Corystospermaceae
Corystospermaceae is a natural family of seed ferns (Pteridospermatophyta) also called Umkomasiaceae, and first based on fossils collected by Hamshaw Thomas from the Burnera Waterfall locality near the Umkomaas River of South Africa [2] The leaves of Dicroidium were recognized by Alex Du Toit [3] to unite all the countries of the Gondwana supercontinent during the Triassic: Africa, South America, India, and Australia. Subsequently, Dicroidium was found in the Triassic of Antarctica and New Zealand,[4] and also the Permian Umm Irna Formation of Jordan.[5] According to the form generic system of paleobotany, leaves are given separate generic names to ovulate and pollen organs, but the discovery of these reproductive organs in Africa by Thomas, and subsequently throughout Gondwana, strengthened Du Toit's concept of a continuous southern supercontinent. Corystospermaceae were also components of Jurassic and Cretaceous floras, declining in the Cretaceous presumably due to the rise of flowering plants, the last representative of the group, Komlopteris cenozoicus, is known from the Eocene of Tasmania.[6]

| Corystospermaceae | |
|---|---|
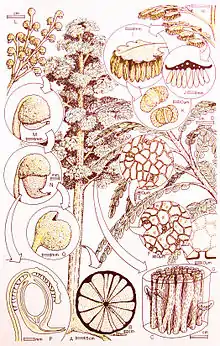 | |
| Umkomasia macleanii reconstructed plant, Late Triassic, Molteno Formation, Umkomaas, South Africa.[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Division: | †Pteridospermatophyta |
| Order: | †Peltaspermales |
| Family: | †Corystospermaceae Thomas 1933 |
| Genera | |
| |
Description
Umkomasiaceae have helmet-like cupules around ovules born in complex large branching structures (Umkomasia). The pollen organ (Pteruchus) has numerous cigar-shaped pollen sacs hanging from epaulette-like blades, again in complex branching structures.

The leaves (Dicroidium) are tied to the fertile organs by similarities of cuticular structure, because their cuticles were robust like those of gymnosperms and unlike the thin leaves of ferns.

See also
References
- Retallack, G.J.; Dilcher, D.L. (1988). "Reconstructions of selected seed ferns". Missouri Botanical Garden Annals. 75: 1010–1057. doi:10.2307/2399379.
- Thomas, H.H. (1933). "On some pteridospermous plants from the Mesozoic rocks of South Africa". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 222: 193–265. doi:10.1098/rstb.1932.0016.
- Du Toit, A.L. (1937). Our wandering continents. Oliver and Boyd, London. pp. 366 pp.
- Retallack,G.J. (1977). "Reconstructing Triassic vegetation of Australasia: a new approach for the biostratigraphy of Gondwanaland". Alcheringa. 1: 247–278. doi:10.1080/03115517708527763.
- Hamad, A.A.; Kerp, H.; Vörding, B. & Bandel, K. (2008). "A late Permian flora with Dicroidium from the Dead Sea region, Jordan". Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology. 149: 85–130. doi:10.1016/j.revpalbo.2007.10.006.
- McLoughlin, Stephen; Carpenter, Raymond J.; Jordan, Gregory J.; Hill, Robert S. (2008). "Seed ferns survived the end-Cretaceous mass extinction in Tasmania". American Journal of Botany. 95 (4): 465–471. doi:10.3732/ajb.95.4.465. ISSN 1537-2197.
External links
- "Fossilworks: Lepidopteris". paleodb.org. Retrieved 2016-03-18.