Calcium cyanide
Calcium cyanide also known as black cyanide,[2] is the calcium salt of cyanide, an inorganic compound with the formula Ca(CN)2. The pure form is a white solid, although rarely observed; commercial samples can be black-gray. It hydrolyses readily (even in moist air) to release hydrogen cyanide. Like other similar cyanides it is very toxic.[3]
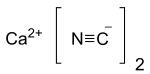 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
calcium dicyanide | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
calcium dicyanide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.856 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ca(CN)2 | |
| Molar mass | 92.1128 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Odor | hydrogen cyanide |
| Density | 1.853 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 640 °C (1,184 °F; 913 K) (decomposes) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, weak acids |
| Structure | |
| rhombohedric | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Non-flammable | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation
Calcium cyanide can be prepared by treating powdered calcium oxide with boiling anhydrous hydrocyanic acid in the presence of an accelerator such as ammonia or water in order to minimize the loss of the hydrocyanic acid by polymerization. It may also be prepared by reacting liquid hydrocyanic acid with calcium carbide. Alternatively calcium cyanide may be prepared by reacting hydrocyanic acid gas with quicklime (CaO) at high temperatures around 400 °C. At higher temperatures around 600 °C calcium cyanimide is formed instead.[4] The material prepared often is contaminated with polymeric derivatives of hydrogen cyanide, hence the black color.
Reactivity
Calcium cyanide hydrolyzes readily to form hydrogen cyanide gas. The presence of acid accelerated evolution of hydrogen cyanide gas. It is reactive toward oxidizing agents. Calcium cyanide is also sometimes used to produce ammonium cyanide by reacting it with ammonium carbonate.
- Ca(CN) 2 + (NH 4)2CO3 → 2 NH 4CN + CaCO3
Uses
Calcium cyanide is used almost exclusively in the mining industry. It serves as an inexpensive source of cyanide in many leaching or vat operation to obtain precious metals such as gold and silver from their ores.[5] It does this by forming coordination complexes with the metals separating them from the ores.[6] It is distributed in either solid flake form or in liquid form.[5] Calcium cyanide's high toxicity to touch, inhale, or ingest makes it useful as a rodenticide. For example, it has been used in the management of the population of Indian crested porcupines (Hystrix indica).[7] Its toxicity has been similarly exploited as an insecticide.[8] However its high toxicity makes it unfavorable in many cases and oftentimes other less damaging chemicals are used instead.[7] It is also used in the making of hydrogen cyanide, ammonium cyanide, and ferrocyanides.
Safety
Like other cyanide salts, this compound is highly toxic and its use is strictly regulated.
References
- http://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/2775
- . "Calcium Cyanide." Merriam-Webster Dictionary. 2001. http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/calcium%20cyanide (accessed April 22, 2012).
- Ernst Gail, Stephen Gos, Rupprecht Kulzer, Jürgen Lorösch, Andreas Rubo and Manfred Sauer "Cyano Compounds, Inorganic" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2004. doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_159.pub2
- . "Production of Hydrocyanic Acid" United States Patent Office. 1933.(accessed April 22, 2012).
- "Use of Cyanide for the Gold Industry" International Cyanide Management Code for the Use of Cyanide in the Gold . 2011. http://www.cyanidecode.org/cyanide_use.php (accessed April 22, 2012).
- . "coordination compound" Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online Academic Edition. 2012. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/136410/coordination-compound.
- . "Evaluation of Aluminium Phosphide Fumigation for the Control of Indian Crested Porcupine (Hystrix indica) in Scrublands*. 2008.
- . "CALCIUM CYANIDE FOR CHINCH-BUG CONTROL" UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS Agricultural Experiment Station. 1924.
