Chylothorax
A chylothorax is an abnormal accumulation of chyle, a type of lipid-rich lymph, in the space surrounding the lung. The lymphatics of the digestive system normally returns lipids absorbed from the small bowel via the thoracic duct, which ascends behind the esophagus to drain into the left brachiocephalic vein. If normal thoracic duct drainage is disrupted, either due to obstruction or rupture, chyle can leak and accumulate within the negative-pressured pleural space. In people on a normal diet, this fluid collection can sometimes be identified by its turbid, milky white appearance, since chyle contains emulsified triglycerides.
| Chylothorax | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Three bottles of chyle drained from a chylothorax | |
| Specialty | Respiratory medicine |
| Symptoms | None, breathlessness |
| Complications | Dehydration, malnutrition, abnormal electrolyte levels, weakened immune system |
| Types | Low output, high output |
| Causes | Complication of surgery, trauma, cancer, infections, lymph vessel abnormalities |
| Diagnostic method | X-ray, CT scan, thoracic MRI, fluid sampling |
| Treatment | Removing fat from the diet, decreasing lymph flow, chest tube, surgery |
| Medication | Octreotide, midodrine, and sirolimus |
| Prognosis | ~10% risk of death |
Chylothorax is a rare but serious condition, as it signals leakage of the thoracic duct or one of its tributaries. There are many treatments, both surgical and conservative.[1] About 2-3% of all fluid collections surrounding the lungs (pleural effusions) are chylothoraces.[2] It is important to distinguish a chylothorax from a pseudochylothorax (a pleural effusion that happens to be high in cholesterol), which has a similar appearance visually but is caused by more chronic inflammatory processes and requires a different treatment.[3]
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of a chylothorax depend its size and the underlying cause. A small chylothorax may not cause any symptoms and only be detected on a chest X-ray performed for another reason. A large chylothorax may lead to breathlessness or a feeling of pressure in the chest, caused by fluid restricting the expansion of the lungs, although large chylothoraces may remain asymptomatic if the chylothorax has accumulated slowly, as the lungs may have had time to become used to the pressure. Fever or chest pain are not usually associated with chylothorax, as chyle does not generate inflammation by itself.[4]
On examination, chylothorax may lead to reduced breath sounds on the affected side, associated with a dull sound when the chest is tapped or percussed. In cases of postoperative chylothorax, the first sign may be persistent drainage from intercostal drains.[1] Large chylothoraces may cause signs related to the loss of nutrients, including features of malnutrition or decreased ability to fight infections.[5] Rapidly accumulating chylothoraces can cause a sudden drop in blood volume, leading to low blood pressure.[5]
Causes
There are three main types of chylothorax: traumatic, non-traumatic, and idiopathic. Historically the most common form of chylothorax was non-traumatic, but traumatic chylothoraces now represent the majority of cases, with most arising as postoperative complications of surgery.[6][7] The most common cause of non-traumatic chylothoraces is cancer.[1] Chylothoraces can also be classified as low- or high-output based on the rate of chyle accumulation: low-output chylothoraces accumulate <500 mL of chyle per 24 hours, while high-output chylothoraces accumulate >1000 mL per 24 hours.[8]
Non-traumatic
Malignancies are the most frequent cause of non-traumatic chylothorax. Cancers like chronic lymphocytic leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma, Kaposi sarcoma, metastatic carcinoma or esophageal cancer are potential causes of chylothorax. Infectious causes are also observed, most often in developing countries. The most common cause of an infectious chylothorax is a complication of tuberculous lymphadenitis. Other possible causative infections include aortitis, histoplasmosis, and filariasis. Chylothorax can also be congenital, and may co-occur with other lymphatic malformations like lymphangiectasis and lymphangiomatosis. Other conditions like tuberous sclerosis, congenital heart disease, trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), Noonan syndrome, or Turner syndrome (missing X chromosome) are also possible causes of congenital chylothorax. Other, more rare causes of congenital chylothorax include Castleman's disease, yellow nail syndrome, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, sarcoidosis, venous thrombosis, thoracic radiation, macroglobulinemia, amyloidosis, and a goiter. These diseases cause chylothorax by obstructing or destroying the thoracic duct. Also, parenteral nutrition has been a possible cause; a quick dose of total parenteral nutrition can overwhelm the thoracic duct, causing the chyle to leak into the surrounding pleural space.[1]
Traumatic
Iatrogenic chylothorax after surgery is the most common variety of chylothorax.[1] It is a common and serious complication of a pneumonectomy.[9] It is especially common in surgeries requiring mediastinal dissection.[5] The probability of chylothorax depends on the type of surgery. The surgery with the highest risk of chylothorax is an esophagostomy, with a 5-10% risk of chylothorax. Lung resection and mediastinal node dissection have the second highest risk, with 3-7% risk. Other operations like mediastinal tumor resection, thoracic aneurysm repair, sympathectomy, and any other surgeries that take place in the lower neck or the mediastinum can lead to chylothorax. Chylotharax after trauma but not after surgery has also been described after central line placement, pacemaker implantation, and embolization of a pulmonary arteriovenous malformation. Blunt trauma to the chest region is another cause of chylothorax, which has occurred after blast injuries and even simple injuries from coughing or sneezing.[1]
Mechanism
The main mechanism of chylothorax is the leaking of chyle from the thoracic duct, usually caused by a disturbance affecting the structural integrity of the thoracic duct.[5] For example, placement of a central venous catheter can potentially disrupt drainage of lymph into the subclavian veins, followed by the thoracic duct, resulting in chylothorax.[5] The disturbances cause the pressure in the thoracic duct to increase. Soon, collateral channels form, which eventually drain into the thorax.[10] Trauma affecting the thoracic duct is the most common disturbing mechanism.
Whether a chylothorax occurs in the left or right pleural space is a consequence of the thoracic duct's anatomic location in the body and depends on the level where the duct was injured. If the thoracic duct is injured above the fifth thoracic vertebra, then a left-sided chylothorax results.[5] Conversely, a thoracic duct injury below that level will lead to the formation of a right-sided chylothorax.[5] Chylothoraces most commonly occur in the right pleural space (50% of cases).[5] Left-sided and bilateral chylothoraces are less common and occur in 33% and 17% of cases, respectively.[5]
In the case of cancer, invasion into the thoracic duct or collateral lymph channels can obstruct lymph. In the case of mediastinal lymphadenopathy, the enlarged lymph node causes compression of the lymphatic channels and thoracic duct. This impedes the centripetal drainage of the flow of lymph from the edges of the lung parenchyma and pleural surfaces. This causes the chyle to ooze extensively into the pleural cavity, leading to a chylothorax. In the case of yellow nail syndrome, or lymphedema, chylothorax is caused by hypoplasia or dilation of the lymph vessels. In rare cases, like in hepatic chylothorax, chylous ascites crosses the diaphragm into the pleural cavity. In idiopathic cases like genetic disorders, the mechanism is not known.[5] Up to three liters of chyle can easily drain into the pleural space daily.[10]
Diagnosis

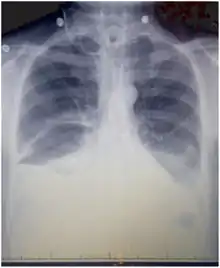
Chest X-rays can detect a chylothorax. It appears as a dense, homogenous area that obscures the costophrenic and cardiophrenic angles. Ultrasounds can also detect a chylothorax, which appears as an echoic region that is isodense with no septation or loculation. However, neither a normal chest x-ray nor an ultrasound can differentiate a chylothorax from any other type of pleural effusion.[1]
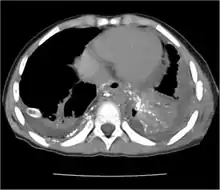
The cisterna chyli can be found in a thoracic MRI, making it possible to confirm chylothorax. However, MRI is not the ideal method to scan the thorax, and so it is rarely used. Another diagnostic technique is conventional lymphangiography. It is rarely used since there are equally sensitive yet less invasive techniques available to identify a chylothorax. Lymphangiography procedures use the contrast dye agent lipiodol, which is injected into the lymphatic vessels. The chylothorax shows up on the images and identifies the source any leak in the thoracic duct.[1]
Another, more commonly used type of lymphogram is nuclear lymphoscintigraphy; this procedure requires human pentetic acid labeled Tc99m to be injected into the subcutaneous lesions of both sides of the dorsum of the foot. Then two images, anterior and posterior, are obtained using gamma-ray cameras. This test can be used with an integrated low-dose CT-scan with photon emission to get images that are more precise. Once pleural effusion is detected, a thoracentesis is recommended.[1]
The fluid of a chylothorax may appear milky, serous or serosanguineous. If the appearance of the fluid is not milky, that does not exclude a chylothorax from consideration. Since chyle is rich in triglycerides, a pleural effusion that is rich in triglycerides (>110 mg/dL) confirms the presence of a chylothorax; a pleural effusion that is low in triglyceride content (<50 mg/dL) virtually excludes the diagnosis.[11][12] If a pleural effusion contains triglycerides between 50–110 mg/dL, analysis of the lipoprotein content of the pleural effusion to evaluate for chylomicrons is recommended.[11] If that procedure detects chylomicrons in the fluid, that confirms a chylothorax. Chylothoraces are typically exudative and often contain a high number of lymphocytes and have low levels of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).[11] However, atypical chylothoraces can occur and are transudative in 14% of cases.[11] A milky appearance of pleural fluid is insufficient to confirm the diagnosis of chylothorax as pseudochylothoraces and empyemas can mimic this appearance.[11] Conversely, the absence of a milky appearance does not mean a chylothorax is not present as they may instead appear serous or bloody.[11]
Treatment
The treatment for chylothorax depends on the underlying cause but may include dietary modification, medication to prevent chyle formation including somatostatin/octreotide, midodrine and sirolimus, pleurodesis, and surgical treatment including ligation of the thoracic duct, pleurovenous or pleuroperitoneal shunting or thoracic duct embolization.[1]
Initial
The initial treatment of a chylothorax is usually drainage of the fluid from the pleural space. This may be necessary to restore lung function compromised by the pressure exerted by the chyle on the lungs.[1] Those with large chylothoraces may need nutritional support due to the nutrients lost, primarily to correct protein and electrolyte losses. Once the affected person is hemodynamically and nutritionally stable, then specific treatment can begin.[5]
Conservative
A conservative treatment is changing diet to include fewer long-chain fatty acids, in particular free fatty acids. Since chyle is formed from these acids, chyle formation will reduce, allowing the defects to heal spontaneously. However, this can lead to fat deficiency and malnutrition over time. A possible response to this drawback is a venous fat hemorrhage, in which small and medium-chain fatty acids are given by diet, and long-chain fatty acids are given intravenously. Thoracentesis and an indwelling catheter for use at home is generally used to drain the chylothorax.[1] If a malignant neoplastic chylothorax is present, then treatment with radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy is warranted.
Surgical
Surgery is indicated if the case is post-traumatic, iatrogenic, or refractory to other treatments, in which cases surgery reduces mortality by 40%. One invasive surgical intervention called a thoracic duct ligation involves closing off the thoracic ducts.[1] Surgical pleurodesis is another option and can be undertaken if the affected person fails to respond to conservative treatment and is not a candidate for surgical intervention.[13]
Another treatment option is pleuroperitoneal shunting (creating a communication channel between the pleural space and peritoneal cavity). Since surgery to close the leak is not reliable, talc pleurodesis is recommended; in a case study of 19 people with refractory malignant chylothorax due to lymphoma, it resulted in success for all affected individuals.[5] Chemical pleurodesis is an option, since the leaking of lymphatic fluids is stopped by irritating the lungs and chest wall, resulting in a sterile inflammation. This causes the lung and the chest wall to fuse together, thus preventing lymphatic fluids from leaking into the pleural space.[14]
Prognosis
The morbidity and mortality rates associated with chylothorax have declined as treatments have improved. Malignant, bilateral, and chronic chylothoraces have an inferior prognosis to other types.[5] Currently, the mortality and morbidity rates are about 10% if treated surgically.[1] If cases are post-operative and treated conservatively, mortality rates approach 50%.[5]
Complications
Complications of chylothorax include malnutrition, immunosuppression, dehydration, and respiratory distress.[6] The severity of the complications depends on how quickly the chylothorax accumulated, its size, and its chronicity.[13]
Epidemiology
Chylothoraces are rare and usually occur as a complication of surgeries in the neck and mediastinum. It has no gender or age predisposition. A chylothorax occurs in 0.2-1% of cardiothoracic surgeries, 5-10% of esophagostomies, and 3-7% of lung resections.[1]
Other animals
Horses
Chylothorax is uncommon in horses. Clinical signs and symptoms in foals inlude difficulty breathing, fast breathing, cough, fever, and lethargy. The fluid generally appears opalescent and milky without any odor. A line of fluid is observed on percussion and there are reduced lung sounds. To differentiate between chyle is pseudochyle, which does not clear after centrifugation. There is not much information on the treatment of chylothorax in horses. Supportive care, antimicrobials, drainage of the thorax, and dietary management have been used with success. Surgery has been done in other animals with limited success, but has not yet been reported in horses. Although success has been reported, the prognosis is relatively unknown due to the lack of data.[15]
References
- Rudrappa M, Paul M (2018). "Chylothorax". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29083798. Retrieved 2019-03-05.
- "Chylothorax and Cholesterol Effusion". Pulmonology Advisor. 2019-01-23. Retrieved 2019-03-24.
- Heffner J. "Clinical presentation, diagnosis and management of cholesterol effusions". 8.0. UpToDate. Retrieved 30 October 2014.
- Schild, Hans H; Strassburg, Christian P; Welz, Armin; Kalff, Jörg (2013–2014). "Treatment Options in Patients With Chylothorax". Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 110 (48): 819–826. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2013.0819. ISSN 1866-0452. PMC 3865492. PMID 24333368.
- Nair SK, Petko M, Hayward MP (2007). "Aetiology and management of chylothorax in adults". European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 32 (2): 362–9. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2007.04.024. PMID 17580118.
- Martucci, N; Tracey, M; Rocco, G (November 2015). "Postoperative Chylothorax". Thoracic Surgery Clinics. 25 (4): 523–8. doi:10.1016/j.thorsurg.2015.07.014. PMID 26515952.
- Pillay, TG; Singh, B (March 2016). "A review of traumatic chylothorax". Injury. 47 (3): 545–50. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2015.12.015. PMID 26776461.
- Lyon, S; Mott, N; Koukounaras, J; Shoobridge, J; Hudson, PV (June 2013). "Role of interventional radiology in the management of chylothorax: a review of the current management of high output chylothorax". Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology. 36 (3): 599–607. doi:10.1007/s00270-013-0605-3. PMID 23580112. S2CID 22158968.
- Vallières, E.; Karmy-Jones, R.; Wood, D. E. (1999). "Early complications. Chylothorax". Chest Surgery Clinics of North America. 9 (3): 609–616, ix. ISSN 1052-3359. PMID 10459431.
- Talwar, Arunbh, and Hans J Lee. “A Contemporary Review of Chylothorax.” A Contemporary Review of Chylothorax, 2007, medind.nic.in/iae/t08/i4/iaet08i4p343.pdf.
- Skouras, V; Kalomenidis, I (July 2010). "Chylothorax: diagnostic approach". Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine. 16 (4): 387–93. doi:10.1097/MCP.0b013e328338dde2. PMID 20410823. S2CID 26096783.
- Nadolski, G (December 2016). "Nontraumatic Chylothorax: Diagnostic Algorithm and Treatment Options". Techniques in Vascular and Interventional Radiology. 19 (4): 286–90. doi:10.1053/j.tvir.2016.10.008. PMID 27993324.
- Kumar, Abhishek; Harris, Kassem; Roche, Charles; Dhillon, Samjot Singh (2014-11-01). "A 69-Year-Old Woman with Lymphoma and Chylothorax. Looking Beyond the Usual Suspect". Annals of the American Thoracic Society. 11 (9): 1490–1493. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201406-251CC. ISSN 2329-6933. PMID 25423001.
- Sonoda, A; Jeudy, J; White, CS; Kligerman, SJ; Nitta, N; Lempel, J; Frazier, AA (May 2015). "Pleurodesis: indications and radiologic appearance". Japanese Journal of Radiology. 33 (5): 241–5. doi:10.1007/s11604-015-0412-7. PMID 25791777. S2CID 22780289.
- Weese, Scott; Munroe, Dr Graham; Munroe, Graham (2011-03-15). Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction. CRC Press. p. 476. ISBN 978-1-84076-608-0.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |