Cross pattée
A cross pattée (or cross patty or cross Pate, known also as a cross formée/formy, croix pattée or Tatzenkreuz), is a type of Christian cross with arms that are narrow at the centre, and often flared in a curve or straight line shape, to be broader at the perimeter. The form appears very early in medieval art; for example in a metalwork treasure binding given to Monza Cathedral by Queen Theodelinda (d. 628), and the 8th century lower cover of the Lindau Gospels in the Morgan Library. An early English example from the start of the age of heraldry proper (i.e. about 1200) is found in the arms of Baron Berkeley.
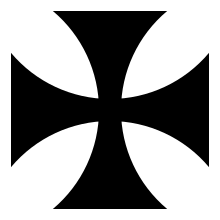
Etymology
The word pattée is a French adjective in the feminine form used in its full context as la croix pattée, meaning literally "footed cross", from the noun patte, meaning foot, generally that of an animal.[1] The cross has 4 splayed feet, each akin to the foot, for example, of a chalice or candelabrum. In German it is called Tatzenkreuz from Tatze, foot, paw. Planché provides a dubious suggestion that the term comes from the Latin verb pateo, to lie open, be spread. He states it to be discernible on the standard of King Stephen (1135–1154).[2]
Variants
Several variants exist as follows:
 With the edges of the arms concave throughout; the "Iron Cross", as generally used on Luftstreitkräfte aircraft in 1915
With the edges of the arms concave throughout; the "Iron Cross", as generally used on Luftstreitkräfte aircraft in 1915 A cross pattée with a sharp point added to the lower limb, as if for use in staking into the ground.
A cross pattée with a sharp point added to the lower limb, as if for use in staking into the ground. With less curvature, used on Luftstreitkräfte aircraft into April 1918, and the basis for the similar cross by the Bundeswehr of modern Germany.
With less curvature, used on Luftstreitkräfte aircraft into April 1918, and the basis for the similar cross by the Bundeswehr of modern Germany. Bolnisi cross, official national symbol of the republic of Georgia, used on flag, coat of arms and various official and unofficial organizations of this country.
Bolnisi cross, official national symbol of the republic of Georgia, used on flag, coat of arms and various official and unofficial organizations of this country. With the ends of the arms convex and curved; sometimes called "Alisee" (French croix pattée alésée arrondie)
With the ends of the arms convex and curved; sometimes called "Alisee" (French croix pattée alésée arrondie) With triangular arms which come close to filling the square
With triangular arms which come close to filling the square With triangular arms that do not fill the square, used on various flags, coats of arms, orders, decorations and medals.
With triangular arms that do not fill the square, used on various flags, coats of arms, orders, decorations and medals. With straight parallel lines at the centre (considered pattée by Rudolf Koch in Book of Signs)
With straight parallel lines at the centre (considered pattée by Rudolf Koch in Book of Signs)
Use in crowns
Many crowns worn by monarchs have jewelled crosses pattées mounted atop the band. Most crowns possess at least four such crosses, from which the half arches rise. Some crowns are designed so that the half-arches can be detached, allowing the circlet to be worn separately on occasion.
A cross pattée is particularly associated with crowns in Christian countries. It is often heavily jewelled, with diamonds and precious stones. The Koh-i-Noor diamond is set in a cross pattée on the Crown of Queen Elizabeth. The British Imperial State Crown has a base of four crosses pattée alternating with four fleurs-de-lis. A cross pattée on the Imperial State Crown holds the Black Prince's Ruby. The cross pattée also features in many of the other British Crowns including the St Edward's Crown, used for coronations, and the Imperial Crown of India created for George V as Emperor of India to wear at the Delhi Durbar of 1911.
Use by Crusaders, Prussia and Germany
Teutonic Knights


This cross is often associated with the Crusades. The heraldic cross pattée was sometimes used by the Teutonic Knights, a Crusader order, though their more usual emblem was a plain straight black cross on white,.
Iron Cross
In 1813, King Frederick William III of Prussia established the Iron Cross as a decoration for military valor, and it remained in use, in various forms, by Prussia and later Germany until 1945. A stylized version of the Iron Cross is used to date by the German army (Bundeswehr) as its symbol of nationality, and is found on vehicles, aircraft and publications.
Prussian and Imperial German Landwehr and Landsturm troops used a Cross Pattée cap badge to distinguish them from regular army troops. A stylized version of the Cross Pattée is used by the modern German military (Bundeswehr) as its symbol of nationality, and is found on vehicles, aircraft and publications, with no border of any kind at the ends of each arm (as was the case with the Balkenkreuz used on German aircraft in 1918-1945).
France
The cross pattée can be found on coats of arms of various French communes.
.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms of Ambacourt
Coat of arms of Ambacourt.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms of Damouzy
Coat of arms of Damouzy Coat of arms of Fontaine-lès-Luxeuil
Coat of arms of Fontaine-lès-Luxeuil.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms of Fontaines-Saint-Martin
Coat of arms of Fontaines-Saint-Martin.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms of Saint-Gondon
Coat of arms of Saint-Gondon
Georgia
The Bolnisi cross (Georgian: ბოლნისის ჯვარი bolnisis ǰvari) is a cross symbol, taken from a 5th-century ornament at the Bolnisi Sioni church, which came to be used as one of the oldest national symbol of Georgia. It was used on the flags and coat of arms of the Kingdom of Georgia and the current Republic of Georgia, with its various organizations and administrative divisions.
 Bolnisi Sioni inscriptions. Oldest Georgian inscription that uses the Asomtavruli script, predating the modern Mkhedruli script, inside Georgia.
Bolnisi Sioni inscriptions. Oldest Georgian inscription that uses the Asomtavruli script, predating the modern Mkhedruli script, inside Georgia.

 Roundel of the Georgian Defense Forces
Roundel of the Georgian Defense Forces Coat of arms of the city of Bolnisi
Coat of arms of the city of Bolnisi
Montenegro
The Montenegrin cross-flag (Krstaš-barjak) has been used in Montenegro since medieval times to represent the state, and lately its military divisions. The earliest documented use of this flag has been recorded in 1687.[3] During the 1990s, it was used as a symbol of Montenegrin independence movement, most notably by the Liberal Alliance of Montenegro. Nowadays, Montenegro's Royal Capital City Cetinje uses krstaš flag as its flag. It is also used as an unofficial alternate Montenegrin flag, as well as by local trademarks and societies related to Montenegro.
 Flag of the Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro
Flag of the Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro Montenegrin flag used in the Battle of Vučji Do, damaged by Ottoman soldiers' bullets. The Н.I. initials indicate Prince Nicholas I. One of the most important historical Montenegrin flags.
Montenegrin flag used in the Battle of Vučji Do, damaged by Ottoman soldiers' bullets. The Н.I. initials indicate Prince Nicholas I. One of the most important historical Montenegrin flags. Flag of Old Royal Capital Cetinje
Flag of Old Royal Capital Cetinje Coat of arms of Nikšić Municipality
Coat of arms of Nikšić Municipality Modern Montenegrin Air Force roundel
Modern Montenegrin Air Force roundel Montenegrin Police Special Counter-Terrorist Unit Insignia
Montenegrin Police Special Counter-Terrorist Unit Insignia Flag of Montenegrins of Serbia
Flag of Montenegrins of Serbia
Poland

 Coat of arms of Podkarpackie Voivodeship
Coat of arms of Podkarpackie Voivodeship Coat of arms of Przemyśl
Coat of arms of Przemyśl Coat of arms of Rzeszów
Coat of arms of Rzeszów Coat of arms of Skierniewice
Coat of arms of Skierniewice
Russia
 Coat of arms of Kirov Oblast
Coat of arms of Kirov Oblast Coat of Arms of Perm Krai
Coat of Arms of Perm Krai.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms of Borisovka, Belgorod Oblast
Coat of arms of Borisovka, Belgorod Oblast
Spain
 Coat of arms of El Bierzo
Coat of arms of El Bierzo Coat of arms of Mondoñedo
Coat of arms of Mondoñedo Coat of arms of Morcín
Coat of arms of Morcín Coat of arms of Oviedo
Coat of arms of Oviedo Coat of arms of Priorat
Coat of arms of Priorat Coat of arms of Sabiñánigo
Coat of arms of Sabiñánigo Coat of arms of Sitges
Coat of arms of Sitges Coat of arms of Villafáfila
Coat of arms of Villafáfila
Sweden
In Sweden, the term "Saint George's Cross" sometimes refers to the cross pattée used by Swedish Freemasons.[4] For example, the cross of the Swedish Order of Freemasons was defined by the King of Sweden in 1928 to be a "red St George's cross with triangular arms".[5]
 Flag of the Swedish Order of Freemasons
Flag of the Swedish Order of Freemasons Coat of arms of the Swedish Order of Freemasons
Coat of arms of the Swedish Order of Freemasons
Ukraine
Military
 Emblem of the Ministry of Defence of Ukraine
Emblem of the Ministry of Defence of Ukraine Emblem of the General Staff
Emblem of the General Staff Emblem of the Defence Intelligence
Emblem of the Defence Intelligence Emblem of the Ukrainian Armed Forces
Emblem of the Ukrainian Armed Forces Emblem of the Ukrainian Ground Forces
Emblem of the Ukrainian Ground Forces Emblem of the Ukrainian Navy
Emblem of the Ukrainian Navy Emblem of the Ukrainian Air Force
Emblem of the Ukrainian Air Force Emblem of the Security Service of Ukraine
Emblem of the Security Service of Ukraine
Volhynia
 Coat of arms of the Volhynian Duchy (Principality)
Coat of arms of the Volhynian Duchy (Principality) Coat of arms of Volhynia with the Muscovite Monomakh's Cap
Coat of arms of Volhynia with the Muscovite Monomakh's Cap Volhynian Voivodeship in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
Volhynian Voivodeship in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth_(1796).gif) Coat of arms of the Russian Volhynian Vice-royaly (Namestnichestvo)
Coat of arms of the Russian Volhynian Vice-royaly (Namestnichestvo) Coat of arms of Volhynian Governorate
Coat of arms of Volhynian Governorate Volhynian Voivodeship in Poland (1920-1939)
Volhynian Voivodeship in Poland (1920-1939) Coat of arms of Rivne Oblast
Coat of arms of Rivne Oblast Coat of arms of Zhytomyr Oblast
Coat of arms of Zhytomyr Oblast
Eastern Podolia
Poltava (Myrhorod [Cossack] Cross)
 Flag of Poltava Oblast
Flag of Poltava Oblast Myrhorod city
Myrhorod city
Other uses
The cross pattée is also placed before the name of the bishop who issues a Catholic imprimatur, and is occasionally found as a map symbol indicating the location of a Christian site.
It appears in the emblem of:
- The Victoria Cross
- The Distinguished Flying Cross (United States)
- The Bundeswehr Cross of Honour for Valour
- The Badge of Honour of the Bundeswehr
- The Order of St. George
- The Order of Bohdan Khmelnytsky
- The Portuguese Football Federation
- F.C. Paços de Ferreira, a Portuguese football club
- C.F. Os Belenenses, a Lisboeta football club
- Casa Pia A.C., a Portuguese sports association
- Mira Mar SC, a Portuguese football club
- Flag of Asturias, a Spanish Principality
- Toulouse FC, a French football club
- The Sir Knight, Geneva Glen Camp's Highest rank in the orders
- The Knights of Columbus, designed in 1883, and called a "cross formée"
- Independent Truck Company, a manufacturer of skating equipment (in the alisée form, with the ends of the arms in the shape of arcs of an enclosing circle)
- The Crossmen Drum and Bugle Corps
- Schneider Cams, a speed equipment manufacturer
- Club de Regatas Vasco da Gama, a South African sports club
- Club de Regatas Vasco da Gama, a Brazilian sports club
- Neath RFC, a rugby team
- The Eaton House Group of Schools
- FC Volyn Lutsk, a Ukrainian football club
- Black Label Society, a heavy metal band
- Flag of the Hispanic People
Firefighters, especially in the United States, commonly use a version with triangular arms for patches and medals, though the cross pattée and the cross of St. Florian are both commonly mistaken for the Maltese cross. The cross pattée is used on the Marksmanship Badge in the United States Army, and United States Marine Corps.
Encoding
In Unicode, a Cross pattée character is encoded under the name "Maltese Cross" in the Dingbats range at code point U+2720 (✠).
The character "X" is rendered as a cross pattée in the Microsoft Wingdings font.
See also
References
- Larousse Dictionnaire de la Langue Francaise Lexis, Paris, 1993, p.1356
- Planché, J.R. The Pursuivant of Arms; or Heraldry Founded upon Facts. London, 1859, p.29
- Cetinje, Official website (English). "Symbols". Retrieved 18 April 2014.
- Nationalencyklopedin, "Georgskors", retrieved 12 August 2010. Swedish.
- Norrgård, Leif (2009-02-18), "Frimurarkorset – symbol med dunkelt ursprung", Frimuraren (in Swedish), Swedish Order of Freemasons, no. 1, pp. 31–32, 1651-35766, archived from the original on 2015-02-03, retrieved 3 February 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cross pattée. |


