% 1,193 | |
| 1980 | 42.3% 1,090 | 56.5% 1,456 | 1.1% 29 |
| 1976 | 31.4% 746 | 68.6% 1,631 | |
| 1972 | 81.6% 1,666 | 18.4% 375 | |
| 1968 | 21.6% 543 | 19.6% 492 | 58.8% 1,475 |
| 1964 | 66.3% 1,572 | 33.7% 799 | |
| 1960 | 34.7% 567 | 65.3% 1,069 | |
| 1956 | 23.6% 356 | 76.4% 1,152 | |
| 1952 | 26.1% 433 | 73.9% 1,224 | |
| 1948 | 8.4% 118 | 68.0% 953 | 23.6% 331 |
| 1944 | 13.4% 117 | 86.5% 756 | 0.1% 1 |
| 1940 | 7.4% 112 | 92.0% 1,399 | 0.6% 9 |
| 1936 | 4.5% 35 | 95.1% 733 | 0.4% 3 |
| 1932 | 3.7% 21 | 95.1% 548 | 1.2% 7 |
| 1928 | 28.2% 192 | 71.8% 489 | |
| 1924 | 2.5% 21 | 95.4% 790 | 2.1% 17 |
| 1920 | 3.6% 16 | 96.4% 432 | |
| 1916 | 13.6% 58 | 78.4% 334 | 8.0% 34 |
Government

The county government is a constitutional body and is granted powers by the Constitution of Georgia. Evans County has a board of commissioners, sheriff, tax commissioner and clerk of court. The original top positions were held by:
- H. Leonard Brewton—First County Commissioner (1915–1920)
- T. Walton Rogers—First County Sheriff (January 1, 1915 – February 24, 1920)
- T.J. Edwards—First County Tax Commissioner (January 1, 1933 – December 25, 1940)
- R.R. Tippins, Sr.—First Clerk of Court (January 1, 1915 – December 31, 1920)
Individuals currently holding Constitutional Offices are:
- Randall Tippins—Sheriff
- Julie E. Mincey—Tax Commissioner
- Kathy P. Hendrix—Clerk of Court
- Darin McCoy-Judge of the Probate Court
Board of Commissioners: The board of commissioners in Evans County is made up of six members elected by the people and led by a chairman elected by the board.[21] The board of commissioners acts as both the legislative and executive branches of government for the county and is charged with financing county programs and paying the salaries of constitutional officers.[63]
The current members of the Board of Commissioners are:[64]
- Sheila Holland – District 1
- Jill Griffin – District 2
- Tony Lewis – District 3
- Brian Croft – District 4
- Wesley Jenkins – District 5
- Irene Burney – District 6
Tax Commissioner: The tax commissioner receives tax returns, maintains tax records for the county, and collects and pays tax funds to the state and local government.[63]
Clerk of Court: The responsibility of the clerk of the court is to maintain court records and supervise registration of property transactions.[63]
Law enforcement and emergency services
Sheriff: The sheriff maintains the peace in the county through enforcement of the law.[63] In Evans County, the sheriff is assisted by eight officers, four deputies and four dispatchers.[21]
Fire department and EMS: The Evans County fire department is located in Claxton and has a fire chief, four dispatchers, and 21 volunteers.[21] Ambulance services are provided by Evans County EMS. EMS has seven full-time employees and four part-time employees.[65]
Evans County is represented in the Georgia General Assembly by State Senator Jack Hill in Georgia Senatorial District 4 and State Representative Bill Werkheiser. The county is represented in Congress by Rick Allen of Georgia's 12th congressional district.[21]
Media
The Claxton Enterprise is a weekly newspaper located in Claxton, Georgia, United States. It primarily serves Evans County, Georgia. The Enterprise was established in 1912 with its first issue being published on December 4, 1912. The current publisher is Mitchell Peace.[4]
Evans County has one local radio station, simultaneously broadcast on both the AM and FM bands. WCLA (1470 AM and 93.7 FM) offers CBS News each hour, while programming Adult Standards music. WCLA broadcasts Claxton High School and Pinewood Christian Academy football, basketball and baseball. WCLA is the Evans County affiliate for both University of Georgia Bulldog football and basketball, as well as Atlanta Braves baseball. The station observed its 57th birthday on July 30, 2015.
Sports and recreation
Sports in Evans County include the Claxton High School athletic program and the Pinewood Christian Academy athletic program. Both schools programs include football; baseball; basketball; track and field; softball; and tennis. Claxton High School also has a golf program. Claxton's boys' track and field were Georgia High School Association champions in 1983 and the boys' basketball team were champions in 1988.[66][67]
The county is home to a handful of public areas which are set aside for recreation. The Evans County Public Fishing Area, located in Claxton, is one such area and contains three lakes of 8, 30 and 84 acres and primitive campsites. Families can also picnic at the lake and an outdoor classroom is available for use. Parks include Bacon Ford Park and the Senior Citizens Park in Claxton.[68] Two parks in Hagan are the Maggie Mae Lewis Children's Park and the Bradley Memorial Park.[69]
Another outdoor recreational area is the Evans Heights Golf Club. The course was designed by Don Cottle, Jr. in 1970 and has Bermuda grass. In total, the course is 6,514 yards.[70]
Communities
| Picture | Town | Foundation | Area | Elevation | Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bellville | 1890 | 1 sq mi (2.5 km2) | 184 ft (56 m) | 123 | |
| Claxton | May 1890 | 1.6 sq mi (4.0 km2) | 184 ft (56 m) | 2,276 | |
|
|
Daisy | 1890 | 1 sq mi (2.7 km2) | 151 ft (46 m) | 126 |
| Hagan | 1890 | 2.2 sq mi (5.7 km2) | 190 ft (58 m) | 898 |
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved June 22, 2014.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- Public Affairs Information Service Bulletin, Accessed August 30, 2008
- Simmons, Dorothy (1999). A History of Evans County, Georgia. The Evans County Historical Society.
- The Tattnall County Heritage Committee (2013). Tattnall County Georgia 1801–1812: The Heritage of Tattnall County. The Tattnall County Heritage Committee.
- "Evans County Courthouse". Retrieved June 18, 2009.
- "Vanishing Georgia, Georgia Archives, University System of Georgia". Retrieved December 9, 2013.
- "New Georgia Encyclopedia: Fort Stewart". Retrieved June 18, 2009.
- "Heart study pioneer, Dr. Curtis G. Hames dies". Archived from the original on May 29, 2010. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 31.
- "Georgia Fraternal Order of Police". Archived from the original on November 26, 2011. Retrieved January 4, 2012.
- Cory Cunningham (June 12, 2008). "Evans County Day set for August". The Claxton Enterprise.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- "Evans County, Georgia detailed profile". Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- "Georgia Soil and Water Conservation Commission Interactive Mapping Experience". Georgia Soil and Water Conservation Commission. Retrieved November 22, 2015.
- "A Tapestry of Time and Terrain: The Coastal Plain, a USGS mapping project". Archived from the original on May 6, 2009. Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- "The Geology of Georgia". Archived from the original on February 5, 2007. Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- Bulletin – Geological survey. 1921. Retrieved August 7, 2009.
- "Locations of Special Concern Animals, Plants and Natural Communities in Evans County, Georgia". Archived from the original on July 20, 2011. Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- "Fingertip Facts" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 8, 2011. Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- "Average Weather for Bellville, GA – Temperature and Precipitation". Retrieved November 29, 2013.
- "Average Weather for Claxton, GA – Temperature and Precipitation". Retrieved November 29, 2013.
- "Average Weather for Daisy, GA – Temperature and Precipitation". Retrieved November 29, 2013.
- "Average Weather for Hagan, GA – Temperature and Precipitation". Retrieved November 29, 2013.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved May 21, 2020.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 22, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved June 22, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 22, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 22, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 14, 2011.
- "Evans County, GA Community Profile". Georgiafacts.org. Archived from the original on November 28, 2013. Retrieved November 28, 2013.
- "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2015.
- "Evans County at a Glance". Archived from the original on April 14, 2013. Retrieved January 21, 2012.
- "Georgia Sales Tax Rates: Evans County". Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- "Job Tax Credit Rankings 2010" (PDF). Retrieved January 14, 2010.
- "A Special Tribute". Archived from the original on July 6, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- "The History of Georgia FruitCake Co". Archived from the original on April 10, 2009. Retrieved June 22, 2009.
- "EDWARDS, Charles Gordon (1878–1931)". Retrieved June 22, 2009.
- "LARSEN, William Washington, (1871–1938)". Retrieved June 22, 2009.
- "Roundup History". Archived from the original on February 2, 2009. Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- Special to the Enterprise (January 25, 2012). "Rattlesnake event undergoes transformation". The Claxton Enterprise.
- "Event History". Archived from the original on July 8, 2011. Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- "Community". Archived from the original on January 29, 2009. Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- Hackle, Al (July 7, 2012). "Chicken to take center stage at new fall event". The Claxton Enterprise. Claxton, Georgia: Mitchell Peace.
- "Foodways: Overview". Retrieved May 12, 2007.
- "National Register of Historic Places: Georgia – Evans County". Archived from the original on November 19, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- "The Claxton Enterprise: Daisy, Georgia". Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- "The Claxton Enterprise: Bellville, Georgia". Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- Johnson, Phariss (2001). Houses of Heart Pine: A Survey of the Antebellum Architecture of Evans County, Georgia. The Evans County Historical Society.
- "Evans Memorial Hospital". Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- "Jack Strickland Rehabilitation Wellness Center". Archived from the original on January 19, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- "Northspring Assisted Living". Archived from the original on January 14, 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- "Health Care". Archived from the original on December 14, 2010. Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- "Georgia Accrediting Commission" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on November 7, 2004. Retrieved May 19, 2007.
- "Public School Review". Retrieved May 20, 2007.
- "Evans County, GA". Archived from the original on February 21, 2013. Retrieved June 29, 2009.
- "Economic Development". Archived from the original on January 7, 2010. Retrieved January 14, 2010.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved March 19, 2018.
- "New Georgia Encyclopedia: Georgia's County Governments". Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- "Evans County Board of Commissioners". Archived from the original on November 6, 2014. Retrieved November 6, 2014.
- "Evans County Emergency Medical Service". Archived from the original on July 27, 2009. Retrieved June 23, 2009.
- "GSHA Boys' Track Champions". Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- "GSHA Boys' Basketball Champions". Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- "The Claxton Enterprise: Claxton, Georgia". Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- "The Claxton Enterprise: Hagan, Georgia". Retrieved June 20, 2009.
- "Evans Heights Golf Club in Claxton, Georgia". Archived from the original on June 5, 2008. Retrieved July 24, 2009.
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 31.
- Jane's All the World's Aircraft (1979–80), 503.
External links
- National Association of Counties
- Evans County historical marker

