Afetes
Afetes (Greek: Αφέτες) is a village and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality South Pelion, of which it is a municipal unit.[2] The municipal unit has an area of 80.744 km2.[3] Population 1,746 (2011). The seat of the municipality was in Neochori. Afetes is situated in the Pelion peninsula, 2 km from the Pagasetic Gulf coast, 4 km southwest of Neochori, 6 km northwest of Argalasti and 23 km southeast of Volos.
Afetes
Αφέτες | |
|---|---|
 Afetes Location within the regional unit 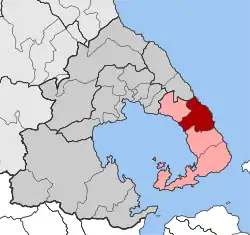 | |
| Coordinates: 39°17′N 23°11′E | |
| Country | Greece |
| Administrative region | Thessaly |
| Regional unit | Magnesia |
| Municipality | South Pelion |
| • Municipal unit | 80.7 km2 (31.2 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 800 m (2,600 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population (2011)[1] | |
| • Rural | 341 |
| • Municipal unit | 1,746 |
| • Municipal unit density | 22/km2 (56/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal code | 370 10 |
| Area code(s) | 24230 |
| Vehicle registration | ΒΟ |
The name Afetes was taken from the ancient port Aphetae. The Persian fleet occupied the bay of Aphetae before the Battle of Artemisium, in 480 BC.[4]
Subdivisions
The municipal unit Afetes is subdivided into the following communities (constituent villages in brackets):
- Afetes (Afetes, Profitis Ilias)
- Kalamaki
- Lampinou
- Neochori (Neochori, Agios Dimitrios, Afyssos, Zervochia, Megali Vrysi, Plaka)
- Syki
Population
| Year | Municipal unit population | Community population |
|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 2,091 | - |
| 2001 | 1,838 | 252 |
| 2011 | 1,746 | 341 |
References
- "Απογραφή Πληθυσμού - Κατοικιών 2011. ΜΟΝΙΜΟΣ Πληθυσμός" (in Greek). Hellenic Statistical Authority.
- Kallikratis law Greece Ministry of Interior (in Greek)
- "Population & housing census 2001 (incl. area and average elevation)" (PDF) (in Greek). National Statistical Service of Greece. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-21.
-
 Smith, William, ed. (1854). "Aphetae". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. 1. London: John Murray. p. 157.
Smith, William, ed. (1854). "Aphetae". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. 1. London: John Murray. p. 157.