Acacia resinistipulea
Acacia resinistipulea is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.
| Acacia resinistipulea | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Clade: | Mimosoideae |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. resinistipulea |
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia resinistipulea | |
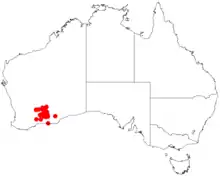 | |
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
Description
The shrub or tree typically grows to a height of 0.8 to 4 metres (3 to 13 ft)[1] and resinous and sparely haired branchlets. Like most species of Acacia it has phyllodes rather than true leaves. The rigid, glabrous to sparsely haired, grey-green to green phyllodes have an asymetrically narrowly elliptic shape and are straight to shallowly recurved with a length of 18 to 25 mm (0.71 to 0.98 in) and a width of 3 to 6 mm (0.12 to 0.24 in) and have many , closely parallel, fine nerves.[2] It blooms from September to November and produces yellow flowers.[1] The simple inflorescences occur singly on the axils and have spherical flower-heads with a diameter of 4 to 5 mm (0.16 to 0.20 in) and contain 23 to 25 golden coloured flowers.[2]
Taxonomy
The species was first formally described by the botanist William Vincent Fitzgerald in 1904 as a part of the work Additions to the West Australian Flora as published in the Journal of the West Australian Natural History Society. It was reclassified as Racosperma resinistipuleum by Leslie Pedley in 2003 then transferred back to genus Acacia in 2006. The only other synonym is Acacia resinostipulea.[3] The plant superficially resembles Acacia formidabilis.[2]
Distribution
It is native to an area in the Wheatbelt and Goldfields-Esperance regions of Western Australia where it is commonly situated around salt lakes, on undulating plains and in low lying areas growing in gravelly sandy or loam or clay loam soils.[1] It has a scattered distribution from around Yellowdine and Coolgardie in the north down to around Boingaring Rocks in the south as a part of open scrubland or Eucalyptus woodland communities where it is often associated with Melaleuca uncinata.[2]
See also
References
- "Acacia resinistipulea". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife.
- "Acacia resinistipulea". World Wide Wattle. Western Australian Herbarium. Retrieved 1 January 2021.
- "Acacia resinistipulea W.Fitzg". Atlas of Living Australia. Global Biodiversity Information Facility. Retrieved 2 January 2021.