Bit shank
The bit shank is the side piece or cheekpiece of a curb bit, part of the bridle, used when riding on horses. The bit shank allows leverage to be added to the pressure of the rider's hands on the bit. Shanks are usually made of metal, may be straight or curved, and may be decorated in some disciplines. The headstall and curb chain or curb strap of the bridle is attached to the top of the shank, and the reins are attached at the bottom. Shanked curb bits are used in western riding for nearly all adult horses, and are seen in English riding disciplines primarily as part of the double bridle used by advanced dressage riders, and on the hybrid pelham bit that includes a ring for a second rein attached at the bit mouthpiece.

Direct pressure snaffle bits have no shanks, instead they have a single bit ring.
Bits that have shanks coming off the mouthpiece create leverage and place pressure on the poll via the crownpiece of the bridle, to the chin groove via the curb chain, and, especially with a "loose jaw" shank, may also touch the sides of the mouth and jaw. The shank and its leverage action is what defines a curb bit as a curb, regardless of mouthpiece. Though most curb bits have a solid mouthpiece, with or without a port, any bit with shanks and leverage is always a "curb" type bit, even if has a jointed mouthpiece. Shanked bits in the curb family include the Weymouth, which is the curb portion of the double bridle; the pelham bit, a single bit ridden with two sets of reins; and the single-reined curb bit.
Parts of the shank
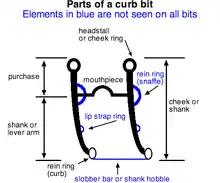

The term shank is generally used interchangeably with the term "cheek" to describe the entire sidepiece of the bit, but shank also may refer just to the lever arm, the portion of the bit that extends from the mouthpiece to the rein ring. The purchase of the bit is the upper portion of the cheek that extends from the mouthpiece to the headstall rings. All shanks have a rein ring at the bottom for the curb rein and a cheek ring at the top to attach the headstall. Some shanks may also add rings or slots to attach a snaffle rein at the mouthpiece, allowing the bit to be used with two sets of reins, making it a pelham bit.
Some shanks, especially on the Weymouth, have small rings placed midway down the shank to attach a lip strap, a helpful addition to the bit for preventing a horse from grabbing at the shanks with its lips. Some shanks on western-style bits are "hobbled" together by a metal bar (sometimes called a "slobber bar" because saliva from the horse's mouth can drop onto it) or even a piece of leather, which has the dual effect of keeping anything from getting wrapped around the shank, such as a lariat, and can limit excessive motion in a loose-jawed shank.
Length and leverage


The length of the shank determines the degree of leverage put on the horse's head and mouth. The leverage ratio for a typical curb bit is 1:4 (where the ratio of upper and lower cheek is 1:3), in that one ounce of pressure by the rider will result in four ounces of pressure on the mouth of the horse. Overall cheek length, from the top of the cheek ring to the bottom of the rein ring, usually cannot exceed 8½ inches for most western horse show disciplines. In Dressage the length of the lever arm portion of the cheek cannot exceed 10 cm. Cheek sizes vary from the Tom Thumb (about 4½ inches long) to bits that exceed the 8½ inch "show legal" maximum cheek length.
The relative ratio between the length of the purchase and the lever arm also affects the amount and type of leverage that is applied to the chin and poll of the horse (producing 1:3 ratio of rein to chin+poll forces in case of the typical curb bit). A long lower shank (lever arm) in relation to the upper shank (purchase) increases the leverage, and thus the pressure, on the curb groove and the bars of the mouth. This design is best suited for a longer-necked horse, as it encourages the horse to both drop its head down and bring its nose in. A somewhat long upper shank in relation to the lower shank increases the pressure on the poll, but does not apply as much pressure on the bars of the mouth. This design is often more helpful on a horse with a short and thick neck, as it encourages the horse to drop its head, but with less pressure to flex the nose in, an act that is physically more difficult for a horse with a thick neck.
Overall, a shorter-shanked bit is usually a milder bit, but also responds quickly when the rider touches the reins. Short shanked bits are usually better for a young horse transitioning from a snaffle to a curb because if the inexperienced horse gets into a place where bit pressure from the rider's hands becomes significant, there is less leverage pressure placed on the horse's head.
However, as the horse becomes more polished in its training, a somewhat longer shanked bit is preferred for its subtlety. Longer shanked bits must rotate back further before applying pressure on the horse's mouth than shorter-shanked bits. Therefore, the horse has more "warning" of a rider's hand movements in a long-shanked bit, allowing it to respond before any significant pressure is applied to its mouth. In this way, a longer shank (up to a point) can allow quieter communication between a well-trained horse and a rider with soft hands, without increasing severity of the mouthpiece.
Shank designs


Shanks come in a variety of types, which may affect the action of the bit. Some shanks are loose-jawed, meaning they swivel at the point where the mouthpiece attaches to the shank. Others have a fixed shank that does not move. Some shanks have a loose, rotating ring for rein attachment, others have a solid, fixed ring molded into the shank itself.
Any moving parts on a shank that allow slight movement in the shanks before the bit engages provide a "warning" to the horse, allowing it to respond to lighter pressure, thus allowing more subtle communication between horse and rider when on a loose rein or when introducing a young horse to curb pressure.
The cheek-to-shank angle also varies, with some straight up and down, others with the shanks curving backward. Some shanks have a dramatic S-curve. Cheek angle influences the angle at which the bit engages and thus way the horse carries its head. Therefore, the type of shank needs to be considered according to the use of the horse. Horses that maintain a more vertical head position, such as dressage horses and western horses trained in the "straight up" or Vaquero tradition generally use a curb bit with straighter shanks. Those that have a nose-out head position when working, such as cutting and roping horses, more commonly use a more curved shank. Shanks on certain western bits that curve back are sometimes called a "grazing bit." Though a horse should never be allowed to graze in a bridle, the term came from the mistaken notion that the turned-back shank was to allow the horse to eat with a bridle. In reality, the design simply allowed the horse to comfortably travel with its nose well ahead of the vertical. An S curve in a shank does not have a major effect on the angle at which the rein engages, but may alter the balance of the bit at the point the lever arm joins the mouthpiece.
Historical description
The Cyclopaedia of 1728 referred to shanks or cheeks as branches and described them as outlined in the paragraph below. Although the language is archaic, the underlying classicical principles are still applicable today:
- The branches of a bridle, in the manage (i.e. a training arena-ed) of horses, are two crooked pieces of iron which support the mouth bit, the chain, and the curb, and which are fastened, on one side to the headstall, on the other to the reins, serving to keep the horse's head under command. Whichever way the branches of the bit incline, the horse's mouth always goes to the contrary.
- The branch is always to be accommodated to the design, either of bringing in, or raising a horse's head, and to the degree. Accordingly, there are strong and hardy branches, gentle branches, rude branches, etc. With regard to their form and structure, branches are either straight, in the form of a pistol, for young horses, to form their mouth; or, after the constable of France's fashion, for horses that already carry their head well, others are in the form of a gigot or leg; others of a bent knee; others in the French fashion, etc.
- Three laws traditionally used in the manage follow:
- That the farther the branch is from the horse's neck, the more effect it will have.
- That short branches, ceteris paribus, are ruder, and their effects more sudden than those of others.
- That the branch be proportioned to the length of the horse's neck.
See also
References
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chambers, Ephraim, ed. (1728). Cyclopædia, or an Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences (1st ed.). James and John Knapton, et al. Missing or empty
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chambers, Ephraim, ed. (1728). Cyclopædia, or an Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences (1st ed.). James and John Knapton, et al. Missing or empty |title=(help)