Blakeney, Norfolk
Blakeney is a coastal village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk.[2] Blakeney lies within the Norfolk Coast AONB (Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty) and the North Norfolk Heritage Coast. The North Norfolk Coastal Path travels along its quayside.[3] The village is 21.1 miles (34.0 km) north west of Norwich, 4.6 miles (7.4 km) NNW of the larger settlement of Holt, 11.5 miles (18.5 km) west of Cromer and 112 miles (180 km) NNE of London.
| Blakeney | |
|---|---|
 The village sign, Blakeney | |
 Blakeney Location within Norfolk | |
| Area | 9.90 km2 (3.82 sq mi) |
| Population | 801 (whole administrative parish, 2011 census)[1] |
| • Density | 81/km2 (210/sq mi) |
| OS grid reference | TG020430 |
| • London | 129 miles (208 km) |
| Civil parish |
|
| District | |
| Shire county | |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | HOLT |
| Postcode district | NR25 |
| Dialling code | 01263 |
| Police | Norfolk |
| Fire | Norfolk |
| Ambulance | East of England |
| UK Parliament | |
The civil parish has an area of 9.9 km² and in the 2001 census had a population of 789 in 402 households. For the purposes of local government, the parish falls within the district of North Norfolk.[4]
Description

Blakeney was a commercial seaport until the early 20th century. Now the harbour is silted up, and only small boats can make their way out past Blakeney Point to the sea. The harbour and surrounding marshes are owned by the National Trust and is a nature reserve where seals can be seen basking on the sand.
Just inland from the harbour is Mariners Hill. This vantage point is believed to be man-made, probably as a lookout point for the harbour. Adjacent to the hill, at the foot of the village's High Street, is the old Guildhall with a 14th-century undercroft.[5][6]
Higher up the village, the Church of St Nicholas has two towers: the main tower is more than 100 ft (30 m) high and a well-known landmark for miles around; the smaller tower was built as a beacon to guide boats into Blakeney Harbour.
History
In the Domesday Book of 1086,[7] Blakeney is recorded under the name Esnuterle (later, Snitterley);[8] the main landholders are noted as Walter Gifford and William de Noyers. The settlement first appears under the name Blakeney in a document which dates from 1340.[7] Around the same period Edward III’s wife, Queen Philippa is said to have dined on fish caught by Blakeney’s fishermen.[7]
Haven
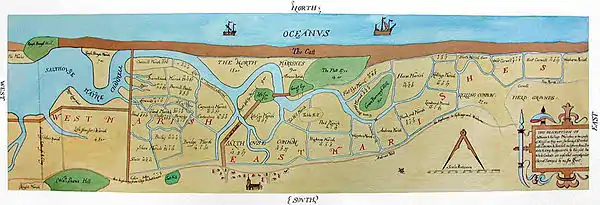
Blakeney Haven was a deeper inlet on the north coast of Norfolk into which the River Glaven flowed. Sheltered behind Blakeney Point, it was a major shipping area in the Middle Ages, with relatively important North Norfolk ports at Wiveton, Cley next the Sea and Blakeney itself. Cley and Wiveton silted up in the 17th century, but Blakeney prospered, especially after the channel to the Haven was deepened in 1817. Packet ships ran from that port to Hull and London from 1840. This trade declined as ships became too large for the harbour, and it is now silted up with access only for small boats[9]
From the 12th century Blakeney had a reputation for acts of piracy: between 1328 and 1350 it is recorded that men of Blakeney boarded two vessels sailing from Flanders and sailed them back to Blakeney haven, where they were stripped of their cargoes. Many a foreign merchant ship which sought shelter in the haven found its cargo stolen. Such was the lawlessness of the residents that the village refused to supply a ship for the battle against the Spanish Armada.[7][8]
'Chapel'
This building now in adjoining Cley next the Sea appears never to have been a chapel and may merely have been a hermitage. Indeed, the calendar of England's Patent Rolls dated 20 April 1343, confirms a grant of alms-seeking across the realms to a local hermit.
Friary
This was among the junior houses of a Carmelite region (distinctio) which included Burnham Norton, King's Lynne and Yarmouth the crypt of its senior house is intact and is converted to part of Norwich's Printing Museum which is run by an active printing firm, Jarrold's in the city.[10]
The northern part of Friary Park by the seashore is a modest caravan park for visitors, with the remainder being the relatively small Friary Farm.
Friary Farmhouse incorporates remains of the Carmelite Friary founded in 1296 with its church consecrated in 1302. This was the gift of Maud de Roos or latterly de Ros, née de Vaux, wife of William de Ros, 1st Baron de Ros who distinguished himself in the Crusades, was knighted and granted land at Cley and Blakeney.
In 1321 their son, William completed the foundation.
The house has a date-stone: "1667 T.R.I" and is made of flint and brick with some stone quoins. Despite modern windows and most exterior work it incorporates medieval walling, a buttress, various blocked openings, fragments of window surrounds and stonework including a re-used carved kneeler on the south-west gable with coat of arms.[11]
Windmill
Blakeney Mill in Friary Park is a Grade II listed building and is chiefly of flint with brick dressings (mostly its upper parts) across its three storeys. It appears on a map of 1769 in this exact location, following earlier mention from the Domesday Book of mills in the village.[12]
Railway
In the 19th century a rail branch line from Holt to a new station at Blakeney was planned by the Midland & Great Northern Joint Railway. The scheme was never completed, although the junction site at High Kelling now serves as Holt station on the North Norfolk Railway. A rival proposal for a branch from Cawston to Cley and Blakeney was put forward by the East Norfolk Railway, but this was also not built.[13]
Tourism
Blakeney is a popular tourist resort during the summer months. The village has two large hotels, one in a historic building,[14] and one with a modern main part but with also with a late 17th-century and 18th-century barn annexe, The Blakeney Hotel[15] as well as having the alternative at the end of the Quay Road of the 15-acre (61,000 m2) caravan site.
Blakeney offers a large range of activities including crabbing, fishing, canoeing and birdwatching. In the area of marshland around Blakeney Point, owned by the National Trust, up to a hundred species of birds can be found throughout the year. Several pubs in the area serve food and real ale.
Wells-next-the-Sea has a miniature and heritage railway 7 miles (11 km) to the west.
The North Norfolk Coastal Path travels along its quayside and varies between a path through salt marshes, raised promenades, sandy beaches and compact villages in this section.
Demography
The population of Blakeney, according to the census of 1801, was 618. This number increased, lagging just behind national population growth in the forty years to 1851, to 1,108 however a gradual decline in population took place until 1931, particularly during the early years of this decline which coincided with the arrival of the railway at Holt to the south and national urban industrialisation – population fell from 1,108 to 641 in 1931. Population growth resumed and saw a growth between 1961 and 2011, to 801 people. Data for 1801–1961 is available at Britain Through Time.[16] The 2001 and 2011 Censuses give detailed information about the village. The settlement's population in 2011 were living in 407 households.[1]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Transport
The village's centre is off the northern side of the A149 coast road from King’s Lynn to Cromer, with a further part of Blakeney community directly adjoining in the residential estates south of this and also several outlying farms.[17] The nearest railway station is at Sheringham, two villages to the east for the Bittern line to Norwich.
The nearest airport is Norwich Airport.
See also
- Blakeney Tower Windmill
- Blakeney (horse), 1969 Epsom Derby winner[18]
- Category:People from Blakeney, Norfolk
References
- 2011 Census
- OS Explorer Map 24 – Norfolk Coast Central. ISBN 0-319-21726-4
- Ordnance Survey (2002). OS Explorer Map 251 – Norfolk Coast Central. ISBN 0-319-21887-2.
- Office for National Statistics & Norfolk County Council (2001). Census population and household counts for unparished urban areas and all parishes. Retrieved 2 December 2005.
- Guildhall Grade II* Historic England. "Details from listed building database (1373987)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- Scheduled Ancient Monument Medieval undercroft Historic England. "Details from listed building database (1014237)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- The Domesday Book, Englands Heritage, Then and Now, Editor: Thomas Hinde, Norfolk page 182/183, Blakeney, ISBN 1-85833-440-3
- Wright, John (2002). "The origins of Blakeney Church". Glaven Historian. 5: 26–34.
- Pevsner, Nikolaus; Wilson, Bill (2002). The Buildings Of England Norfolk I: Norwich and North-East Norfolk. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. pp. 394–397. ISBN 0-300-09607-0.
- The Medieval Carmelite Priory at Norwich: A Chronology Richard Copsey, O.Carm., London, 2006. Retrieved 2013-07-15
- Friary Farmhouse Grade II – Historic England. "Details from listed building database (1253063)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 15 July 2013.
- Blakeney Mill Historic England. "Details from listed building database (1170652)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 15 July 2013.
- The East Norfolk Railway, R.S. Joby p.33
- Manor Hotel Historic England. "Details from listed building database (1039440)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- Barn Annexe immediately west of the Blakeney Hotel Historic England. "Details from listed building database (1039443)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- "Blakeney through time : Population Statistics : Total Population". A Vision of Britain through Time. Retrieved 13 July 2013.
- County A to Z Atlas, Street & Road maps Norfolk, ISBN 978-1-84348-614-5
- Nick Godfrey (22 July 2011). "Arthur Budgett:The only man to have trained and bred two Derby winners in the 20th century". The Independent. Retrieved 17 September 2019.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Blakeney (Norfolk). |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Blakeney, Norfolk. |
- Map sources for Blakeney, Norfolk
- Tide tables for Blakeney.
- Information from Genuki Norfolk on Blakeney.