European Civil Aviation Conference
The European Civil Aviation Conference (ECAC) or Conférence Européenne de l'Aviation Civile (CEAC) is an intergovernmental organization which was established by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the Council of Europe. It is located in Neuilly-sur-Seine in France. Founded in 1955 with 19 member states, the ECAC now totals 44 members, including all 27 EU, 31 of the 32 European Aviation Safety Agency member states, and all 41 EUROCONTROL member states. ECAC "promotes the continued development of a safe, efficient and sustainable European air transport system. In doing so, it seeks to harmonise civil aviation policies and practices amongst its Member States and promote understanding on policy matters between its Member States and other parts of the world".
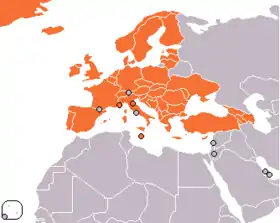
Its strategic priorities are safety, security and the environment.
ECAC Member States are: Albania, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, the Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, the Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, San Marino, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine, and the United Kingdom.
Membership

ECAC, EUROCONTROL and EU members:
- Austria (1955)
- Belgium (1955)
- Bulgaria (1991)
- Croatia (1992)
- Cyprus (1969)
- Czechia (1991)
- Denmark (1955)
- Estonia (1995[1])
- Finland (1955)
- France (1955)
- Germany (1955)
- Greece (1955)
- Hungary (1990)
- Ireland (1955)
- Italy (1955)
- Latvia (1993)
- Lithuania (1992)
- Luxembourg (1955)
- Malta (1979)
- Netherlands (1955)
- Poland (1990)
- Portugal (1955)
- Romania (1991)
- Slovakia (1991)
- Slovenia (1992)
- Spain (1955)
- Sweden (1955)
ECAC and EUROCONTROL members outside the EU:[2]
- Albania (1998)
- Armenia (1995)
- Bosnia and Herzegovina (2002)
- Georgia (2005)
- Moldova (1996)
- Monaco (1989)
- Montenegro (2008)
- North Macedonia (1997)
- Norway (1955)
- Serbia (2002)
- Switzerland (1955)
- Turkey (1955)
- Ukraine (1999)
- United Kingdom (1955)
ECAC-only members:
- Azerbaijan (2002)
- Iceland (1955)
- San Marino (2008)