Capital Connection
The Capital Connection is a long-distance commuter train between Palmerston North and Wellington on the North Island Main Trunk in New Zealand.[3] It is operated by KiwiRail. The service began in 1991. It was the only unsubsidised commuter service in New Zealand, but was subsidised by the regional councils and KiwiRail until 30 June 2018.[4] In 2018 the Government committed to continuation of the train,[5] NZTA planning to invest in refurbishing or replacing rolling stock[6] and Wellington Region paying $6m to 2021.[7]
| Overview | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service type | Commuter rail | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Operating | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Lower North Island, New Zealand | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First service | 15 April 1991 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current operator(s) | KiwiRail | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Former operator(s) | Cityrail (1991–1995) Tranz Metro (1995–2001) Tranz Scenic (1995–present) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ridership | 185,472 trips (2008–2009)[1] 159,641 (2011–2012)[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | https://www.greatjourneysofnz.co.nz/northern-explorer/book/other-services/capital-connection/ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
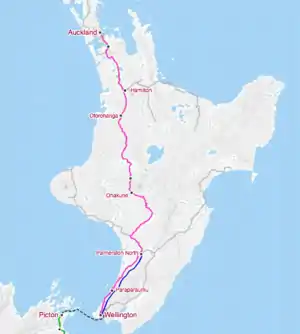
| Start | Palmerston North | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stops | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| End | Wellington | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance travelled | 136 km (85 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average journey time | 2 hours, 6 minutes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service frequency | Daily each way (Mon-Fri) No service Sat, Sun, and Public Holidays | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| On-board services | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class(es) | Standard class only | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Seating arrangements | Airline-style Alcove with table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sleeping arrangements | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Auto-rack arrangements | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Catering facilities | On-board café | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Observation facilities | Large windows in all carriages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baggage facilities | Overhead racks Baggage carriages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rolling stock | New Zealand DF class locomotives S class carriages (ex-British Rail Mark 2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating speed | 65 km/h (40 mph) average | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Route
History
The service started on Monday 15 April 1991 as the Cityrail Express, with "Cityrail EXPRESS Palmerston North – Wellington" emblazoned on carriage sides.
Operator
.jpg.webp)
From 1991 the train was operated by New Zealand Rail suburban passenger division Cityrail, which was re-branded Tranz Metro in 1995 when New Zealand Rail itself was rebranded Tranz Rail. In 2001, with the partial sale of Tranz Scenic (the long-distance passenger division of Tranz Rail), the company sought to separate its commercial passenger rail operations from its subsidised services (which remained in Wellington under Tranz Metro), operation of the train was transferred to Tranz Scenic.
Service
The train operates Monday-Friday from Palmerston North to Wellington in the morning, returning in the evening.
Weekend services
On Sunday 19 June 1994 a weekend service from Palmerston North to Wellington and return started. The power/baggage van, catering car and 50-seat (alcove-style with tables) day car (ex Masterton) made up the consist. It attracted minimal patronage and was withdrawn in 1994.
Future
Concerns were raised that once the Kapiti Line services were extended north from Paraparaumu to Waikanae, the Capital Connection would lose passengers. In 2010 KiwiRail stated it would consider changes after evaluating what impact the metro system has on the Capital Connection's patronage.[8] The extension to Waikanae was opened in 2011. By July 2012 the future of the service seemed to be very uncertain.[9] KiwiRail announced it would make a decision on the service in August 2012. Patronage dropped by 26,000 trips per annum (from 185,472 trips in the 2008–09 financial year[1] to 159,641 in the 2011–12 financial year.)[2]
The Greater Wellington Regional Council and the Horowhenua District Council proposed partial funding but needed the NZ Transport Agency (NZTA) to agree to continue the service. NZTA's public transport funding criteria require that a service must reduce traffic on a congested road.[10] In August 2012 Greater Wellington Regional Council and Horizons (Manawatū-Whanganui Regional Council) proposed a business case for a subsidy which was evaluated by NZTA.[2]
The business case argued that:
- Greater Wellington Regional Council should integrate the service and its rolling stock into its Metlink service;
- A $311,000 subsidy from NZTA and $216,000 subsidy from Greater Wellington and Horizons Regional Council (to be shared proportionate to patronage) be paid to KiwiRail;
- These subsidies to continue for five years.[2]
In March 2013 the Member of Parliament for Palmerston North, Iain Lees-Galloway, presented a petition of 2,000 signatures supporting the service at a parliamentary select committee hearing.[11] In May 2014 he said that he was not surprised at the drop in patronage following a fare rise.[12]
In April 2013 KiwiRail said to keep the service operating, it would have increased ticket prices by 40 percent, and have at least 61 passengers on board in each direction. But it only increased fares by 10% from May.[13]
On 1 July 2015, KiwiRail confirmed, that funding had been approved by Horizons Regional Council and the Greater Wellington Regional Council signing off their Long Term plans, including a subsidy for the service for another three years. KiwiRail Scenic Journeys said there would be maintenance and repairs for each of the carriages, at staggered intervals over the next 12 months, to improve the service.
In 2016 it was reported patronage on the service had increased for the first time in three years.[14]
In 2019, the GWRC proposed replacing the Capital Connection and Wairarapa Connection trains with 15 four-car bi-mode multiple units by 2025. These trains are estimated to cost $415 million.[15][16]
The "infrastructure spendup" announced on 30 January 2020 included some upgrading of the present rolling stock but not the proposed hybrid trains (see New Zealand Upgrade Programme).[17]
Truncation to Waikanae proposal
In November 2014, Palmerston North City Councillor Chris Teo-Sherrell suggested truncating the service to Waikanae, to connect with services operated by Tranz Metro.[18]
Multi-service proposal
In December 2016, Palmerston North Mayor Grant Smith suggested the service should run more than once during the daytime.[19] Smith argued the train could return to Palmerston North at 8:30 am after arriving at Wellington in the morning, returning to Wellington for the evening run.[19]
Rolling stock and motive power

The service began using standard NZR 56-foot carriages: the first of two power-baggage vans from the Bay Express, a 50-seat Southerner car, a 42-seat Northerner car and a 37-seat Northerner catering car. When the Northerner and Southerner cars were returned to their respective trains and patronage continued to increase a former Masterton commuter car was refurbished to the same standard, with the same 50 alcove-style seats as the Southerner car, but with sheepskin seat covers. Later, a former Endeavour car with luggage space at one end and a former Picton – Greymouth car, both from on the Masterton commuter run, were refurbished for the service. Later still, up to five more Masterton cars, a Northerner car, the second Northerner catering car and the sole InterCity spare buffet car saw service. Before these carriages were replaced, the service was regularly running with a van and eight cars.
British Rail carriages
On Monday 15 November 1999 a new train entered service, made up of seven (later eight) British Rail Mark 2 cars and the second former Southerner modular 11 kW power and baggage van, with 90 kW generator and larger luggage space made up from the middle and expanded non-handbrake end compartments. The new cars are about three metres longer than the older cars and more spacious inside, with more headroom, full air-conditioning, 60 seats per car (28 in the servery car), and twin power sockets at the foot of each pair of seats. Seating arrangement is both alcove and airline-style, using their British Rail InterCity 72 seats. Since October 2016, fire suppressed DFB class locomotives have been assigned to the service.
They have been repainted from Tranz Scenic standard "Cato blue" into Capital Connection livery.
| Class | BR type | Number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| S | 2D FO | 3170 | |
| S | 2D FO | 3177 | |
| S | 2D FO | 3184 | |
| S | 2D FO | 3190 | |
| S | 2D FO | 3200 | Servery carriage |
| S | 2D FO | 3207 | |
| S | 2D FO | 3211 | |
| S | 2E FO | 3245 | |
| AG | 130 | Baggage/generator carriage |
References
- "Ratepayers face bill to keep capital train service". The Manawatu Standard. 12 January 2010. Retrieved 13 January 2010.
- "Capital Connection business plan" (PDF).
- "Capital Connection: Commuting made easy". Tranz Scenic. Archived from the original on 19 August 2007. Retrieved 30 August 2007.
- "Regional Transport Committee 07 March 2017 PASSENGER RAIL WORKING PARTY UPDATE" (PDF). Horizons Regional Council.
- "Update on Budget 2018" (PDF). www.horizons.govt.nz. 17 May 2018. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- "Transitional rail (new activity class)". www.nzta.govt.nz. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- "WELLINGTON REGIONAL LAND TRANSPORT PLAN 2015 2018 MID–TERM UPDATE" (PDF).
- ELLINGHAM, JIMMY (7 January 2010). "City rail link to capital in jeopardy". The Manawatu Standard. Palmerston North: Fairfax New Zealand. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
- "Axe hovers over Capital Connection". Stuff/Fairfax. 17 May 2012.
- "Last bid to save rail service". Manawatu Standard. 27 July 2012. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- "MP tries new tack to save train". Stuff/Fairfax. 1 March 2013.
- "Fare rise cuts use of train". Stuff/Fairfax. 5 May 2014.
- "Fares rise on threatened train service". 3 News NZ. 15 April 2013. Archived from the original on 3 July 2013.
- "More people board the Capital Connection train". 17 August 2016.
- "Regional Council plans new trains for Wellington but it'll take six years". Stuff (Fairfax). 11 August 2019.
- "Greater Wellington seeks funding for new trains". Greater Wellington Regional Council. 8 August 2019.
- "New hybrid trains for Wellington snubbed in government transport package". Stuff (Fairfax). 30 January 2020.
- MATHEW GROCOTT. "Waikanae rail connection proposed".
- "Wellington and Palmerston North commuters could soon catch train twice a day". 10 December 2016.