Elvucitabine
Elvucitabine is an experimental nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), developed by Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. for the treatment of HIV infection.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
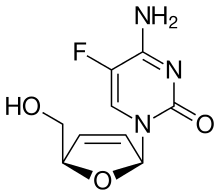
| Formula | C9H10FN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 227.195 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Elvucitabine belongs to a class (group) of HIV drugs called nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs).[1] NRTIs block an HIV enzyme called reverse transcriptase. (An enzyme is a protein that starts or increases the speed of a chemical reaction). By blocking reverse transcriptase, NRTIs prevent HIV from multiplying and can reduce the amount of HIV in the body.
Elvucitabine is similar in chemical structure to the FDA-approved NRTIs lamivudine (brand name Epivir) and emtricitabine (brand name Emtriva). However, in vitro studies have suggested that elvucitabine may work on certain HIV strains against which other NRTIs, such as lamivudine and emtricitabine, no longer work. (In vitro studies are studies done in test tubes or other laboratory equipment and not on animals or humans).
Studies have also suggested that elvucitabine may be effective against hepatitis B virus (HBV).[2]
Currently, it is in Phase II clinical trials.[3]
References
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 2014-11-22.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Elvucitabine". AIDSmeds.com. November 5, 2007. Archived from the original on March 21, 2008. Retrieved March 21, 2008.